
Concept explainers
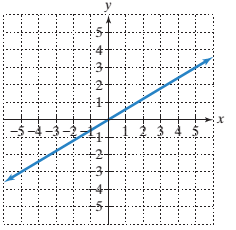
a)
The x−intercept of the line in the graph.
To calculate the x−intercept and y−intercept from the graph:
To find the x−intercept of a given line on a graph, the point where the line is intersecting the x−axis is the x−intercept and the point where the line is intersecting the y axis is the y−intercept.
To calculate the line’s slope:
Pick two points on the line and determine their coordinates.
Determine rise: the difference in y−coordinates of these two points.
Determine run: the difference in x−coordinates for these two points.
Divide the difference in y−coordinates by the difference in x−coordinates (rise/run or slope).
Given:
Line passing through the origin.
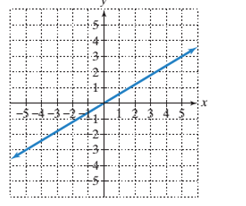
b)
The y−intercept of the line in the graph.
To calculate the x−intercept and y−intercept from the graph:
To find the x−intercept of a given line on a graph, the point where the line is intersecting the x−axis is the x−intercept and the point where the line is intersecting the y axis is the y−intercept.
To calculate the line’s slope:
Pick two points on the line and determine their coordinates.
Determine rise: the difference in y−coordinates of these two points.
Determine run: the difference in x−coordinates for these two points.
Divide the difference in y−coordinates by the difference in x−coordinates (rise/run or slope).
Given:
Line passing through the origin.
c)
The slope of line.
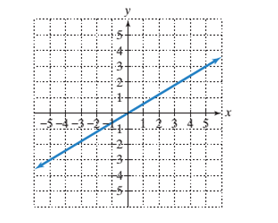
To calculate the x−intercept and y−intercept from the graph:
To find the x−intercept of a given line on a graph, the point where the line is intersecting the x−axis is the x−intercept and the point where the line is intersecting the y axis is the y−intercept.
To calculate the line’s slope:
Pick two points on the line and determine their coordinates.
Determine rise: the difference in y−coordinates of these two points.
Determine run: the difference in x−coordinates for these two points.
Divide the difference in y−coordinates by the difference in x−coordinates (rise/run or slope).
Given:
Line passing through the origin.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Introductory and Intermediate Algebra for College Students (5th Edition)
- Kate, Luke, Mary and Nancy are sharing a cake. The cake had previously been divided into four slices (s1, s2, s3 and s4). The following table shows the values of the slices in the eyes of each player. What is fair share to nancy? S1 S2 S3 S4 Kate $4.00 $6.00 $6.00 $4.00 Luke $5.30 $5.00 $5.25 $5.45 Mary $4.25 $4.50 $3.50 $3.75 Nancy $6.00 $4.00 $4.00 $6.00arrow_forwardKate, Luke, Mary and Nancy are sharing a cake. The cake had previously been divided into four slices (s1, s2, s3 and s4). The following table shows the values of the slices in the eyes of each player. S1 S2 S3 S4 Kate $4.00 $6.00 $6.00 $4.00 Luke $5.30 $5.00 $5.25 $5.45 Mary $4.25 $4.50 $3.50 $3.75 Nancy $6.00 $4.00 $4.00 $6.00 how much is the cak worth to maryarrow_forwardKate, Luke, Mary and Nancy are sharing a cake. The cake had previously been divided into four slices (s1, s2, s3 and s4). The following table shows the values of the slices in the eyes of each player. What is the threshold of fair share for Luke? S1 S2 S3 S4 Kate $4.00 $6.00 $6.00 $4.00 Luke $5.30 $5.00 $5.25 $5.45 Mary $4.25 $4.50 $3.50 $3.75 Nancy $6.00 $4.00 $4.00 $6.00arrow_forward
- 2. A microwave manufacturing firm has determined that their profit function is P(x)=-0.0014x+0.3x²+6x-355 , where is the number of microwaves sold annually. a. Graph the profit function using a calculator. b. Determine a reasonable viewing window for the function. c. Approximate all of the zeros of the function using the CALC menu of your calculator. d. What must be the range of microwaves sold in order for the firm to profit?arrow_forwardA clothing manufacturer's profitability can be modeled by p (x)=-x4 + 40x² - 144, where .x is the number of items sold in thousands and p (x) is the company's profit in thousands of dollars. a. Sketch the function on your calculator and describe the end behavior. b. Determine the zeros of the function. c. Between what two values should the company sell in order to be profitable? d. Explain why only two of the zeros are considered in part c.arrow_forwardCCSS REASONING The number of subscribers using pagers in the United States can be modeled by f(x) = 0.015x4 -0.44x³ +3.46x² - 2.7x+9.68 where x is the number of years after 1990 and f(x) is the number of subscribers in millions. a. Graph the function. b. Describe the end behavior of the graph. c. What does the end behavior suggest about the number of pager subscribers? d. Will this trend continue indefinitely? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forward
- Can you help me solve this?arrow_forwardName Assume there is the following simplified grade book: Homework Labs | Final Exam | Project Avery 95 98 90 100 Blake 90 96 Carlos 83 79 Dax 55 30 228 92 95 79 90 65 60 Assume that the weights used to compute the final grades are homework 0.3, labs 0.2, the final 0.35, and the project 0.15. | Write an explicit formula to compute Avery's final grade using a single inner product. Write an explicit formula to compute everyone's final grade simultane- ously using a single matrix-vector product.arrow_forward1. Explicitly compute by hand (with work shown) the following Frobenius inner products 00 4.56 3.12 (a) ((º º º). (156 (b) 10.9 -1 0 2)), Fro 5')) Froarrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





