
Concept explainers
a)
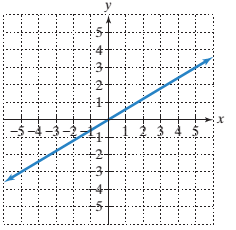
The x−intercept of the line in the graph.
To calculate the x−intercept and y−intercept from the graph:
To find the x−intercept of a given line on a graph, the point where the line is intersecting the x−axis is the x−intercept and the point where the line is intersecting the y axis is the y−intercept.
To calculate the line's slope:
Pick two points on the line and determine their coordinates.
Determine rise: the difference in y−coordinates of these two points.
Determine run: the difference in x−coordinates for these two points.
Divide the difference in y−coordinates by the difference in x−coordinates (rise/run or slope).
Given:
Line passing through the origin.
(b)
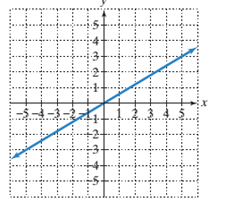
The y−intercept of the line in the graph.
To calculate the x−intercept and y−intercept from the graph:
To find the x−intercept of a given line on a graph, the point where the line is intersecting the x−axis is the x−intercept and the point where the line is intersecting the y axis is the y−intercept.
To calculate the line's slope:
Pick two points on the line and determine their coordinates.
Determine rise: the difference in y−coordinates of these two points.
Determine run: the difference in x−coordinates for these two points.
Divide the difference in y−coordinates by the difference in x−coordinates (rise/run or slope).
Given:
Line passing through the origin.
(c)
The slope of line.
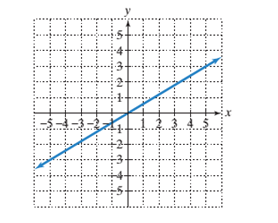
To calculate the x−intercept and y−intercept from the graph:
To find the x−intercept of a given line on a graph, the point where the line is intersecting the x−axis is the x−intercept and the point where the line is intersecting the y axis is the y−intercept.
To calculate the line's slope:
Pick two points on the line and determine their coordinates.
Determine rise: the difference in y−coordinates of these two points.
Determine run: the difference in x−coordinates for these two points.
Divide the difference in y−coordinates by the difference in x−coordinates (rise/run or slope).
Given:
Line passing through the origin.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Introductory Algebra for College Students (7th Edition)
- what model best fits this dataarrow_forwardRound as specified A) 257 down to the nearest 10’s place B) 650 to the nearest even hundreds, place C) 593 to the nearest 10’s place D) 4157 to the nearest hundreds, place E) 7126 to the nearest thousand place arrow_forwardEstimate the following products in two different ways and explain each method  A) 52x39 B) 17x74 C) 88x11 D) 26x42arrow_forward
- Find a range estimate for these problems A) 57x1924 B) 1349x45 C) 547x73951arrow_forwardDraw the image of the following figure after a dilation centered at the origin with a scale factor of 14 退 14 12- 10 5- + Z 6 的 A X 10 12 14 16 18 G min 3 5arrow_forwardkofi makes a candle as a gift for his mom. The candle is a cube with a volume of 8/125 ft cubed. Kofi wants to paint each face of the candle exepct for the bottom. what is the area he will paint?arrow_forward
- 10 6 9. 8 -7- 6. 5. 4- 3. 2 1- -1 0 -1 2 3 4 ·10 5 6 7 00 8 6 10arrow_forwardWeek 3: Mortgages and Amortiza X + rses/167748/assignments/5379530?module_item_id=23896312 11:59pm Points 10 Submitting an external tool Gider the following monthly amortization schedule: Payment # Payment Interest Debt Payment Balance 1 1,167.34 540.54 626.80 259,873.20 2 1,167.34 539.24 628.10 259,245.10 3 1,167.34 With the exception of column one, all amounts are in dollars. Calculate the annual interest rate on this loa Round your answer to the nearest hundredth of a percent. Do NOT round until you calculate the final answer. * Previous a Earrow_forwardCafé Michigan's manager, Gary Stark, suspects that demand for mocha latte coffees depends on the price being charged. Based on historical observations, Gary has gathered the following data, which show the numbers of these coffees sold over six different price values: Price Number Sold $2.70 765 $3.50 515 $2.00 990 $4.30 240 $3.10 325 $4.00 475 Using simple linear regression and given that the price per cup is $1.85, the forecasted demand for mocha latte coffees will be cups (enter your response rounded to one decimal place).arrow_forward
- Given the correlation coefficient (r-value), determine the strength of the relationship. Defend your answersarrow_forward??!!arrow_forwardrections: For problem rough 3, read each question carefully and be sure to show all work. 1. Determine if 9(4a²-4ab+b²) = (6a-3b)² is a polynomial identity. 2. Is (2x-y) (8x3+ y³) equivalent to 16x4-y4? 3. Find an expression that is equivalent to (a - b)³. Directions: For problems 4 and 5, algebraically prove that the following equations are polynomial identities. Show all of your work and explain each step. 4. (2x+5)² = 4x(x+5)+25 5. (4x+6y)(x-2y)=2(2x²-xy-6y²)arrow_forward

 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning





