
Subpart (a):
Demand and supply.
Subpart (a):
Answer to Problem 4P
Explanation of Solution
When the supply decreases with constant demand curve, it will lead to a decrease in the
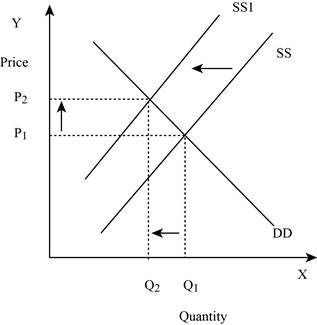
Figure -1
In Figure -1, the horizontal axis measures the quantity supplied and the vertical axis measures the price of the balls. ‘DD’ represents the demand and the demand curve shifts from DD to DD1; ‘SS’ represents the supply curve and the supply curve shifts from SS to SS1. Decrease in supply will lead to a decrease in the equilibrium quantity from ‘Q1 to Q2’ and an increase in the equilibrium price from ‘P1 to P2’.
Concept introduction:
Demand: Demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in the given period of time.
Supply: Supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in the given period of time.
Subpart (b):
Demand and supply.
Subpart (b):
Answer to Problem 4P
Price shifts down and quantity shifts down – b.
Explanation of Solution
When the demand decreases with constant supply curve, it will lead to a decrease in the equilibrium quantity and equilibrium price. This is shown below in Figure -2:
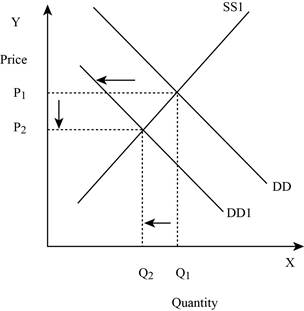
Figure -2
In Figure -2, the horizontal axis measures the quantity supplied and the vertical axis measures the price of the balls. ‘DD’ represents the demand and the demand curve shifts to the left from DD to DD1; ‘SS’ represents the supply curve. Decrease in supply will lead to a decrease in the equilibrium quantity from ‘Q1 to Q2’ and the equilibrium price from ‘P1 to P2’.
Concept introduction:
Demand: Demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in the given period of time.
Supply: Supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in the given period of time.
Subpart (c):
Demand and supply.
Subpart (c):
Answer to Problem 4P
Price shifts down and quantity shifts up – c.
Explanation of Solution
When the demand is constant with an increase in the supply curve, it will lead to a decrease in the equilibrium price and an increase in the equilibrium quantity. This is shown below in Figure -3:
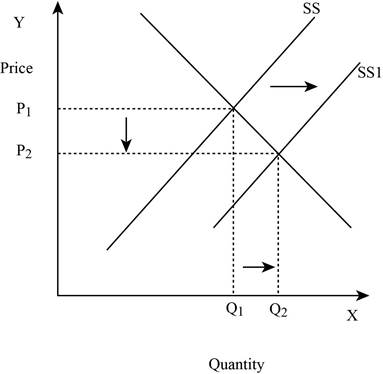
Figure -3
In Figure -3, the horizontal axis measures the quantity supplied and the vertical axis measures the price of the balls. ‘DD’ represents the demand and ‘SS’ represents the supply curve and the supply curve shifts to the right from SS to SS1. Increase in supply will lead to a decrease in the equilibrium price from ‘P1 to P2’ and an increase in the equilibrium quantity from ‘Q1 to Q2’.
Concept introduction:
Demand: Demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in the given period of time.
Supply: Supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in the given period of time.
Subpart (d):
Demand and supply.
Subpart (d):
Answer to Problem 4P
Price will indeterminate and quantity shifts up – d.
Explanation of Solution
When both the demand and supply increases, it will lead to an increase in the equilibrium quantity and the change in price is indeterminate. This is because an increase in the supply puts a downward pressure on the equilibrium price. This is shown below in Figure – 4:
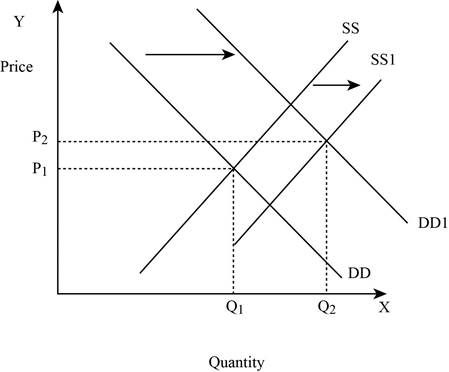
Figure -4
In Figure -4, the horizontal axis measures the quantity supplied and the vertical axis measures the price of the balls. ‘DD’ represents the demand curve and ‘SS’ represents the supply curve. Due to the increase in supply and demand, the supply curve shifts to the right from SS to SS1 and the demand curve shifts from DD to DD1. An increase in the supply leads to an increase in the equilibrium price from ‘P1 to P2’ and the equilibrium quantity from ‘Q1 to Q2’.
Concept introduction:
Demand: Demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in the given period of time.
Supply: Supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in the given period of time.
Subpart (e):
Demand and supply.
Subpart (e):
Answer to Problem 4P
Price shifts up and quantity shifts up – e.
Explanation of Solution
If the demand increases with constant supply, it leads to an increase in the equilibrium quantity and equilibrium price. This is shown below in Figure – 5:
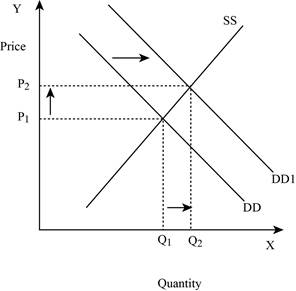
Figure -5
In Figure -5, the horizontal axis measures the quantity supplied and the vertical axis measures the price of the balls. ‘DD’ represents the demand curve and ‘SS’ represents the supply curve. Due to an increase in demand, the demand curve will shift the curve to the right from DD to DD1. An increase in demand will increase the equilibrium price from ‘P1 to P2’ and increases the equilibrium quantity from ‘Q1 to Q2’.
Concept introduction:
Demand: Demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in the given period of time.
Supply: Supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in the given period of time.
Subpart (f):
Demand and supply.
Subpart (f):
Answer to Problem 4P
Price shifts down and quantity indeterminate – f.
Explanation of Solution
If the supply increases with a decrease in demand, it leads to a decrease in the equilibrium price because both the curves put a pressure on the equilibrium price. Thus, an increase in supply increases the equilibrium quantity and a decrease in demand lead to a decrease in the equilibrium quantity. This is shown below in Figure – 6:
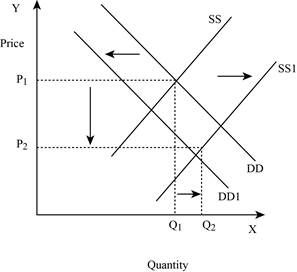
Figure -6
In Figure -6, the horizontal axis measures the quantity supplied and the vertical axis measures the price of the balls. ‘DD’ represents the demand curve and ‘SS’ represents the supply curve. Due to a decrease in demand and an increase in supply, demand curve will shift the curve to the left from DD to DD1. An increase in supply will lead to an increase in the equilibrium quantity from ‘P1 to P2’ and increases the equilibrium quantity from ‘Q1 to Q2’.
Concept introduction:
Demand: Demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in the given period of time.
Supply: Supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in the given period of time.
Subpart (g):
Demand and supply.
Subpart (g):
Answer to Problem 4P
Price shifts up and quantity indeterminate – g.
Explanation of Solution
If the supply decreases with an increase in demand, it will lead to an increase in the equilibrium price because both the curve put a pressure on the equilibrium price. An increase in demand will lead to an increase in the equilibrium quantity. This is shown below in Figure – 7:
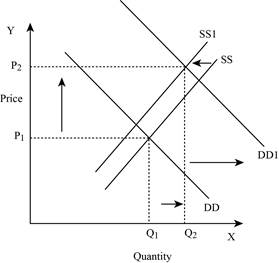
Figure -7
In Figure -7, the horizontal axis measures the quantity supplied and the vertical axis measures the price of the balls. ‘DD’ represents the demand and ‘SS’ represents the supply curve. Due to a decrease in supply and an increase in demand, the supply curve will shift the curve to the left from SS to SS1 and the demand curve shifts the curve to the right, which leads to an increase in the equilibrium price from ‘P1 to P2’ and the equilibrium quantity from ‘Q1 to Q2’.
Concept introduction:
Demand: Demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in the given period of time.
Supply: Supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in the given period of time.
Subpart (h):
Demand and supply.
Subpart (h):
Answer to Problem 4P
Price indeterminate and quantity shifts down – h.
Explanation of Solution
If both the supply and demand decreases, then it lead to a decrease in the equilibrium quantity and the change in equilibrium price is indeterminate. This is because a decrease in supply puts an upward pressure on the equilibrium price. This is shown below in Figure – 8:
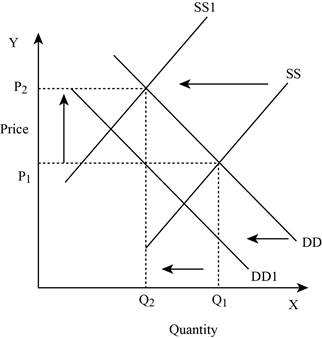
Figure -8
In Figure -8, the horizontal axis measures the quantity supplied and the vertical axis measures the price of the balls. ‘DD’ represents the demand and ‘SS’ represents the supply curve. Due to a decrease in supply and a decrease in demand, the supply curve will shift the curve to the left from SS to SS1 and the demand curve shifts the curve to the left, which lead to an increase in the equilibrium price from ‘P1 to P2’ and a decrease in the equilibrium quantity from ‘Q1 to Q2’.
Concept introduction:
Demand: Demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in the given period of time.
Supply: Supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in the given period of time.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Macroeconomics
- 17. Given that C=$700+0.8Y, I=$300, G=$600, what is Y if Y=C+I+G?arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Write explanation in paragraphs and if you use currency use USD currency: 10. What is the mechanism or process that allows the expenditure multiplier to “work” in theKeynesian Cross Model? Explain and show both mathematically and graphically. What isthe underpinning assumption for the process to transpire?arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’reexplaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Write it all in paragraphs: 2. Give an overview of the equation of exchange (EoE) as used by Classical Theory. Now,carefully explain each variable in the EoE. What is meant by the “quantity theory of money”and how is it different from or the same as the equation of exchange?arrow_forward
- Zbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwh Zbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwh Zbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwhZbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwhZbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwharrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all:arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’reexplaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 4. Draw a Keynesian AD curve in P – Y space and list the shift factors that will shift theKeynesian AD curve upward and to the right. Draw a separate Classical AD curve in P – Yspace and list the shift factors that will shift the Classical AD curve upward and to the right.arrow_forward
- Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 10. What is the mechanism or process that allows the expenditure multiplier to “work” in theKeynesian Cross Model? Explain and show both mathematically and graphically. What isthe underpinning assumption for the process to transpire?arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 15. How is the Keynesian expenditure multiplier implicit in the Keynesian version of the AD/ASmodel? Explain and show mathematically. (note: this is a tough one)arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 13. What would happen to the net exports function in Europe and the US respectively if thedemand for dollars rises worldwide? Explain why.arrow_forward
 Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971493Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971493Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning





