
a.
Record the given events in T-accounts.
a.
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
T-account refers to an individual account, where the increase or decrease in the value of specific asset, liability,
This account is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.’ An account consists of the three main components which are as follows:
- (a) The title of the account
- (b) The left or debit side
- (c) The right or credit side
Record the given events in T-accounts as follows:
| Cash | |
| 1. 40,000 | 6. 8,000 |
| 2. 2,000 | 8. 1,000 |
| 3. 9,000 | 9. 7,200 |
| 7. 17,000 | 10. 6,000 |
| 11. 4,000 | |
| 12. 840 | |
| Bal. 40,960 | |
| 4. 24,000 | 7. 17,000 |
| Bal. 7,000 | |
| Interest Receivable | |
| 19. 900 | |
| Bal. 900 | |
| Supplies | |
| 5. 840 | 17. 1,600 |
| 8. 1,000 | |
| Bal. 240 | |
| Prepaid Rent | |
| 9. 7,200 | 18. 1,800 |
| Bal. 5,400 | |
| Land | |
| 6. 8,000 | |
| Bal. 8,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | |
| 12. 840 | 5. 840 |
| 13. 300 | |
| 14. 250 | |
| Bal. 550 | |
| Unearned Revenue | |
| 15. 6,000 | 3. 9,000 |
| Bal. 3,000 | |
| Salaries Payable | |
| 16. 1,800 | |
| Bal. 1,800 | |
| Common Stock | |
| 1. 40,000 | |
| Bal. 40,000 | |
| Dividends | |
| 11. 4,000 | |
| Bal. 4,000 | |
| Service Revenue | |
| 2. 2,000 | |
| 4. 24,000 | |
| 15. 6,000 | |
| Bal. 32,000 | |
| Interest Revenue | |
| 19. 900 | |
| Bal. 900 | |
| Advertising Expense | |
| 13. 300 | |
| Bal. 300 | |
| Rent Expense | |
| 18. 1,800 | |
| Bal. 1,800 | |
| Salaries Expense | |
| 10. 6,000 | |
| 16.1,800 | |
| Bal. 7,800 | |
| Supplies Expense | |
| 17. 1,600 | |
| Bal. 1,600 | |
| Utilities Expense | |
| 14. 250 | |
| Bal. 250 | |
b.
Prepare a before-closing
b.
Explanation of Solution
Before-closing trial balance:
Before-closing trial balance is a summary of all the ledger accounts, and it contains the balances of all the accounts after the
Prepare a before-closing trial balance of Company L as follows:
| Company L | ||
| Before-closing trial balance for 2016 | ||
| Accounts | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 40,960 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 7,000 | |
| Interest receivable | 900 | |
| Supplies | 240 | |
| Prepaid Rent | 5,400 | |
| Land | 8,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | 550 | |
| Unearned Revenue | 3,000 | |
| Salaries Payable | 1,800 | |
| Common Stock | 40,000 | |
| Dividends | 4,000 | |
| Service Revenue | 32,000 | |
| Interest revenue | 900 | |
| Salaries expense | 7,800 | |
| Advertising Expense | 300 | |
| Utilities Expense | 250 | |
| Supplies Expense | 1,600 | |
| Rent expense | 1,800 | |
| Totals | 78,250 | 78,250 |
Table (1)
Therefore, the total of debit, and credit columns of before-closing trial balance is $78,250 and agree.
c.
Indicate the event that affects the
c.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
Income statement is a financial statement that shows the net income or net loss by deducting the expenses from the revenues and vice versa.
Balance Sheet:
Balance sheet summarizes the assets, the liabilities, and the stockholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Statement of cash flows:
The financial statement that shows the changes in cash flows from operating, investing, and financing activities is referred to as statement of cash flows.
Indicate the event that affects the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows and also indicated whether the increases (+), decreases (-), or does not affect (NA) each element of the financial statements as follows:
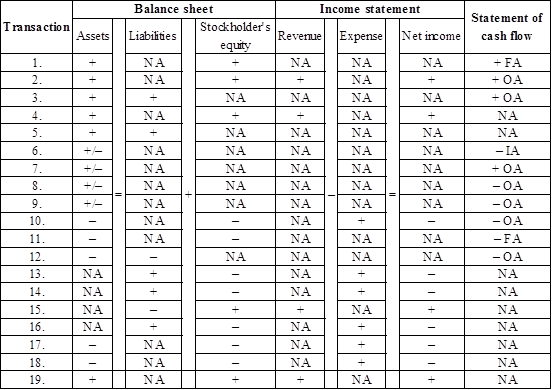
Table (2)
1. Issuance of common stock: In this transaction, cash and common stock accounts are affected. Cash account increases the value of assets account, and common stock increases the value of stockholders’ equity in the balance sheet. Issuance of common stock is considered as the financing activity of business and it increases the value of cash in the cash flow statement.
2. Provided services for cash: In this transaction, cash and service revenue accounts are affected. Cash account increases the value of assets account, and service revenue increases the value of stockholder’s equity in the balance sheet. Provided service for cash is considered as an operating activity of business, and it increases the value of operating cash in the cash flow statement.
3. Cash received for service performed in the future: In this transaction, cash and unearned revenue accounts are affected. Cash account increases the value of assets account, and unearned revenue increases the value of liabilities in the balance sheet. Cash received for service performed in the future is considered as an operating activity of business, and it increases the value of operating cash in the statement of cash flow.
4. Service provided on account: In this transaction, accounts receivable and service revenue accounts are affected. Accounts receivable increases the value of assets, and service revenue increases the value of stockholder’s equity in the balance sheet. In the income statement, service revenue increases the value of revenue account and net income.
5. Supplies purchased on account: In this transaction, supplies and accounts payable accounts are affected. Supplies increase the value of assets, and accounts payable increases the value of liabilities in the balance sheet.
6. Purchase of land for cash: In this transaction, land and cash accounts are affected. Land increases the value of assets account and cash decreases the value of assets in the balance sheet. Purchase of land in cash is considered as an investing activity of a business, and it decreases the value of cash in the cash flow statement.
7. Cash received from customer: In this transaction, cash and accounts receivable accounts are affected. Cash increases the value of assets, and accounts receivable decreases the value of assets in the balance sheet. Cash received from customer is considered as an operating activity of business, and it increases the value of operating cash in cash flow statement.
8. Purchase of supplies in cash: In this transaction, supplies and cash accounts are affected. Supplies increase the value of assets, and cash decreases the value of assets in the balance sheet. Purchase of supplies for cash is considered as an operating activity of business, and it decreases the value of operating cash in the cash flow statement.
9. Paid advance rent for one year: In this transaction, prepaid rent and cash accounts are affected. Prepaid rent increases the value of assets account, and cash decreases the value of assets in balance sheet. Paid advance rent for office space is considered as an operating activity of business, and it decreases the value of operating cash in the cash flow statement.
10. Salaries paid to employees: In this transaction, salaries expense and cash accounts are affected. Salaries expense decreases the value of stockholder’s equity, and cash decreases value of assets in the balance sheet. In the income statement, salaries expense increases the value of expense, and decreases the net income of business. Paid cash for salaries expense is considered as an operating activity of business, and it decreases the value of operating cash in the cash flow statement.
11. Paid cash dividends to stockholders: In this case, dividends and cash accounts are affected. Dividends decrease the value of stockholder’s equity and cash decreases the value of assets in the balance sheet. Dividends paid to stockholders are considered as a financing activity of the business, and it decreases the value of financing cash in the cash flow statement.
12. Cash paid to creditors: In this case, cash and accounts payable accounts are affected. Cash decreases the value of assets and accounts payable decreases the value of liabilities in the balance sheet. Cash paid to creditors is considered as an operating activity of business, and it decreases the operating cash in the cash flow statement.
13. Advertising expense incurred on account: In this transaction, advertising expense and accounts payable accounts are affected. Advertising expense decreases the value of stockholder’s equity, and accounts payable increases the value of liabilities in the balance sheet. In the income statement, advertising expense increases the expense account, and decreased the net income.
14. Utilities expense incurred on account: In this transaction, utilities expense and accounts payable accounts are affected. Utilities expense decreases the value of stockholder’s equity, and accounts payable increases the value of liabilities in the balance sheet. In the income statement, advertising expense increases the expense account, and decreased the net income.
15. Service revenue recognized for prior performance: In this case, service revenue and unearned revenue accounts are affected. Unearned revenue decreases the value of liabilities and service revenue increases the value of stockholder’s equity in the balance sheet. In the income statement, service revenue increases the revenue account and net income.
16. Salaries expense incurred at the end of the accounting 2016: In this transaction, salaries expense and salaries payable accounts are affected. Salaries expense decreases the stockholder’s equity, and salaries payable increases the value of liabilities in the balance sheet. In the income statement, salaries expense increased the expense account and decreased the value of net income.
17. Supplies expense incurred at the end of the account period: In this transaction, salaries expense and supplies accounts are affected. Salaries expense decreases the value of stockholder’s equity, and supplies decreases value of assets in the balance sheet. In the income statement, salaries expense increases the value of expense and decreased the net income of business.
18. Recognized four month prepaid rent at the end of the accounting period: In this transaction, rent expense and prepaid rent accounts are affected. Rent expense decreases the value of stockholder’s equity, and prepaid rent decreases the value of assets in the balance sheet. In the income statement, rent expense increases the expense account and decreased the net income.
19. Interest revenue recognized at the end of the accounting year: In this case, cash and interest revenue accounts are affected. Cash increases the value of cash, and interest revenue increases the value of stockholder’s equity in the balance sheet. In the income statement, interest revenue increases the value of revenue and net income.
Note:
FA = Financing activity, OA = Operating activity, and IA = Investing activity
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Fundamental Financial Accounting Concepts, 9th Edition
- Please provide problem with accounting questionarrow_forwardCan you explain the correct methodology to solve this general accounting problem?arrow_forwardNicole Manufacturing had 780 units in beginning work in process on September 1, 2023. During the month, an additional 2,600 units were started in production. At the end of September, 1,150 units remained in work in process. How many units were completed during September?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





