
A
To find:The number of shoes and jeans that the individual buys, if jeans cost $20 and shoes cost $20.
A
Answer to Problem 3.1P
At the given constraints and the data, the individual will be able to buy 5 pairs of both jeans and shoes.
Explanation of Solution
First, let us assume that the income of the individual is represented by, I = $200. While the jeans is represented by J, PJ for
So, the equation denoting the budget constraint of the individual can be defined as follows:
Since, the individual buys the two goods in the same number,
J=S
Now,
PJ=$20, and PS=$20; and J=S
Now, by substituting the price of two goods in the above equation,
Thus, we can see that the individual will be able to buy only 5 units of both jeans and shoes.
The budget constraint details the combinations of goods and services that an individual may acquire at the possible prices, within the income level of the individual.
B
To find:The number of shoes and jeans that the individual will buy after increase in price of jeans to $30
B
Answer to Problem 3.1P
The individual, according to the given data, will be able to purchase 4 units of both shoes and jeans.
Explanation of Solution
Now, the price of Jeans is, PJ=$30, and the price of Shoes is, PJ=$20.
Substituting the prices into equation,
Thus, at the given constraint, the individual will be able to buy 4 units of both jeans and shoes.
The budget constraint details the combinations of goods and services that an individual may acquire at the possible prices, within the income level of the individual.
C
To plot:The budget constraints from parts A and B on a graph.
C
Answer to Problem 3.1P
We can notice on the graph that the indifference curves have transformed into L-shape, showing that the jeans and shoes are bought in an equal proportion meaning that they are perfect complements.
Explanation of Solution
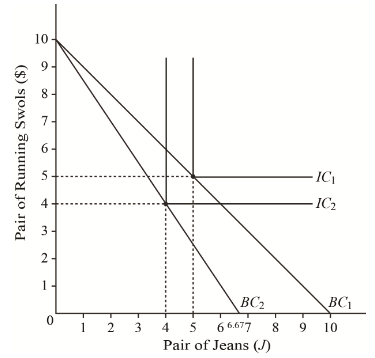
Through plotting the budget constraints and indifference curves on the graph, it is that the BC1 and IC1 represent the budget constraint and the indifference curve, representing the price of Jeans, PJ=$20, and the price of shoes, PS=$20, respectively.
Similarly, the BC2 and IC2represent the budget constraint and the indifference curve, representing the price of Jeans, PJ=$30, and the price of shoes, PS=$20, respectively.
It is noticed on the graph that the indifference curves have transformed into L-shape, showing that the jeans and shoes are bought in an equal proportion. Meaning that they are perfect complements.
The budget constraint details the combinations of goods and services that an individual may acquire at the possible prices, within the income level of the individual.
D
To find: the change that can be attributed by the change in utility levels among the parts A and B
D
Answer to Problem 3.1P
Since, the individual is purchasing the jeans and shoes in a fixed proportion, the changes in utility levels, represented by IC1 and IC2, can be attributed completely to the income effect.
Explanation of Solution
By looking at the graph, it can be noticed that the utility levels IC1 and IC2 are perpendicular, meaning that the purchases of shoes and jeans are made in a fixed proportion.
Hence, the changes in utility levels are attributed entirely to the income effect.
Introduction: The budget constraint details the combinations of goods and services that an individual may acquire at the possible prices, within the income level of the individual.
E
To Find:the number of jeans that the individual will purchase at different prices of$30, $20, $10, and $5.
E
Answer to Problem 3.1P
At a price of $30, the demanded pair of jeans are 4;
at $20, 5 pairs;
at $10, 6 pairs;
at $5, 8 pairs are demanded.
Explanation of Solution
Jeans priced at $30, and Shoes priced at $20, the pair of jeans demanded are as follows:
Jeans priced at $20, and Shoes priced at $20, the pair of jeans demanded are as follows:
Jeans priced at $10, and Shoes priced at $20, the pair of jeans demanded are as follows:
Jeans priced at $5, and Shoes priced at $20, the pair of jeans demanded are as follows:
Introduction: The budget constraint details the combinations of goods and services that an individual may acquire at the possible prices, within the income level of the individual.
F
To plot: using the
F
Answer to Problem 3.1P
The demand curve is sloping downward.
Explanation of Solution
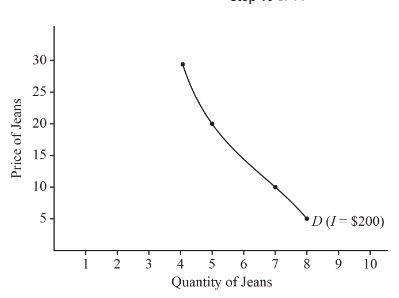
By looking at the demand curve plotted on the graph, we can notice that with every increase in the price of Jeans, the demand has increased.
Introduction: The budget constraint details the combinations of goods and services that an individual may acquire at the possible prices, within the income level of the individual.
G
To plot:the demand curve on a graphsupposing that the income of the individual rises to $300, also to derive the demand for jeans at each price level.
G
Answer to Problem 3.1P
The demand curve has extended with an increase in the income level of the individual.
Explanation of Solution
By substituting the new income level in the derived equation, itis seen that the following demand pattern is observed at every price change:
| Price of Jeans | Demand for Jeans |
| $30 | 6 |
| $20 | 7 |
| $10 | 10 |
| $5 | 12 |
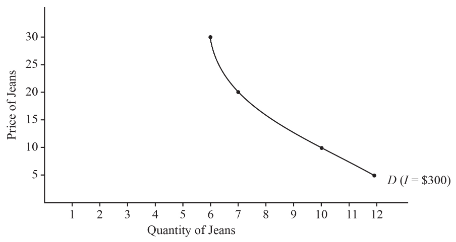
Through plotting this new demand curve with an increased income level, it is noticed that the demand curve has extended with an increase in the income level of the individual.
Introduction: The budget constraint details the combinations of goods and services that an individual may acquire at the possible prices, within the income level of the individual.
H
To find:supposing that the price of the shoes rises to $30 per pair,the effect on demand curves drawn in parts B and C.
H
Answer to Problem 3.1P
The demand curve will shift to the left showing a decline in the demand for jeans at the given price levels.
Explanation of Solution
As stated, the demand for jeans and shoes is in a fixed proportion. Hence, with an increase in the price of shoes, the demand for both jeans and shoes will show a decline. Thus, it is noticed that the demand curve will shift to left, representing a decline in the demand for jeans at the given price levels.
Introduction: The budget constraint details the combinations of goods and services that an individual may acquire at the possible prices, within the income level of the individual.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
EBK INTERMEDIATE MICROECONOMICS AND ITS
- 4. Supply and Demand. The table gives hypothetical data for the quantity of electric scooters demanded and supplied per month. Price per Electric Scooter Quantity Quantity Demanded Supplied $150 500 250 $175 475 350 $200 450 450 $225 425 550 $250 400 650 $275 375 750 a. Graph the demand and supply curves. Note if you prefer to hand draw separately, you may and insert the picture separately. Price per Scooter 300 275 250 225 200 175 150 250 400 375425475 350 450 550 650 750 500 850 Quantity b. Find the equilibrium price and quantity using the graph above. c. Illustrate on your graph how an increase in the wage rate paid to scooter assemblers would affect the market for electric scooters. Label any new lines in the same graph above to distinguish changes. d. What would happen if there was an increase in the wage rate paid to scooter assemblers at the same time that tastes for electric scooters increased? 1ངarrow_forward3. Production Costs Clean 'n' Shine is a competitor to Spotless Car Wash. Like Spotless, it must pay $150 per day for each automated line it uses. But Clean 'n' Shine has been able to tap into a lower-cost pool of labor, paying its workers only $100 per day. Clean 'n' Shine's production technology is given in the following table. To determine its short-run cost structure, fill in the blanks in the table. Fill in the columns below. Outpu Capita Labor TFC TVC TC MC AFC AVC ATC 1 0 30 1 1 70 1 2 120 1 3 160 1 4 190 1 5 210 1 6 a. Over what range of output does Clean 'n' Shine experience increasing marginal returns to labor? Over what range does it experience diminishing marginal returns to labor? (*answer both questions) b. As output increases, do average fixed costs behave as described in the text? Explain. C. As output increases, do marginal cost, average variable cost, and average total cost behave as described in the text? Explain. d. Looking at the numbers in the table, but without…arrow_forward2. Elasticity and the Minimum Wage - The following graph depicts two labor markets for cashiers. We assume the same supply curve (cashiers respond similarly to wage offers in each city) but different demand functions (employer demand is more elastic – more responsive to wages - in one city than the other, perhaps because one has higher quality retail stores than the other). The y-axis shows hourly wages in dollars; the x-axis shows the number of employees in hundreds. Wage 12 11 29 10 9 00 8 7 Supply 5 4 3 2 1 D2 12 D1 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Employment 11 With minimum wage of 8 dollars: A. What is the equilibrium level of employment before the minimum wage is imposed? B. A) According to the graph and given a minimum wage of 8 dollars, how many workers would employers want to hire if the demand for workers in City #1 looked like D1? B) How does that number compare to the market equilibrium employment? C. A) In City #1 (with demand curve D1), would there be an excess supply of…arrow_forward
- The demand function for organic apples is given by Qd = 20 – 2P while the supply function is given by Qs = 4P – 10.a. Solve for the equilibrium P* and Q*.b. Carefully graph the D & S curves. Include all intercepts and P* and Q* (**enlarge your graph so you can better show the questions below use graphing paper**)i. Suppose that the government legislates a $1/gallon to be collected from the buyer. Identify the new equation for the demand curve. Plot the new demand curve (on the same graph as b).ii. Solve for the new equilibrium PT* and QT* and indicate on your graph. On the same graph, indicate the P that consumers pay (PC) and the P that producers get to keep (PS).c. On another graph with the original D and S curves, impose the same tax ($1/gallon) to sellers. Identify the new equation for the supply curve. Plot the new supply curve. i. Solve for the new equilibrium PT* and QT* and indicate on your graph. On thesame graph, indicate the P that consumers pay (PC) and the P that…arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardExplain and evaluate the impact of legislation on the U.S. criminal justice system, specifically on the prison population and its impact on poverty and the U.S. economy. Include significant elements and limitations such as the War on Drugs and the First Step Act.arrow_forward
- Given the following petroleum tax details, calculate the marginal tax rate and explain its significance: Total Revenue: $500 million Cost of Operations: $200 million Tax Rate: 40% Additional Royalty: 5% Profit-Based Tax: 10%arrow_forwardUse a game tree to illustrate why an aircraft manufacturer may price below the current marginal cost in the short run if it has a steep learning curve. (Hint: Show that learning by doing lowers its cost in the second period.) Part 2 Assume for simplicity the game tree is illustrated in the figure to the right. Pricing below marginal cost reduces profits but gives the incumbent a cost advantage over potential rivals. What is the subgame perfect Nash equilibrium?arrow_forwardAnswerarrow_forward
- M” method Given the following model, solve by the method of “M”. (see image)arrow_forwardAs indicated in the attached image, U.S. earnings for high- and low-skill workers as measured by educational attainment began diverging in the 1980s. The remaining questions in this problem set use the model for the labor market developed in class to walk through potential explanations for this trend. 1. Assume that there are just two types of workers, low- and high-skill. As a result, there are two labor markets: supply and demand for low-skill workers and supply and demand for high-skill workers. Using two carefully drawn labor-market figures, show that an increase in the demand for high skill workers can explain an increase in the relative wage of high-skill workers. 2. Using the same assumptions as in the previous question, use two carefully drawn labor-market figures to show that an increase in the supply of low-skill workers can explain an increase in the relative wage of high-skill workers.arrow_forwardPublished in 1980, the book Free to Choose discusses how economists Milton Friedman and Rose Friedman proposed a one-sided view of the benefits of a voucher system. However, there are other economists who disagree about the potential effects of a voucher system.arrow_forward
 Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning





