
a.
Calculate equity investment balance as of January 1, 2019.
a.
Explanation of Solution
An acquisition of assets is the purchase of a corporation by purchasing its assets rather than its stock. An acquisition is when one company acquires most or all of the shares of another company to gain control over that company. An investment in equity is money which is invested in a company by buying that company's shares in the stock market. Typically, those shares are traded in a stock exchange.
The balance of the Equity Investment account at the beginning of the year equals the subsidiary's Stockholders' Equity plus the [A] assets' undepreciated and unamortized balances. Since the [A] assets with a useful life have now been depreciated or amortized for 4 years, the Equity Investment account's starting balance is as follows:
BOY
Common stock of subsidiary is
APIC of subsidiary is
Calculate BOY
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| BOY Stockholders Equity | |
| Patent | |
| Goodwill | |
| Equity investment balance |
Table (1)
Hence, the equity investment balance as of January 1, 2019 is
b.
Exhibit computations to yield the parent company's reported Equity Income in its income
statement during 2019.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Equity income is money generated from stock dividends that investors can access by buying dividend-declared stocks or by buying funds that invest in dividend-declared stocks.
The computations to yield the parent company’s reported Equity Investment is as follows:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Subsidiary net income | |
| Less: | |
| Equity Income |
Table (1)
Working notes:
Subsidiary’s net income is
Depreciation/Amortization is
Hence, the equity income reported by the parent is
c.
Exhibit computations to yield the parent company's reported Equity Investment.
c.
Explanation of Solution
An investment in equity is money which is invested in a company by buying that company's shares in the stock market. Typically, those shares are traded in a stock exchange.
The computations to yield the parent company’s reported Equity Investment is as follows:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Beginning Equity Investment | |
| Equity Income | |
| Less: Dividends | |
| Ending Equity Investment |
Table (1)
Working notes:
BOY retained earnings of subsidiary is
Common stock of subsidiary is
APIC of subsidiary is
Calculate BOY stockholders equity of subsidiary:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| BOY Stockholders Equity | |
| Patent | |
| Goodwill | |
| Equity investment balance |
Table (1)
Equity income of parent company is
Dividends of the subsidiary is
Hence, the ending equity investment reported by the parent is
d.
Prepare the consolidation entries for the year ended Dec 31, 2019.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Consolidated financial statements are a group of entities financial statements that are presented as those of a single economic entity. They are the financial statements of a group in which the parent company and its subsidiaries introduce their assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, expenses and
Consolidated accounting is used to club a parent company's financial information and one or more subsidiaries. The parent prepares consolidated financial statements through
The required consolidation journal entries are as follows:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Post Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| [C] Equity Income (P) | ||||
| Dividends (S) | ||||
| Equity Investment (P) | ||||
| (To eliminate all changes in the Equity Investment account, leaving only beginning balance in the account) | ||||
| [E] Common Stock (S) at BOY | ||||
| APIC (S) at BOY | ||||
| Retained Earnings (S) at BOY | ||||
| Equity Investment (P)at BOY | ||||
| (To eliminate the portion of the investment account related to the book value of the subsidiary's Stockholders' Equity at BOY) | ||||
| [A] Patent (S) at BOY | ||||
| Goodwill (S) at BOY | ||||
| Equity Investment (P) at BOY | ||||
| (To assign the remaining Equity Investment account (i.e., unamortizedBOY AAP) to appropriate asset & liability accounts) | ||||
|
[D] Operating expenses | ||||
| Patent | ||||
|
(To record depreciation and amortization expense for the [A] assets) | ||||
| [I] No intercompany transactions |
Table (1)
e.
Prepare the consolidation spreadsheet for the year ended December 31, 2019.
e.
Explanation of Solution
Consolidated financial statements are a group of entities financial statements that are presented as those of a single economic entity. They are the financial statements of a group in which the parent company and its subsidiaries introduce their assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, expenses and cash flows as those of a single business organization.
A consolidated balance sheet provides a parent company's assets and liabilities and all of its subsidiaries in a legal document, without any differentiation on which items pertain to which companies.
Consolidation worksheet is an instrument used to prepare a parent's consolidated financial statements and their subsidiaries. It demonstrates the individual book values of companies, the adjustments and eliminations necessary, and the consolidated final values.
The consolidated spreadsheet for the year ended December 31, 2019x is shown below:
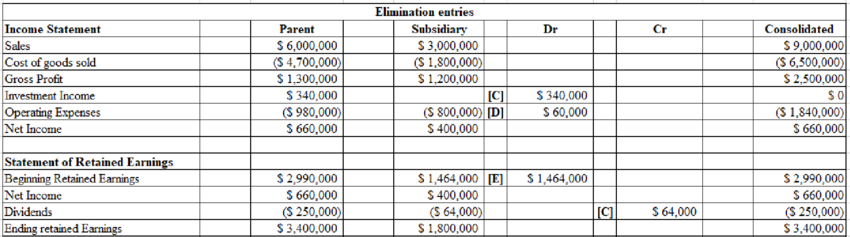
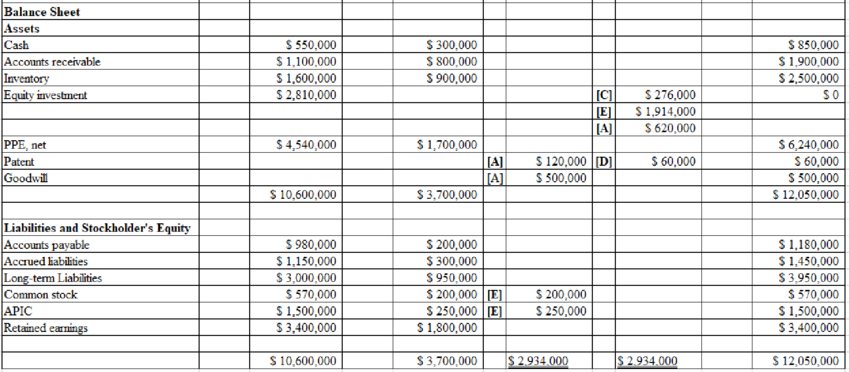
f.
