
Concept explainers
1.
Prepare the journal entries to record the each of the transactions and events for Solution B.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entries.
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| December 2 | Advertising expense | 655 | 1,025 | |
| Cash | 101 | 1,025 | ||
| (To record the advertising expense) | ||||
| December 3 | Repairs and expense-Computer | 684 | 500 | |
| Cash | 101 | 500 | ||
| (To record the repairs and expenses) | ||||
| December 4 | Cash | 101 | 3,950 | |
| Accounts receivable | 106 | 3,950 | ||
| (To record the accounts receivable) | ||||
| December 10 | Wages expense | 623 | 750 | |
| Cash | 101 | 750 | ||
| (To record the wages expense) | ||||
| December 14 | Cash | 101 | 1,500 | |
| Unearned computer service revenue |
236 | 1,500 | ||
| (To record the unearned service revenue) | ||||
| December 15 | Cash | 101 | 1,100 | |
| Accounts payable | 201 | 1,100 | ||
| (To record the accounts payable) | ||||
| December 20 | Cash | 101 | 5,625 | |
| Computer service revenue | 403 | 5,625 | ||
| (To record the computer service revenue) | ||||
| December 28 | Cash | 101 | 3,000 | |
| Accounts receivable | 106 | 3,000 | ||
| (To record the travel expense) | ||||
| December 29 | Mileage expense | 676 | 192 | |
| Cash | 101 | 192 | ||
| (To record the mileage expense) | ||||
| December 31 | Dividends | 319 | 1,500 | |
| Cash | 1,500 | |||
| (To record the payment of dividends) |
Table (1)
2.
Prepare the
2.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries: Adjusting entries are those entries which are recorded at the end of the year, to update the income statement accounts (revenue and expenses) and
Prepare the adjusting entries as on 31st December 2015.
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| December 31 | Computer supplies expense | 652 | 3,065 | |
| Computer | 126 | 3,065 | ||
| (To record the adjusting entry for supplies used) | ||||
| December 31 | Insurance expense | 637 | 555 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 128 | 555 | ||
| (To record the adjusting entry for insurance expense) | ||||
| December 31 | Wages expense | 623 | 500 | |
| Wages payable | 210 | 500 | ||
| (To record the adjusting entry for wages expense) | ||||
| December 31 | 613 | 1,250 | ||
| 168 | 1,250 | |||
| (To record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense, Computer) | ||||
| December 31 | Depreciation expense-Office equipment | 612 | 400 | |
| Accumulated depreciation-Office equipment | 164 | 400 | ||
| (To record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense, Office equipment) | ||||
| December 31 | Rent expense | 640 | 2,475 | |
| Prepaid rent | 131 | 2,475 | ||
| (To record the adjusting entry for rent expense) |
Table (2)
3.
Prepare the adjusted
3.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusted trial balance:
Adjusted trial balance is a summary of all the ledger accounts, and it contains the balances of all the accounts after the adjustment entries are journalized, and posted.
Prepare the adjusted trial balance as of 31st December 2015.
| Solution B | ||
| Adjusted trial balance | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2015 | ||
| Particulars | Debit($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 48,372 | |
| Accounts receivable | 5,668 | |
| Computer supplies | 580 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 1,665 | |
| Prepaid rent | 825 | |
| Office equipment | 8,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation, Office | 400 | |
| Computer equipment | 20,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation, Computer | 1,250 | |
| Accounts payable | 1,100 | |
| Wages payable | 500 | |
| Unearned computer service revenue | 1,500 | |
| Common stock | 73,000 | |
| 0 | ||
| Dividends | 7,100 | |
| Computer services revenue | 31,284 | |
| Depreciation expense, Office | 400 | |
| Depreciation expense, Equipment | 1,250 | |
| Wages expense | 3,875 | |
| Insurance expense | 555 | |
| Rent expense | 2,475 | |
| Computer supplies expense | 3,065 | |
| Advertising expense | 2,753 | |
| Mileage expense | 896 | |
| Miscellaneous expense | 250 | |
| Repairs expense, computer | 1,305 | |
| Totals | $109,034 | $109,034 |
Table (3)
4.
Prepare the income statement for the three months ended 31st December 2015.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
Income statement is a financial statement that shows the net income or net loss by deducting the expenses from the revenues and vice versa.
