
Concept explainers
Given the financial statements for Jones Corporation and Smith Corporation shown here:
a. To which one would you, as credit manager for a supplier, approve the extension of (short-term) trade credit? Why? Compute all ratios before answering.
b. In which one would you buy stock? Why?
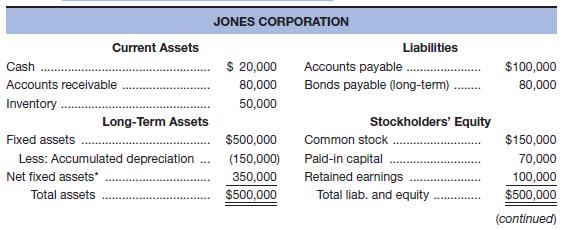
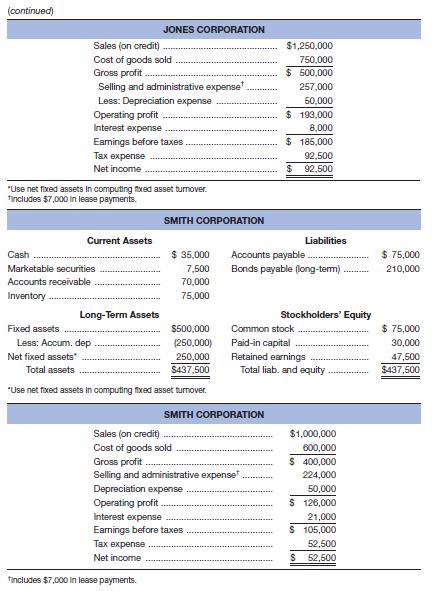
a.
To calculate: The relevant ratios so that the decision for the extension of short term trade credit can be taken.
Introduction:
Shortterm trade credit:
It is the type of credit that is granted to a business or an individual or a fixed loan for a period of not more than 12 months or 1 year.
Answer to Problem 37P
The Smith Corporation would get the extension of the short term trade credit as their liquidity ratios are better than those of the Jones Corporation; the suppliers and lenders are most concerned with the liquidity ratios.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of ratios for the Smith Corporation:
Calculation of current ratio:
Calculation of quick ratio:
Calculation of debt to total asset ratio:
Calculation of times interest ratio:
Calculation of fixed charge ratio:
Calculation of ratios for the Jones Corporation:
Calculation of current ratio:
Calculation of quick ratio:
Calculation of debt to total asset ratio:
Calculation of times interest ratio:
Calculation of fixed charge ratio:
b.
To determine: The company whose stock should be bought.
Introduction:
Stock:
Also termed as ordinary shares, it is a type of security that represents the corporate equity ownership. It is the best means to earn real rate of return ahead of inflation in the long run.
Answer to Problem 37P
The stocks of the Jones Corporation should be bought as their profit margin and return on assets are higher compared to the Smith Corporation; shareholders are mostly concerned with profitability.
But the return on equity is more for the Smith Corporation because it has taken a bigger financial risk. The times interest ratio and fixed charges ratio are higher for the Jones Corporation, which clearly reflects that their interest and fixed charges are well covered.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of ratios for the Smith Corporation:
Calculation of profit margin:
Calculation of return on assets:
Calculation of return on equity:
Calculation of debt to total asset ratio:
Calculation of times interest ratio:
Calculation of fixed charge ratio:
Calculation of ratios for the Jones Corporation:
Calculation of profit margin:
Calculation of return on assets:
Calculation of return on equity:
Calculation of debt to total asset ratio:
Calculation of times interest ratio:
Calculation of fixed charge ratio:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
EBK FOUNDATIONS OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
- If image is blurr then comment i will write values in comment . dont amswer with unclear data i will give unhelarrow_forwardQUESTION #1: ABC Inc. is debating the purchase of a new digital printer that will replace an older printer. The printer they acquired 2 years ago for $500,000 is worth $220,000 today and will have a salvage value of $80,000 after 5 more years. The printer generates revenues of $750,000 per year. The costs of operating the printer are $480,000 per year. The company currently has $110,000 invested in net operating working capital. The investment in net operating working capital will remain at this level for the remaining 5 years of the project. The new printer will cost $830,000. It will cost $60,000 to install the new printer. The new printer will generate revenues of $1,120,000 per year. In addition, the costs of operating the new printer will be $550,000 per year. The company will have to increase its investment in net operating working capital to $175,000 at time zero. The investment in operating new working capital will remain at this level for the remaining 5 years of the…arrow_forwardQUESTION #1: ABC Inc. is debating the purchase of a new digital printer that will replace an older printer. The printer they acquired 2 years ago for $500,000 is worth $220,000 today and will have a salvage value of $80,000 after 5 more years. The printer generates revenues of $750,000 per year. The costs of operating the printer are $480,000 per year. The company currently has $110,000 invested in net operating working capital. The investment in net operating working capital will remain at this level for the remaining 5 years of the project. The new printer will cost $830,000. It will cost $60,000 to install the new printer. The new printer will generate revenues of $1,120,000 per year. In addition, the costs of operating the new printer will be $550,000 per year. The company will have to increase its investment in net operating working capital to $175,000 at time zero. The investment in operating new working capital will remain at this level for the remaining 5 years of the…arrow_forward
- QUESTION #1: A) What is the Net Operating Profit After Tax (NOPAT) for 2024?B) What is the Operating Cash Flow for 2024? C) What is the Free Cash Flow for 2024? Note: Marketable securities are non-operating current assets, and short-term debt (bank loan) is a non-operating current liability. Both of these items are excluded from the calculation of net operating working capital. D) If the stock trades for $85 per share at the end of 2024, and there are 315,000 shares outstanding, what is the MVA in 2024? E) Given that the firm’s WACC is 14%, what is the EVA during 2024? F) Create common size income statement and balance sheet for 2024, 2023 and 2022. G) Using 2022 as the base year, create income statement and balance sheet percentage change analysis for 2024 and 2023. QUESTION #2: In addition to the AAA Ltd. financial statements in Problem One, you are given more information as follows. Sales are forecast to increase by 80% in 2025. Short-term Debt, Long-term Debt, and Common…arrow_forwardQUESTION #1: ABC Inc. is debating the purchase of a new digital printer that will replace an older printer. The printer they acquired 2 years ago for $500,000 is worth $220,000 today and will have a salvage value of $80,000 after 5 more years. The printer generates revenues of $750,000 per year. The costs of operating the printer are $480,000 per year. The company currently has $110,000 invested in net operating working capital. The investment in net operating working capital will remain at this level for the remaining 5 years of the project. The new printer will cost $830,000. It will cost $60,000 to install the new printer. The new printer will generate revenues of $1,120,000 per year. In addition, the costs of operating the new printer will be $550,000 per year. The company will have to increase its investment in net operating working capital to $175,000 at time zero. The investment in operating new working capital will remain at this level for the remaining 5 years of the…arrow_forwardSolve!arrow_forward
- QUESTION #1: A) What is the Net Operating Profit After Tax (NOPAT) for 2024?B) What is the Operating Cash Flow for 2024? C) What is the Free Cash Flow for 2024? Note: Marketable securities are non-operating current assets, and short-term debt (bank loan) is a non-operating current liability. Both of these items are excluded from the calculation of net operating working capital. D) If the stock trades for $85 per share at the end of 2024, and there are 315,000 shares outstanding, what is the MVA in 2024? E) Given that the firm’s WACC is 14%, what is the EVA during 2024? F) Create common size income statement and balance sheet for 2024, 2023 and 2022. G) Using 2022 as the base year, create income statement and balance sheet percentage change analysis for 2024 and 2023. QUESTION #2: In addition to the AAA Ltd. financial statements in Problem One, you are given more information as follows. Sales are forecast to increase by 80% in 2025. Short-term Debt, Long-term Debt, and Common…arrow_forwardEthical dilemma: Staci Sutter worsk for IIBS as an analyst and is responsible for assigning a value to the stock of ProTech Incorporated that will soon be sold as an IPO. The financial information that Staci has been given suggests that the company is financially strong. Although she has not been able to validate information a friend provided to her via e-mail, Staci is concerned that the financial information she has been provided by ProTech might paint a better financial picture than actually exists. Staci’s concern has been inflated as the result of pressure from her boss to set a good price for the IPO. In addition, it has been reported (rumored) that Staci’s boss is a friend (perhaps close) with the CEO of ProTech. Staci has completed her analysis based on the information she was provided by ProTech, and she is ready to assign a price to the company’s stock. But, if the additional, unconfirmed information she has is correct, the price she sets might differ from what her analysis…arrow_forwardAfter checking her inventory, Yao-lin discovered she had excess supplies in her warehouse. How does she account for this?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning





