
Introduction To Computing Systems
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781260150537
Author: PATT, Yale N., Patel, Sanjay J.
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 3, Problem 29E
Program Plan Intro
OR operation:
- OR function needs two inputs and produces one output.
- It is also known as binary logical function.
- If one of the inputs or both the inputs are “1”, then one-bit OR operation produces the output as “1”.
- If both the inputs are “0”, then OR operation produces the output “0”.
- The following diagram depicts the one-bit OR operation,
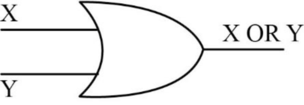
- The truth table for OR operation is as follows,
| X | Y | Z=X OR Y |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
- In the above table, “X” and “Y” are the inputs, and “Z” is the output.
- In the above table, when “X=0”, and “Y=0”, the output “Z” is “0”, because both the inputs “X” and “Y” contains the value “0”.
- When “X=0”, and “Y=1”, the output “Z” is “1”, because one of the input “Y” contains the value “1”.
- When “X=1”, and “Y=0”, the output “Z” is “1”, because one of the input “X” contains the value “1”.
- When “X=1”, and “Y=1”, the output “Z” is “1”, because both the inputs “X” and “Y” contains the value “1”.
AND function:
- AND function needs two inputs and produces one output.
- It is also known as binary logical function.
- If one or both the inputs are “0”, then one-bit AND operation produces the output “0”.
- If both inputs are “1”, then AND operation produces the output as “1”.
- The following diagram depicts the AND operation,
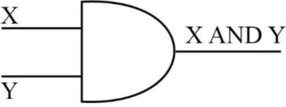
- The truth table for AND operation is as follows,
| X | Y | X AND Y |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
- In the above table, “X” and “Y” are inputs, and “Z” is output.
- When “X=0”, and “Y=0”, the output is “0”, because both the inputs “X” and “Y” contains the value “0”.
- When “X=0”, and “Y=1”, the output is “0”, because one of the input “X” contains the value “0”.
- When “X=1”, and “Y=0”, the output is “0”, because one of the input “Y” contains the value “0”.
- When “X=1”, and “Y=1”, the output is “1”, because both the inputs “X” and “Y” contains the value “1”.
NOR function:
- The NOR operation produces the output which is the negation of the result of “OR” operation.
- If one or both the inputs are “1”, then NOR operation produces the output as “0”.
- If both the inputs are “0”, then NOR operation produces the output “1”.
- The following diagram depicts the NOR operation,
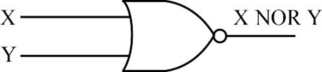
- The truth table for NOR operation is as follows,
| X | Y | Z=X OR Y |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
NAND function:
- The NAND operation produces the output which is the negation of the result of “AND” operation.
- If one or both the inputs are “0”, then NAND operation produces the output “1”.
- If both inputs are “0”, then NAND operation produces the output as “0”.
- The following diagram depicts the NAND operation,
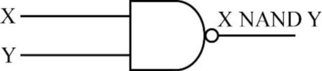
- The truth table for NAND operation is as follows,
| X | Y | X NAND Y |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Need help making python code for this!
2.7 LAB: Smallest of two numbers
Instructor note:
Note: this section of your textbook contains activities that you will complete for points. To ensure your work is scored, please access this page from the assignment link provided in the CTU Virtual Campus. If you did not access this page via the CTU Virtual Campus, please do so now.
I help understanding this question
d'y + 4dy +3y = a, Initial Conditions: y(0) = 5 & y'(0)=0
Where a = 10
a) Find y(t) =yh(t) +yp(t) in time domainIs the system over-damped, under-damped, or critical?
b) Find y(t) using Laplace Transforms
Chapter 3 Solutions
Introduction To Computing Systems
Ch. 3 - Prob. 1ECh. 3 - Replace the missing parts in the following circuit...Ch. 3 - A two-input AND and a two-input OR are both...Ch. 3 - Replace the missing parts in the following circuit...Ch. 3 - Complete a truth table for the transistor-level...Ch. 3 - For the transistor-level circuit in Figure 3.38,...Ch. 3 - Prob. 7ECh. 3 - The transistor-level circuit below implements the...Ch. 3 - What does the following transistor circuit do?
Ch. 3 - For what values of A, B, C, D, E, and F will the...
Ch. 3 - A student knew that an inverter contained one...Ch. 3 - The following logic diagram produces the logical...Ch. 3 - The following logic circuits consist of two...Ch. 3 - Fill in the truth table for the logical expression...Ch. 3 - Fill in the truth table for a two-input NOR...Ch. 3 - Prob. 19ECh. 3 - How many output lines will a 16-input multiplexer...Ch. 3 - Prob. 21ECh. 3 - Given the following truth table, generate the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 23ECh. 3 - Prob. 24ECh. 3 - Logic circuit 1 in Figure 3.39 has inputs A, B, C....Ch. 3 - You know a byte is eight bits. We call a four-bit...Ch. 3 - Prob. 28ECh. 3 - Prob. 29ECh. 3 - Say the speed of a logic structure depends on the...Ch. 3 - Recall that the adder was built with individual...Ch. 3 - For this question, refer to the figure that...Ch. 3 - Prob. 35ECh. 3 - A comparator circuit has two 1-bit inputs A and B...Ch. 3 - If a computer has eight-byte addressability and...Ch. 3 - Prob. 38ECh. 3 - Refer to Figure 3.21, the diagram of the...Ch. 3 - Given a memory that is addressed by 22 bits and is...Ch. 3 - Prob. 42ECh. 3 - Prob. 43ECh. 3 - Prob. 44ECh. 3 - Prob. 47ECh. 3 - Refer to Figure 3.32. Why are lights 1 and 2...Ch. 3 - Prob. 49ECh. 3 - We have learned that we can write one bit of...Ch. 3 - A student decided to design a latch as shown...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Given f(t)=a sin(ßt) a = 10 & ß = 23 Find the Laplace Transform using the definition F(s) = ∫f(t)e-stdtarrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardObtain the MUX design for the function F(X,Y,Z) = (0,3,4,7) using an off-the-shelf MUX with an active low strobe input (E).arrow_forward
- I cannot program smart home automation rules from my device using a computer or phone, and I would like to know how to properly connect devices such as switches and sensors together ? Cisco Packet Tracer 1. Smart Home Automation:o Connect a temperature sensor and a fan to a home gateway.o Configure the home gateway so that the fan is activated when the temperature exceedsa set threshold (e.g., 30°C).2. WiFi Network Configuration:o Set up a wireless LAN with a unique SSID.o Enable WPA2 encryption to secure the WiFi network.o Implement MAC address filtering to allow only specific clients to connect.3. WLC Configuration:o Deploy at least two wireless access points connected to a Wireless LAN Controller(WLC).o Configure the WLC to manage the APs, broadcast the configured SSID, and applyconsistent security settings across all APs.arrow_forwardusing r language for integration theta = integral 0 to infinity (x^4)*e^(-x^2)/2 dx (1) use the density function of standard normal distribution N(0,1) f(x) = 1/sqrt(2pi) * e^(-x^2)/2 -infinity <x<infinity as importance function and obtain an estimate theta 1 for theta set m=100 for the estimate whatt is the estimate theta 1? (2)use the density function of gamma (r=5 λ=1/2)distribution f(x)=λ^r/Γ(r) x^(r-1)e^(-λx) x>=0 as importance function and obtain an estimate theta 2 for theta set m=1000 fir the estimate what is the estimate theta2? (3) use simulation (repeat 1000 times) to estimate the variance of the estimates theta1 and theta 2 which one has smaller variance?arrow_forwardusing r language A continuous random variable X has density function f(x)=1/56(3x^2+4x^3+5x^4).0<=x<=2 (1) secify the density g of the random variable Y you find for the acceptance rejection method. (2) what is the value of c you choose to use for the acceptance rejection method (3) use the acceptance rejection method to generate a random sample of size 1000 from the distribution of X .graph the density histogram of the sample and compare it with the density function f(x)arrow_forward
- using r language a continuous random variable X has density function f(x)=1/4x^3e^-(pi/2)^4,x>=0 derive the probability inverse transformation F^(-1)x where F(x) is the cdf of the random variable Xarrow_forwardusing r language in an accelerated failure test, components are operated under extreme conditions so that a substantial number will fail in a rather short time. in such a test involving two types of microships 600 chips manufactured by an existing process were tested and 125 of them failed then 800 chips manufactured by a new process were tested and 130 of them failed what is the 90%confidence interval for the difference between the proportions of failure for chips manufactured by two processes? using r languagearrow_forwardI want a picture of the tools and the pictures used Cisco Packet Tracer Smart Home Automation:o Connect a temperature sensor and a fan to a home gateway.o Configure the home gateway so that the fan is activated when the temperature exceedsa set threshold (e.g., 30°C).2. WiFi Network Configuration:o Set up a wireless LAN with a unique SSID.o Enable WPA2 encryption to secure the WiFi network.o Implement MAC address filtering to allow only specific clients to connect.3. WLC Configuration:o Deploy at least two wireless access points connected to a Wireless LAN Controller(WLC).o Configure the WLC to manage the APs, broadcast the configured SSID, and applyconsistent security settings across all APs.arrow_forward
- A. What will be printed executing the code above?B. What is the simplest way to set a variable of the class Full_Date to January 26 2020?C. Are there any empty constructors in this class Full_Date?a. If there is(are) in which code line(s)?b. If there is not, how would an empty constructor be? (create the code lines for it)D. Can the command std::cout << d1.m << std::endl; be included after line 28 withoutcausing an error?a. If it can, what will be printed?b. If it cannot, how could this command be fixed?arrow_forwardCisco Packet Tracer Smart Home Automation:o Connect a temperature sensor and a fan to a home gateway.o Configure the home gateway so that the fan is activated when the temperature exceedsa set threshold (e.g., 30°C).2. WiFi Network Configuration:o Set up a wireless LAN with a unique SSID.o Enable WPA2 encryption to secure the WiFi network.o Implement MAC address filtering to allow only specific clients to connect.3. WLC Configuration:o Deploy at least two wireless access points connected to a Wireless LAN Controller(WLC).o Configure the WLC to manage the APs, broadcast the configured SSID, and applyconsistent security settings across all APs.arrow_forwardTransform the TM below that accepts words over the alphabet Σ= {a, b} with an even number of a's and b's in order that the output tape head is positioned over the first letter of the input, if the word is accepted, and all letters a should be replaced by the letter x. For example, for the input aabbaa the tape and head at the end should be: [x]xbbxx z/z,R b/b,R F ① a/a,R b/b,R a/a, R a/a,R b/b.R K a/a,R L b/b,Rarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Boolean Algebra - Digital Logic and Logic Families - Industrial Electronics; Author: Ekeeda;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u7XnJos-_Hs;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Boolean Algebra 1 – The Laws of Boolean Algebra; Author: Computer Science;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EPJf4owqwdA;License: Standard Youtube License