Prepare the income statement for the year ended 31st December 2015.
| Solution B | ||
| Income statement | ||
| For the three months ended December 31, 2015 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenues | ||
| Computer service revenue | 31,284 | |
| Total revenue | 31,284 | |
| Expenses | ||
| Depreciation expense, Office | 400 | |
| Depreciation expense, Computer | 1,250 | |
| Wages expense | 3,875 | |
| Insurance expense | 555 | |
| Rent expense | 2,475 | |
| Computer Supplies expense | 3,065 | |
| Advertising expense | 2,753 | |
| Property taxes expense | 4,825 | |
| Mileage expense | 896 | |
| Repairs expense, Computer | 1,305 | |
| Total Expenses | 16,824 | |
| Net income | $14,460 | |
Table (4)
5.
Prepare the statement of retained earnings for the three months ended 31st December 2015.
5.
Explanation of Solution
Statement of Retained Earnings:
Statement of retained earnings shows, the changes in the retained earnings, and the income left in the company after payment of the dividends, for the accounting period.
Prepare the statement of retained earnings for the year ended 31st December 2015.
| Solution B | ||
| Statement of Retained Earnings | ||
| For the three months ended 31st December 2015 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Retained earnings, Beginning | 0 | |
| Add: Net income | 14,460 | |
| Subtotal | 14,460 | |
| Less: Dividends | 7,100 | |
| Retained earnings, Ending | $7,360 | |
Table (5)
6.
Prepare the balance sheet as on 31st December 2015.
6.
Explanation of Solution
Balance sheet:
This financial statement reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and stockholders (stockholders’ equity) over those resources. The resources of the company are assets which include money contributed by stockholders and creditors. Hence, the main elements of the balance sheet are assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity.
Prepare the balance sheet as on 31st December 2015.
| Solution B | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| As an December 31, 2015 | ||
| Particulars | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| ASSETS | ||
| Current Assets: | ||
| Cash | 48,372 | |
| Accounts receivable | 5,668 | |
| Computer Supplies | 580 | |
| Prepaid rent | 825 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 1,665 | |
| Total Current Assets | 57,110 | |
| Office Equipment | 8,000 | |
| Less: Accumulated depreciation, Equipment | 400 | 7,600 |
| Computer equipment | 20,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation, Computer equipment | 1,250 | 18,750 |
| Total assets | $83,460 | |
| LIABILITIES | ||
| Current Liabilities: | ||
| Accounts payable | 1,100 | |
| Wages payable | 500 | |
| Unearned Computer service revenue | 1,500 | |
| Total current liabilities | 3,100 | |
| Long-liabilities: | 0 | |
| Total liabilities | 3,100 | |
| Stockholders’ equity | ||
| Paid-in capital | ||
| Common stock | 73,000 | |
| Retained earnings | 7,360 | |
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | 80,360 | |
| Total liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | $83,460 | |
Table (6)
7.
Record and post the necessary closing entries as of 31st December 2015.
7.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries: The journal entries prepared to close the temporary accounts to Retained Earnings account are referred to as closing entries. The revenue, expense, and dividends accounts are referred to as temporary accounts because the information and figures in these accounts is held temporarily and consequently transferred to permanent account at the end of accounting year.
Prepare the closing entry for revenue accounts.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31 | Computer services revenue | 403 | 31,284 | |
| Income summary | 901 | 31,284 | ||
| (To close the revenues account) |
Table (7)
In this closing entry, revenue accounts are closed by transferring the amount of revenue accounts to the income summary account in order to bring the revenue account balance to zero. Hence, debit the revenue accounts and credit income summary account.
Prepare the closing entry for expenses account.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31 | Income summary | 901 | 16,824 | |
| Depreciation expense-Office equipment | 612 | 400 | ||
| Depreciation expense- Computer Equipment | 613 | 1,250 | ||
| Wages expense | 623 | 3,875 | ||
| Insurance expense | 637 | 555 | ||
| Rent expense | 640 | 2,475 | ||
| Computer Supplies expense | 652 | 3,065 | ||
| Advertising expense | 655 | 2,753 | ||
| Mileage expense | 676 | 896 | ||
| Miscellaneous expense | 677 | 250 | ||
| Repairs expense | 684 | 1,305 | ||
| (To close the expenses account) |
Table (8)
In this closing entry, expenses account is closed by transferring the amount of expenses to the income summary in order to bring the expenses account balance to zero. Hence, debit the income summary account and credit all expenses account.
Prepare closing entry for income summary account.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31 | Income Summary | 901 | 14,460 | |
| Retained Earnings | 308 | 14,460 | ||
| (To close the income summary account) |
Table (9)
Closing entry of income summary account:
In this closing entry, income summary account is closed by transferring the amount of income summary (profit) to the retained earnings in order to bring the income summary account balance to zero. Hence, debit the income summary account and credit retained earnings account.
Prepare closing entry for dividend account.
Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31 | Retained Earnings | 318 | 7,100 | |
| Dividends | 7,100 | |||
| (To close the dividends account) |
Table (10)
In this closing entry, dividend account is closed by transferring the amount of dividend to the retained earnings in order to bring the dividend account balance to zero. Hence, debit the retained earnings account and credit dividend account.
8.
Prepare the post-closing trial balance as on 31st December 2015.
8.
Explanation of Solution
Post-closing trial balance:
The post-closing trial balance is a summary of all ledger accounts, and it shows the debit and the credit balances after the closing entries are journalized and posted. The post-closing trial balance contains only permanent (balance sheet) accounts, and the debit and the credit balances of permanent accounts should agree.
Prepare the post-closing trial balance as on 31st December 2015.
| Solution B | ||
| Adjusted trial balance | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2015 | ||
| Particulars | Debit($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 48,372 | |
| Accounts receivable | 5,668 | |
| Computer supplies | 580 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 1,665 | |
| Prepaid rent | 825 | |
| Office equipment | 8,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation, Office | 400 | |
| Computer equipment | 20,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation, Computer | 1,250 | |
| Accounts payable | 1,100 | |
| Wages payable | 500 | |
| Unearned computer service revenue | 1,500 | |
| Common stock | 73,000 | |
| Retained earnings | 7,360 | |
| Totals | $85,110 | $85,110 |
Table (11)
1, 2 and 7
Post the transactions to the general ledger.
1, 2 and 7
Explanation of Solution
Post the transactions to the general ledger.
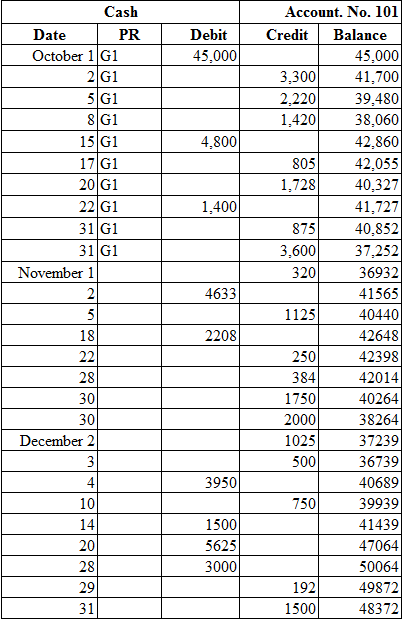
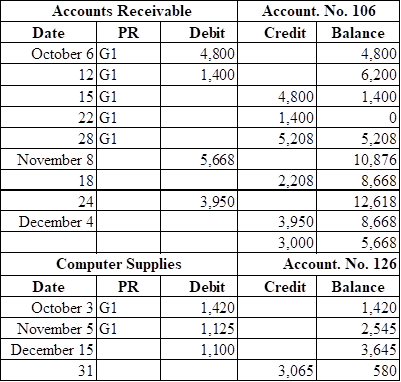


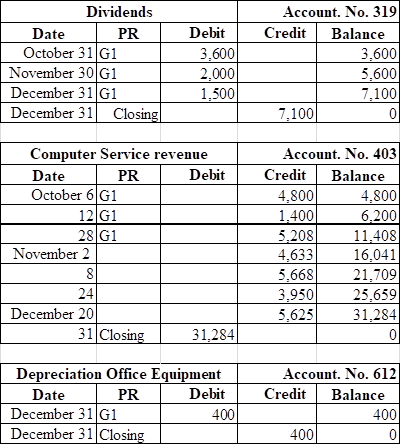


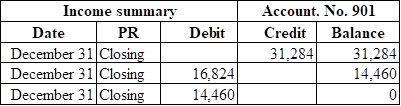
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING FUNDAMENTALS W/CO
- Subject = General Accountarrow_forwardInnovative Products operations for the year produced a margin of safety (M/S) ratio of 30% and a contribution margin (C/M) ratio of 60%. The company's fixed costs amounted to $75,000. Compute and interpret the following: Contribution Provide answerarrow_forwardAccounting?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





