
Subpart (a):
Demand and supply.
Subpart (a):
Answer to Problem 4P
Explanation of Solution
When the supply decreases with constant demand curve, it will lead to a decrease in the
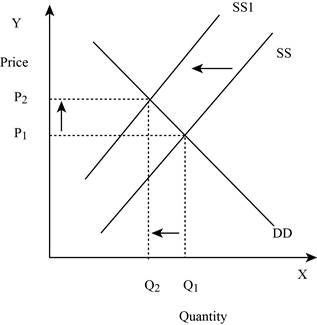
Figure -1
In Figure -1, the horizontal axis measures the quantity supplied and the vertical axis measures the price of the balls. ‘DD’ represents the demand and the demand curve shifts from DD to DD1; ‘SS’ represents the supply curve and the supply curve shifts from SS to SS1. Decrease in supply will lead to a decrease in the equilibrium quantity from ‘Q1 to Q2’ and an increase in the equilibrium price from ‘P1 to P2’.
Concept introduction:
Demand: Demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in the given period of time.
Supply: Supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in the given period of time.
Subpart (b):
Demand and supply.
Subpart (b):
Answer to Problem 4P
Price shifts down and quantity shifts down – b.
Explanation of Solution
When the demand decreases with constant supply curve, it will lead to a decrease in the equilibrium quantity and equilibrium price. This is shown below in Figure -2:
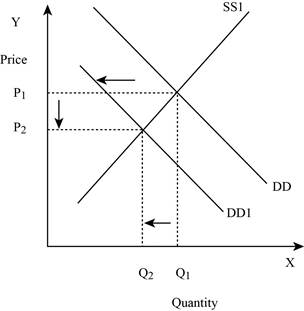
Figure -2
In Figure -2, the horizontal axis measures the quantity supplied and the vertical axis measures the price of the balls. ‘DD’ represents the demand and the demand curve shifts to the left from DD to DD1; ‘SS’ represents the supply curve. Decrease in supply will lead to a decrease in the equilibrium quantity from ‘Q1 to Q2’ and the equilibrium price from ‘P1 to P2’.
Concept introduction:
Demand: Demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in the given period of time.
Supply: Supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in the given period of time.
Subpart (c):
Demand and supply.
Subpart (c):
Answer to Problem 4P
Price shifts down and quantity shifts up – c.
Explanation of Solution
When the demand is constant with an increase in the supply curve, it will lead to a decrease in the equilibrium price and an increase in the equilibrium quantity. This is shown below in Figure -3:
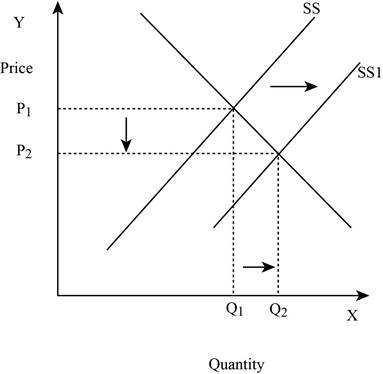
Figure -3
In Figure -3, the horizontal axis measures the quantity supplied and the vertical axis measures the price of the balls. ‘DD’ represents the demand and ‘SS’ represents the supply curve and the supply curve shifts to the right from SS to SS1. Increase in supply will lead to a decrease in the equilibrium price from ‘P1 to P2’ and an increase in the equilibrium quantity from ‘Q1 to Q2’.
Concept introduction:
Demand: Demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in the given period of time.
Supply: Supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in the given period of time.
Subpart (d):
Demand and supply.
Subpart (d):
Answer to Problem 4P
Price will indeterminate and quantity shifts up – d.
Explanation of Solution
When both the demand and supply increases, it will lead to an increase in the equilibrium quantity and the change in price is indeterminate. This is because an increase in the supply puts a downward pressure on the equilibrium price. This is shown below in Figure – 4:
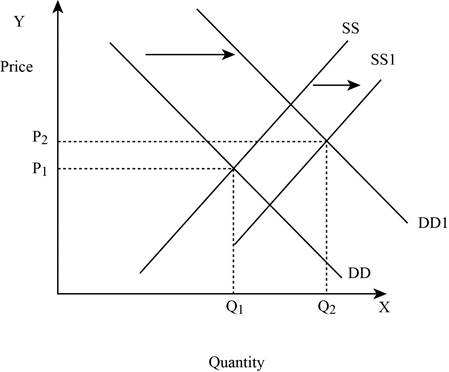
Figure -4
In Figure -4, the horizontal axis measures the quantity supplied and the vertical axis measures the price of the balls. ‘DD’ represents the demand curve and ‘SS’ represents the supply curve. Due to the increase in supply and demand, the supply curve shifts to the right from SS to SS1 and the demand curve shifts from DD to DD1. An increase in the supply leads to an increase in the equilibrium price from ‘P1 to P2’ and the equilibrium quantity from ‘Q1 to Q2’.
Concept introduction:
Demand: Demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in the given period of time.
Supply: Supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in the given period of time.
Subpart (e):
Demand and supply.
Subpart (e):
Answer to Problem 4P
Price shifts up and quantity shifts up – e.
Explanation of Solution
If the demand increases with constant supply, it leads to an increase in the equilibrium quantity and equilibrium price. This is shown below in Figure – 5:
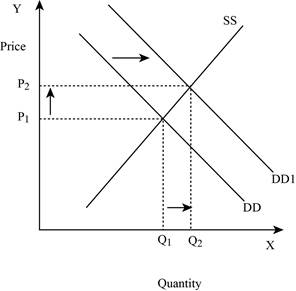
Figure -5
In Figure -5, the horizontal axis measures the quantity supplied and the vertical axis measures the price of the balls. ‘DD’ represents the demand curve and ‘SS’ represents the supply curve. Due to an increase in demand, the demand curve will shift the curve to the right from DD to DD1. An increase in demand will increase the equilibrium price from ‘P1 to P2’ and increases the equilibrium quantity from ‘Q1 to Q2’.
Concept introduction:
Demand: Demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in the given period of time.
Supply: Supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in the given period of time.
Subpart (f):
Demand and supply.
Subpart (f):
Answer to Problem 4P
Price shifts down and quantity indeterminate – f.
Explanation of Solution
If the supply increases with a decrease in demand, it leads to a decrease in the equilibrium price because both the curves put a pressure on the equilibrium price. Thus, an increase in supply increases the equilibrium quantity and a decrease in demand lead to a decrease in the equilibrium quantity. This is shown below in Figure – 6:
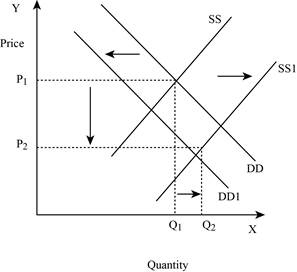
Figure -6
In Figure -6, the horizontal axis measures the quantity supplied and the vertical axis measures the price of the balls. ‘DD’ represents the demand curve and ‘SS’ represents the supply curve. Due to a decrease in demand and an increase in supply, demand curve will shift the curve to the left from DD to DD1. An increase in supply will lead to an increase in the equilibrium quantity from ‘P1 to P2’ and increases the equilibrium quantity from ‘Q1 to Q2’.
Concept introduction:
Demand: Demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in the given period of time.
Supply: Supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in the given period of time.
Subpart (g):
Demand and supply.
Subpart (g):
Answer to Problem 4P
Price shifts up and quantity indeterminate – g.
Explanation of Solution
If the supply decreases with an increase in demand, it will lead to an increase in the equilibrium price because both the curve put a pressure on the equilibrium price. An increase in demand will lead to an increase in the equilibrium quantity. This is shown below in Figure – 7:
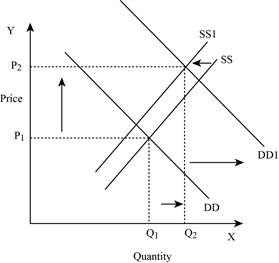
Figure -7
In Figure -7, the horizontal axis measures the quantity supplied and the vertical axis measures the price of the balls. ‘DD’ represents the demand and ‘SS’ represents the supply curve. Due to a decrease in supply and an increase in demand, the supply curve will shift the curve to the left from SS to SS1 and the demand curve shifts the curve to the right, which leads to an increase in the equilibrium price from ‘P1 to P2’ and the equilibrium quantity from ‘Q1 to Q2’.
Concept introduction:
Demand: Demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in the given period of time.
Supply: Supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in the given period of time.
Subpart (h):
Demand and supply.
Subpart (h):
Answer to Problem 4P
Price indeterminate and quantity shifts down – h.