Perform the test for potential
f.
Explanation of Solution
An acquisition of assets is the purchase of a corporation by purchasing its assets rather than its stock. An acquisition is when one company acquires most or all of the shares of another company to gain control over that company. An investment in equity is money which is invested in a company by buying that company's shares in the stock market. Typically, those shares are traded in a stock exchange.
Goodwill is an intangible asset associated with one company being purchased from another. In particular, goodwill is the portion of the purchase price which is higher than the sum of the net fair value of all the assets purchased during the acquisition and the liabilities assumed during the acquisition process. If the acquired assets are not a business, then as an asset acquisition, the reporting entity shall account for the transaction or other event. Goodwill impairment is an accounting charge recorded by companies when the carrying value of the goodwill on the financial statements exceeds its fair value. Goodwill is recorded in accounting after a company retains assets and liabilities, and needs to pay a price that exceeds its identifiable net value. Goodwill impairment testing must be performed annually and every year on about the same date. Companies can either choose to run the quantitative impairment test specifically, or take advantage of the opportunity to undertake a qualitative impairment test. If a company chooses to perform a qualitative impairment test, then the company must perform a quantitative impairment test if the appropriate events and circumstances signify that it is more probable than not that a reporting unit's fair value is lower than its carrying amount
Because the fair value of the subsidiary ($2.5 million) is less than the book value of the equity investment account ($2,810,000), Goodwill is therefore potentially impaired and you should continue to the second part of the impairment test. Goodwill impairment is an accounting charge recorded by companies when the carrying value of the goodwill on the financial statements exceeds its fair value. The amount of the impairment is the difference between these two amounts (i.e., $310,000), provided that the difference is not greater than the Goodwill balance (i.e., $500,000). The fair value of the identifiable net assets provided in the problem (other than Goodwill) is irrelevant. Hence, the goodwill asset is found to be impaired.
Goodwill is an intangible asset associated with one company being purchased from another. Goodwill impairment is an accounting charge recorded by companies when the carrying value of the goodwill on the financial statements exceeds its fair value.
Goodwill with the following
| Date | Accounting Explanation | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Equity income from S | |||
| Equity investment | |||
| (to write down the book value of goodwill) |
Table (1)
Goodwill will now be reported at $190,000 on the consolidated balance sheet, and a loss on goodwill write- down will be reported in the consolidated income statement. Thereafter, the goodwill asset cannot be written up if the fair value of the subsidiary improves.
g.
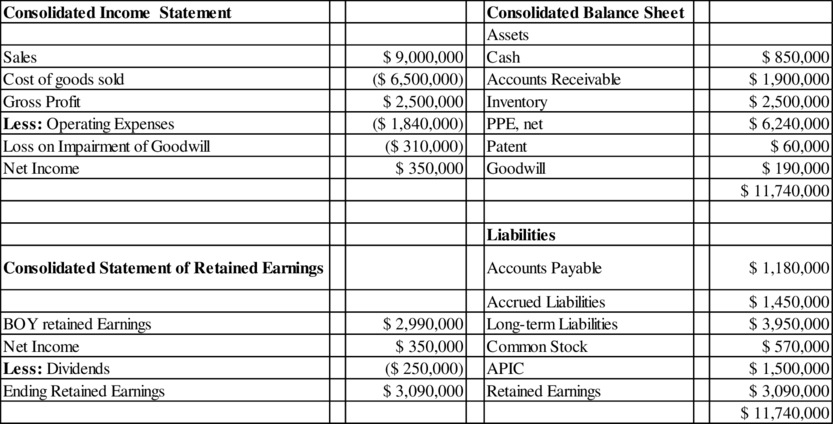
Prepare the consolidated balance sheet and the consolidated income statement and consolidated statement of retained earnings for the year ended December 31, 2019.
g.
Explanation of Solution
Consolidated financial statements are a group of entities financial statements that are presented as those of a single economic entity. They are the financial statements of a group in which the parent company and its subsidiaries introduce their assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, expenses and cash flows as those of a single business organization.
A consolidated balance sheet provides a parent company's assets and liabilities and all of its subsidiaries in a legal document, without any differentiation on which items pertain to which companies.
A consolidated income statement describes an overall view of the organization as a
whole, instead of its component parts. Any money owed between the companies included
in the statement will not be regarded.
The retained earnings statement (retained earnings statement) is a financial report explaining the adjustments in a company's retained earnings over a specified period.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
ADVANCED ACCOUNTING
- Account Question answer wanted.arrow_forwardThe total manufacturing costs incurred for the year are $324,000. The overhead cost was 58% of the direct labor cost, and the direct material cost was $49,000. Direct labor cost was _____.arrow_forwardWhat are the variable maintenance cost per unit?arrow_forward
- A business purchases depreciable equipment for 215 and sells it a few years later for 172. At the time of the sale, accumulated depreciation totals 123. If the company's tax rate is 35, what is the total after-tax cash flow that will result from selling this asset?arrow_forwardWhat is the stock price? General Accountingarrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting question using the correct accounting procedures?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





