
Concept explainers
a)
Interpretation:
The group should be determined to which Z belongs in the following Lewis structure and along with an example of such a compound or ion which actually exists.
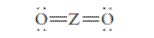
Concept Introduction:
Number of lone pair and bond pair electrons on an atom can give the number of valence electrons. This is indicated by the group number of an atom.
Group number is equal to the valence shell electrons of an atom or electrons present in the outermost shell. Valence shell electrons of the atom take part in the bonding.
Formal charge on an atom is defined as the charge assigned to the atom in a molecule. It is assigned to an atom or molecule by assuming that the electrons in
Formal charge is equal to
b)
Interpretation:
The group should be determined to which Z belongs in the following Lewis structure and along with an example of such a compound or ion which actually exists.
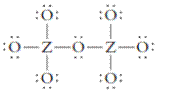
Concept Introduction:
Number of lone pair and bond pair electrons on an atom can give the number of valence electrons. This is indicated by the group number of an atom.
Group number is equal to the valence shell electrons of an atom or electrons present in the outermost shell. Valence shell electrons of the atom take part in the bonding.
Formal charge on an atom is defined as the charge assigned to the atom in a molecule. It is assigned to an atom or molecule by assuming that the electrons in chemical bonds are shared equally between atoms, apart from relative electronegativity.
Formal charge is equal to
c)
Interpretation:
The group should be determined to which Z belongs in the following Lewis structure and along with an example of such a compound or ion which actually exists.
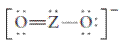
Concept Introduction:
Number of lone pair and bond pair electrons on an atom can give the number of valence electrons. This is indicated by the group number of an atom.
Group number is equal to the valence shell electrons of an atom or electrons present in the outermost shell. Valence shell electrons of the atom take part in the bonding.
Formal charge on an atom is defined as the charge assigned to the atom in a molecule. It is assigned to an atom or molecule by assuming that the electrons in chemical bonds are shared equally between atoms, apart from relative electronegativity.
Formal charge is equal to
d)
Interpretation:
The group should be determined to which Z belongs in the following Lewis structure and along with an example of such a compound or ion which actually exists.
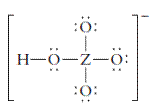
Concept Introduction:
Number of lone pair and bond pair electrons on an atom can give the number of valence electrons. This is indicated by the group number of an atom.
Group number is equal to the valence shell electrons of an atom or electrons present in the outermost shell. Valence shell electrons of the atom take part in the bonding.
Formal charge on an atom is defined as the charge assigned to the atom in a molecule. It is assigned to an atom or molecule by assuming that the electrons in chemical bonds are shared equally between atoms, apart from relative electronegativity.
Formal charge is equal to
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
OWLV2 FOR OXTOBY/GILLIS/BUTLER'S PRINCI
- (4 pts - 2 pts each part) A route that can be taken to prepare a hydrophobic (water-repellent) aerogel is to start with trichloromethylsilane, CH3SiCl3 as the silicon source. a. What is the chemical reaction that this undergoes to form a product with Si-OH groups? Write as complete of a chemical equation as you can. CI CI-SI-CH3 CI b. The formation of a byproduct is what drives this reaction - what is the byproduct (if you didn't already answer it in part (a)) and how/why does it form?arrow_forwardb) Circle the substrate that would not efficiently generate a Grignard reagent upon reaction with Mg in ether. CI Br ד c) Circle the Grignard reagents that contain incompatible functional groups. MgBr HO MgBr MgBr MgBr MgBr HO MgBrarrow_forwardQ2: Predict all organic product(s), including stereoisomers when applicable. PCC OH a) CH2Cl2 Page 2 of 5 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 HW Problem Sets b) .OH Na2Cr2O7, H+ OH PCC CH2Cl2 c) OHarrow_forward
- d) Circle the substrates that will give an achiral product after a Grignard reaction with CH3MgBr. Harrow_forwardQ4: Predict the organic products for the following reactions. Then draw curved arrow electron- pushing mechanism for the reactions. a) NaBH4 EtOH Page 4 of 5 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 HW Problem Sets b) 요 1. Et₂O H MgBr 2. H+, H₂Oarrow_forward5Helparrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER





