
Concept explainers
a.
Identify the events as asset source (AS), asset use (AU), asset exchange (AE), or claims exchange (CE).
a.
Explanation of Solution
Identify the events as asset source (AS), asset use (AU), asset exchange (AE), or claims exchange (CE).
| Event No. | Event type |
| 1a. | AS |
| 1b. | AE |
| 2. | AU |
| 3. | AU |
| 4a. | AS |
| 4b. | AU |
| 5a. | AU |
| 5b. | AS |
| 6. | AU |
| 7. | AU |
| 8. | AU |
Table (1)
- ■ Asset source: All the transactions which increase assets either by borrowing from creditors (increase liabilities), or by earning operating revenues (increase in
stockholders’ equity ) are referred to as asset source transactions. - ■ Asset use: All the transactions which decrease assets either by paying off liabilities (decrease in liabilities), or by paying operating expenses (decrease in stockholders’ equity) are referred to as asset use transactions.
- ■ Asset exchange: All the transactions which increase assets and decrease assets simultaneously, with no effect on the total assets value are referred to as asset exchange transactions.
- ■ Claims exchange: All the transactions which include exchange of liabilities for equity are referred to as claims exchange transactions.
b.
Record each event in a statements model.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Horizontal statements model: The model that represents all the financial statements,
Record each event in a statements model.
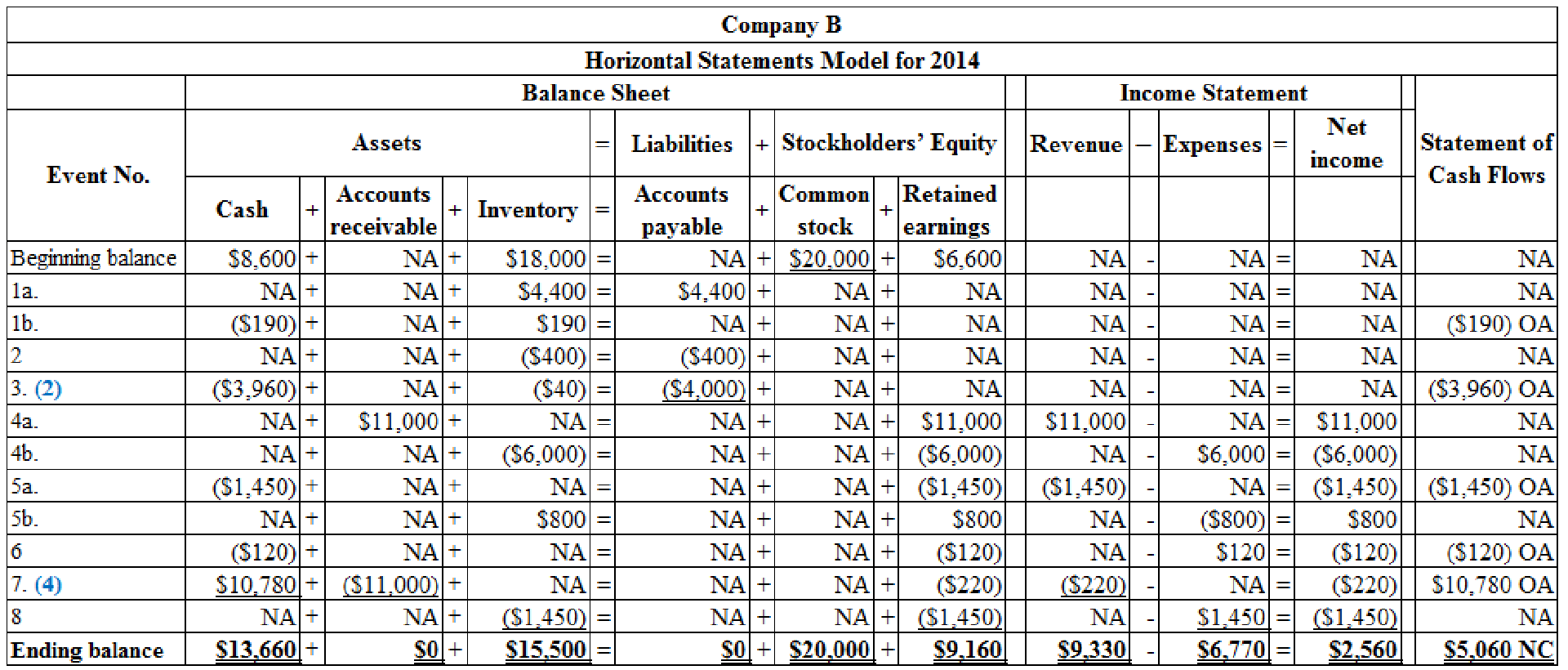
Table (2)
Working Note:
(1) Compute purchase discount.
(2) Compute the cash paid for inventory purchased.
(3) Compute sales discount.
(4) Compute cash received.
c.
Prepare a multistep income statement, statement of stockholders’ equity, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows for Company B.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Multi-step income statement: The income statement represented in multi-steps with several subtotals, to report the income from principal operations, and separate the other expenses and revenues which affect net income, is referred to as multi-step income statement.
Prepare a multistep income statement for Company B for the year ended December 31, 2014.
| Company B | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2014 | ||
| Net sales | $9,330 | |
| Less: Cost of goods sold (5) | ($6,650) | |
| Gross margin | $2,680 | |
| Less: Operating expenses: | ||
| Transportation-out | ($120) | |
| Net income | $2,560 | |
Table (3)
Working Note:
(5) Determine the amount of cost of goods sold.
Statement of stockholders’ equity: The statement which reports the changes in stock, paid-in capital,
Prepare a statement of stockholders’ equity for Company B for the year ended December 31, 2014.
| Company B | ||
| Statement of Stockholders’ Equity | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2014 | ||
| Beginning common stock | $20,000 | |
| Add: Stock issued | $0 | |
| Ending common stock | $20,000 | |
| Beginning retained earnings | $6,600 | |
| Add: Net income | $2,560 | |
| Ending retained earnings | $9,160 | |
| Total stockholders’ equity | $29,160 | |
Table (4)
Balance sheet: This financial statement reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and stockholders (stockholders’ equity) over those resources. The resources of the company are assets which include money contributed by stockholders and creditors. Hence, the main elements of the balance sheet are assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity.
Prepare the balance sheet for Company B as at December 31, 2014.
| Company B | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| December 31, 2014 | ||
| Assets | ||
| Cash | $13,660 | |
| Merchandise inventory | $15,500 | |
| Total assets | $29,160 | |
| Liabilities | $0 | |
| Stockholders’ equity | ||
| Common stock | $20,000 | |
| Retained earnings | $9,160 | |
| Total stockholders’ equity | $29,160 | |
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $29,160 | |
Table (5)
Statement of cash flows: Statement of cash flows reports all the cash transactions which are responsible for inflow and outflow of cash and the result of these transactions is reported as ending balance of cash at the end of reported period.
Prepare the statement of cash flows for Company B for the year ended December 31, 2014.
| Company B | ||
| Statement of Cash Flows | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2014 | ||
| Cash flows from operating activities: | ||
| Inflow from customers (6) | $9,330 | |
| Outflow for inventory (7) | ($4,150) | |
| Outflow for expenses | ($120) | |
| Net cash flow from operating activities | $5,060 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities | $0 | |
| Cash flows from financing activities | $0 | |
| Net change in cash | $5,060 | |
| Add: Beginning cash balance | $8,600 | |
| Ending cash balance | $13,660 | |
Table (6)
Working note:
(6) Determine the
(7) Determine the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
SURVEY OF ACCOUNTING-ACCESS
- If annual demand is 60,000 units, the ordering cost is $30 per order, and the holding cost is $6 per unit per year, what is the optimal order quantity using the fixed-order quantity model?arrow_forwardcorrect answerarrow_forwardDuring its first year, Maple Corp. showed a $20 per-unit profit under absorption costing but would have reported a total profit of $18,000 less under variable costing. Suppose production exceeded sales by 600 units and an average contribution margin of 60% was maintained. a. What is the fixed cost per unit? b. What is the sales price per unit? c. What is the variable cost per unit? d. What is the unit sales volume if total profit under absorption costing was $220,000?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





