
The magnitude and location of the hydrostatic force on the vertical rectangular plate.
Answer to Problem 3.6.1P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Length of the rectangular plate = 4 m
Width of the rectangular plate = 2 m
Formula used:
where, F is the hydrostatic force
A is the surface area
Calculation:
The given figure is shown below:
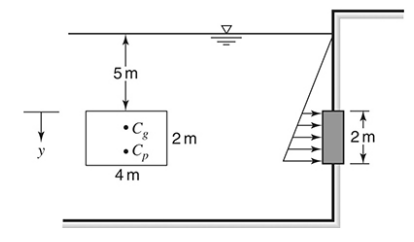
The vertical distance to the centroid is calculated as:
The hydrostatic force is calculated as:
The location of the hydrostatic force is calculated as:
Conclusion:
The magnitude and location of the hydrostatic force on the vertical rectangular plate are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING
- Assume that the moist unit weight of sand in Problem 1 to be 122 lb/ft3, the saturated unit weight of sand 130 and clay 120 lb/ft 3. What should be the thickness of a soil layer of a unit weight of 120 lb/ft 3 that would cause consolidation settlement of 0.1 ft in 100 days?arrow_forwardDefine the allowable bearing capacity of a circular foundation of a radius 2R=10 ft using theTerzaghi's bearing capacity equation for a local failure. In your calculations assume two scenarios:a) that the ground water table matches the bottom of the foundation, and b) that the ground watertable is 6 ft below the bottom of the foundation. Use a factor of safety of 2.8, and the dry unit weightabove the ground water table.arrow_forwardFor the square foundation below determine: a) ultimate settlement and b) settlement after 140days due to consolidation of the clay layer. Base your calculations on the values at the midpoint ofthe layer.arrow_forward
- Evaluate all reactions & internalforces using Moment DistributionE=29000ksi I=400in^(4) for all members.arrow_forwardA silty sand sample failed during a consolidated-undrained triaxial test at F1=280 kPa andF3=170 kPa. With the assumption that c=0 and A=0.65, determine the consolidated-undrainedfriction angle Ncu and a drained friction angle N. If a consolidated-undrained test on such a soil isconducted at a confining pressure F3 =340 kPa, what will be major total and effective stresses andthe pore water pressure at failure? What will be the maximum shear stress J during a "slow" directshear test, if the vertical stress Fv=160 kPa?arrow_forwardCheck the adequacy of a 15ft long A992 W12x65 beam-column shown in figure (1). The axial loads and end moments have been obtained from 2nd order analysis of the gravity loads. The frame and loading are symmetric. Assume that (Cb) is 1.06. PD-85k, PL-220k MD-15k-ft, ML-45k-ft Le-8.6ft MD-18k-ft, ML-52kfarrow_forward
- *13-12. The control linkage for a machine consists of two L2 steel rods BE and FG, each with a diameter of 1 in. If a device at G causes the end G to freeze up and become pin connected, determine the maximum horizontal force P that could be applied to the handle without causing either of the two rods to buckle. The members are pin connected at A, B, D, E, and F. P 12 in. C G F B 2 in. E 4 in. 4 in. A D + -15 in.- + -20 in.-arrow_forward13-31. The steel bar AB has a rectangular cross section. If it is pin connected at its ends, determine the maximum allowable intensity w of the distributed load that can be applied to BC without causing bar AB to buckle. Use a factor of safety with respect to buckling of 1.5. Est = 200 GPa, σy 360 MPa. = B W 5 m 3 m -20 mm 30 mm x x A 20 mm y Carrow_forwardProblem 1: A man-made 30 ft tall, 1.5:1 slope is to be build as shown in the figure. The soil is homogeneous with shear strength parameters c = 400 psf and φ = 290 . The moist unit weight of the soil is 119 pcf above the groundwater table and the saturated unit weight is 123 pcf below. Using the ordinary method of slices, compute the Factor of Safety (FS) along the trial failure surface shown. (Hint: Please note the unit weight is changing within the same slice.) Note 1: Use the same number of slices and dimensions as provided. Document ALL the calculations of weight (W) for each slice. Note 2: Document your solutions by following the same approach illustrated in the class, including a summary table showing all the variables and calculations involved in assessing FS.arrow_forward
 Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning



