
1
To record: The
1
Explanation of Solution
Journal:
Journal is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
The journal entries for given transactions of Company R are as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| 2015 | Cash | 20,000 | ||
| February 15 | Common stock | 20,000 | ||
| (To record the common stock issued) | ||||
| 2015 | Cash | 35,000 | ||
| May, 20 | Account receivable | 30,000 | ||
| Service revenue | 65,000 | |||
| (To record the service revenue provided to customer on account and in cash) | ||||
| 2015 | Salaries expense | 23,000 | ||
| August 31 | Cash | 23,000 | ||
| (To record the cash received from issuance of common stock) | ||||
| 2015 | Prepaid rent | 12,000 | ||
| October 1 | Cash | 12,000 | ||
| (To record payment of one-year advance rent) | ||||
| 2015 | Supplies | 22,000 | ||
| November 17 | Accounts payable | 22,000 | ||
| (To record the purchase of supplies on account) | ||||
| 2015 | Dividends | 2,000 | ||
| December 30 | Cash | 2,000 | ||
| (To record the payment of dividend to stockholder) | ||||
Table (1)
2
To record: The adjusting entry for prepaid insurance.
2
Explanation of Solution
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
Adjusting entries of Company R are as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| 2015 | Salaries expense | 4,000 | ||
| December 31 | Salaries payable | 4,000 | ||
| (To record salaries expense incurred at the end of accounting year) | ||||
| 2015 | Rent expense | 3,000 | ||
| December 31 | Prepaid rent | 3,000 | ||
| (To record the rent expense incurred at the end of the accounting period) | ||||
| 2015 | Supplies expense | 25,000 | ||
| December 31 | Supplies | 25,000 | ||
| (To record supplies expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | ||||
| 2015 | Unearned revenue | 5,000 | ||
| December 31 | Service revenue | 5,000 | ||
| (To record service revenue recognized at the end of the accounting year) |
Table (2)
3
To prepare: The adjusted
3
Explanation of Solution
Adjusted trial balance:
Adjusted trial balance is a summary of all the ledger accounts, and it contains the balances of all the accounts after the adjustment entries are journalized, and posted.
Adjusted trial balance of Company R is as follows:
| Company R | ||
| Adjusted Trial Balance | ||
| December 31, 2015 | ||
| Accounts | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | $30,000 | |
|
| 30,000 | |
| Supplies | 5,000 | |
| Prepaid Rent | 9,000 | |
| Land | 60,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | $22,000 | |
| Salaries Payable | 4,000 | |
| Common Stock | 70,000 | |
|
| 25,000 | |
| Dividends | 2,000 | |
| Service Revenue | 70,000 | |
| Salaries Expense | 27,000 | |
| Rent Expense | 3,000 | |
| Supplies Expense | 25,000 | |
| Total | $191,000 | $191,000 |
Table (3)
Therefore, the total of debit, and credit columns of adjusted trial balance is $191,000 and agree.
4
To prepare: An income statement,
4
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
This is the financial statement of a company which shows all the revenues earned and expenses incurred by the company over a period of time.
Statement of stockholders’ equity:
This statement reports the beginning stockholder’s equity and all the changes, which led to ending stockholder’s’ equity. Additional capital, net income from income statement is added to and drawings are deducted from beginning stockholder’s equity to arrive at the result of closing balance of stockholders’ equity.
Classified balance sheet:
This is the financial statement of a company which shows the grouping of similar assets and liabilities under subheadings.
Income statement:
Income statement of Company R is as follows:
| Company R | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2015 | ||
| ($) | ($) | |
| Revenues: | ||
| Service revenue | 70,000 | |
| Total revenues | 70,000 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Rent expense | 3,000 | |
| Salaries expense | 27,000 | |
| Supplies expense | 25,000 | |
| Total expenses | 55,000 | |
| Net income | 15,000 | |
Table (4)
Therefore, the net income of Company R is $15,000.
Statement of stockholder’s equity:
The statement of stockholder’s equity of Company R for the year ended December 31, 2015 is as follows:
| Company R | |||
| Statement of Stockholders’ Equity | |||
| For the period ended December 31, 2015 | |||
| Common stock ($) | Retained earnings ($) | Total stockholders' equity ($) | |
| Balance at January 1 | 50,00 | $25,000 | $75,000 |
| Issuance of common stock | 20,000 | 20,000 | |
| Add: Net income for 2018 | 15,000 | 15,000 | |
| Less: Dividends | -2,000 | -2,000 | |
| Balance at December 31 | $70,000 | $38,000 | $108,000 |
Table (5)
Therefore, the total stockholder’s equity of Company R for the year ended December 31, 2015 is $108,000.
Classified balance sheet:
Classified balance sheet of Company R is as follows:
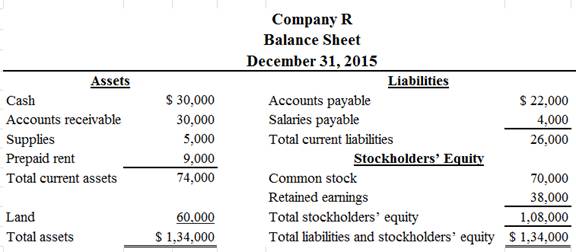
Figure (1)
Therefore, the total assets of Company R are $134,000, and the total liabilities and stockholders’ equity are $134,000.
5
To prepare: The closing entries of Company R.
5
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries:
Closing entries are those journal entries, which are passed to transfer the final balances of temporary accounts, (all revenues account, all expenses account and dividend) to the retained earnings. Closing entries produce a zero balance in each temporary account.
Closing entries of Company R is as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 2015 | Service revenue | 70,000 | ||
| December 31 | Retained earnings | 70,000 | ||
| (To close all revenue account) | ||||
| 2015 | Retained earnings | 55,000 | ||
| December 31 | Salaries expense | 27,000 | ||
| Rent expense | 3,000 | |||
| Supplies expense | 25,000 | |||
| (To close all the expenses account) | ||||
| 2015 | Retained earnings | 2,000 | ||
| December 31 | Dividends | 2,000 | ||
| (To close the dividends account) | ||||
Table (6)
Closing entry for revenue account:
In this closing entry, the service revenue account is closed by transferring the amount of service revenue to the retained earnings in order to bring the revenue accounts balance to zero.
Closing entry for expenses account:
In this closing entry, salaries expense, rent expense, and supplies expense are closed by transferring the amount of all expenses to the retained earnings in order to bring all the expense accounts balance to zero.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Financial accounting
- return on his investments. Cost accounting questionsarrow_forwardWhat is the profit margin for both the child and the store ?arrow_forwardErik Furnishings has sales of $462,000 and a cos tof goods sold of $193,000. What is the gross profit margin? A) 48.7% B) 58.2% C) 60.3% D) 2.6% E) 55.0%arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