Explanation of Solution
If both the supply and demand decreases, then it lead to a decrease in the equilibrium quantity and the change in equilibrium price is indeterminate. This is because a decrease in supply puts an upward pressure on the equilibrium price. This is shown below in Figure – 8:
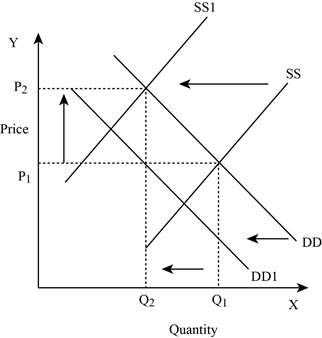
Figure -8
In Figure -8, the horizontal axis measures the quantity supplied and the vertical axis measures the price of the balls. ‘DD’ represents the demand and ‘SS’ represents the supply curve. Due to a decrease in supply and a decrease in demand, the supply curve will shift the curve to the left from SS to SS1 and the demand curve shifts the curve to the left, which lead to an increase in the equilibrium price from ‘P1 to P2’ and a decrease in the equilibrium quantity from ‘Q1 to Q2’.
Concept introduction:
Demand: Demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in the given period of time.
Supply: Supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in the given period of time.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Economics (Irwin Economics)
- Using the graph on the right, determine the per unit prices of capital and labour. 20- Given the information provided about the isocost lines, we know that the per unit price of capital is TC=$100 and the per unit price of labour is 16- TC $80 ○ A. $50; $20 ○ B. $2; $5 ○ C. $5; $2 ○ D. $20; $50 E. not determinable; not determinable Quantity of K 12 TC $60 TC $40 0 10 20 30 Quantity of L 40arrow_forwardThe diagram to the right contains isocost lines A and B. If the price of capital is the same for both lines, then the difference between isocost line A and isocost line B is that OA. the total cost is larger along B. B. the level of output is lower along A. C. both capital and labour are cheaper along A. OD. labour is more expensive along A. ○ E. labour is more expensive along B. Capital Labourarrow_forwardFor the firm whose cost curves are shown at right, the minimum efficient scale is ○ A. between 60 and 140 units of production. OB. about 20 units of production. OC. about 60 units of production. OD. about 100 units of production. OE. the level of fixed cost corresponding to SRATC2. SRATC₁ LRAC SRATC4 SRATC₂ SRATC3 เนด เad iso C 20 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 Output per Periodarrow_forward
- SRATC₂ SRATC3 In the figure, increasing long-run average total costs for the firm are confined to the output range OA. where the LRAC curve is downward sloping. B. above 80 units of output. O C. above 50 units of output. OD. between 50 and 80 units of output. SRATC₁ OE. between 10 and 100 units of output. ---- SRATC LRAC 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Output per Periodarrow_forwardFor the firm whose cost curves are shown at right, the minimum efficient scale is OA. between 10 and 50 units of production. OB. about 80 units of production. O C. the level of fixed cost corresponding to SRATC₁. OD. about 10 units of production. ○ E. about 50 units of production. Cost per Unit SRATC₁ LRAC SRATC2 SRATC4 SRATC3 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Output per Period 90 100arrow_forward• 3 different people working at any companies under the BPO industry in the Philippines. • What are the 3 different Vision, Mission, Duties and Responsibilities and Career Path of these people in their companies under the BPO industry?arrow_forward
- Module 6 ⚫(1902) Buckner C X | (1902) How to d x (1902) Buckner F X (1902) Productic X WP Videoplayer Canvas Login | Ir x | + Σ R mybrcc.instructure.com/courses/417310/discussion_topics/3420114?module_item_id=20155705 Spring 2025 Home Announcements Modules Syllabus Grades 8 People BRCC-_Library DLASC Module 6 Discussion - Business Costs Relaunch to update For this discussion, think about where you work or a business you have a significant amount of knowledge about. What is a common product that the business sells? What are the main costs the business has to incur in order to be able to sell that product? Which of these costs are fixed and which are variable? How much additional costs would be incurred if it were to sell one additional unit of that product (marginal cost)? Write a discussion thread about this business, the product it commonly sells, and your answers to the above questions. Also, respond to at least two threads created by your classmates. In these responses, share what…arrow_forwardRefer to the video to answer the following: • what are all the key policies or all the strategies the Philippine government should prioritize to accelerate sustainable economic growth? • these should consider the Philippines current economic challenges, including inflation, unemployment, and the need for digital transformation. "The Philippines' Strong Economic Growth" (YouTube link: https://youtu.be/1YtEoGp2ZeM?siJQfIv5kbu0txVsLL.)arrow_forwardsolve about this qarrow_forward
 Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971493Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971493Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning





