
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
Step – 1
The skeletal structure and charge has to be drawn.
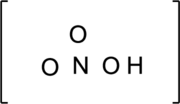
Step – 2
The total number of valence electrons is determined.
Step – 3
Connect the atoms using single bond.
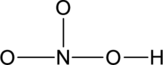
Step – 4
Start placing the lone pairs electrons around the atoms, giving each an octet. Do not exceed the 24 available electrons.
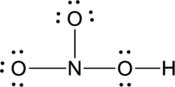
Step – 5
A final electron count indicates that each atom has eight valence electrons surrounding it.
(b)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
Step – 1
The skeletal structure and charge has to be drawn.
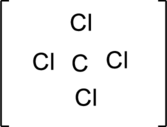
Step – 2
The total number of valence electrons is determined.
Step – 3
Connect the atoms using single bond.
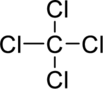
Step – 4
Start placing the lone pairs electrons around the atoms, giving each an octet. Do not exceed the 32 available electrons.
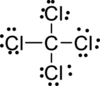
Step – 5
A final electron count indicates that each atom has eight valence electrons surrounding it.
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
Step – 1
The skeletal structure and charge has to be drawn.
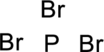
Step – 2
The total number of valence electrons is determined.
Step – 3
Connect the atoms using single bond.
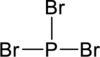
Step – 4
Start placing the lone pairs electrons around the atoms, giving each an octet. Do not exceed the 26 available electrons.
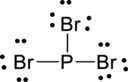
Step – 5
A final electron count indicates that each atom has eight valence electrons surrounding it.
(d)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
Step – 1
The skeletal structure and charge has to be drawn.
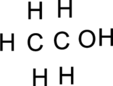
Step – 2
The total number of valence electrons is determined.
Step – 3
Connect the atoms using single bond.
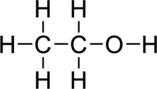
Step – 4
Start placing the lone pairs electrons around the atoms, giving each an octet. Do not exceed the 20 available electrons.
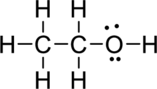
Step – 5
A final electron count indicates that each atom has eight valence electrons surrounding it.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Connect 1-Semester Access Card for General, Organic, and Biochemistry
- What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.arrow_forwardWhat is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forward
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





