
a.
Record the
a.
Explanation of Solution
Journal:
Journal is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, and expenses.
Record the journal entries for the given transactions as follows:
1. Provided $185,000 of service on account
| Date | Account Titles | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| 185,000 | |||
| Service Revenue | 185,000 | ||
| (To record the service performed on account) |
Table (1)
- Accounts receivable is an asset account, and it increases the value of asset by $185,000. Hence, debit the accounts receivable account for $185,000.
- Service revenue is a component of
stockholder’s equity , and it increases the value of stockholder’s equity by $185,000. Hence, credit the service revenue account for $185,000.
2. Incurred $45,800 of operating expense on account
| Date | Account Titles | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Operating Expenses | 45,800 | ||
| Accounts Payable | 45,800 | ||
| (To record operating expense incurred on account) |
Table (2)
- Operating expense is a component of stockholder’s equity, and it decreases the value of stockholder’s equity by $45,800. Hence, debit the operating expense account for $45,800.
- Accounts payable is a liability account, and it increases the value of liability by $45,800. Hence, credit the liability account by $45,800.
3. Collected $140,000 of accounts receivable
| Date | Account Titles | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 140,000 | ||
| Accounts Receivable | 140,000 | ||
| (To record cash received from credit customer) |
Table (3)
- Cash is an asset account, and it increases the value of asset by $140,000. Hence, debit the cash account for $140,000.
- Accounts receivable is an asset account, and it decreases the value of asset by $140,000. Hence, credit the accounts receivable account for $140,000.
4. Paid $120,000 cash for salaries expense
| Date | Account Titles | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Salaries Expense | 120,000 | ||
| Cash | 120,000 | ||
| (To record salaries expense paid in cash) |
Table (4)
- Salaries expense is a component of stockholder’s equity, and it decreases the value of stockholder’s equity by $120,000. Hence, debit the salaries expense account for $120,000.
- Cash is an asset account, and it decreases the value of assets account by $120,000. Hence, credit the cash account for $120,000.
5. Paid $31,400 cash as a partial payment on accounts payable
| Date | Account Titles | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Accounts Payable | 31,400 | ||
| Cash | 31,400 | ||
| (To record cash paid to creditors) |
Table (5)
- Accounts payable is a liability account, and it decreases the value of liability by $31,400. Hence, debit the accounts payable account by $31,400.
- Cash is an asset account, and it decreases the value of assets account by $31,400. Hence, credit the cash account for $31,400.
6. Paid a $10,000 cash dividend to stockholders
| Date | Account Titles | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Dividends | 10,000 | ||
| Cash | 10,000 | ||
| (To record dividends paid to stockholders) |
Table (6)
- Dividends are a component of stockholder’s equity, and it decreases the value of stockholder’s equity by $10,000. Hence, debit the dividend account for $10,000.
- Cash is an asset account, and it decreases the value of assets account by $10,000. Hence, credit the cash account for $10,000.
b.
Open T-account and record the given transactions in the T-account.
b.
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
T-account refers to an individual account, where the increase or decrease in the value of specific asset, liability, stockholder’s equity, revenue, and expenditure items are recorded.
This account is referred as T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’. An account consists of the three main components which are as follows:
- (a) The title of the account
- (b) The left or debit side
- (c) The right or credit side
Open T-account and record the given transactions in the T-account as follows:
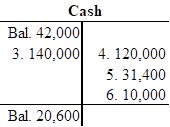
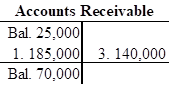
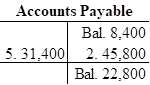
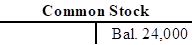
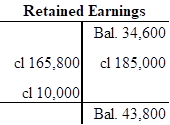
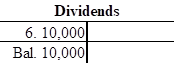
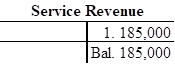
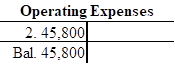
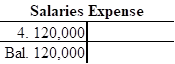
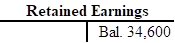
c.
Show the given transaction in the horizontal statements model.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Show the given transaction in the horizontal statements model as follows:
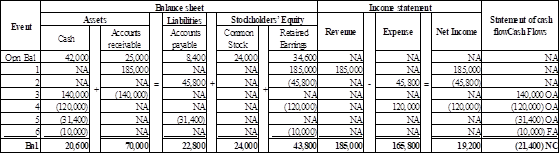
Table (7)
d.
Record and
d.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries:
Closing entries are those journal entries, which are passed to transfer the final balances of temporary accounts, (all revenues account, all expenses account and dividend) to
Record and post the closing entries to T-account as follows:
Closing journal entries:
| Date | Account Titles | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Service Revenue | 185,000 | ||
| Retained Earnings | 185,000 | ||
| (To close the revenue account) | |||
| Retained Earnings | 165,800 | ||
| Operating Expenses | 45,800 | ||
| Salaries Expense | 120,000 | ||
| (To close all the expense account) | |||
| Retained Earnings | 10,000 | ||
| Dividends | 10,000 | ||
| (To close dividends account) |
Table (8)
Closing entry for revenue account:
In this closing entry, the service revenue account is closed by transferring the amount of service revenue to retained earnings in order to bring the revenue account balance to zero. Hence, debit the service revenue account for $185,000, and credit the retained account for $185,000.
Closing entry for expenses account:
In this closing entry, operating and salaries expense accounts are closed by transferring the amount of operating and salaries expense to the retained earnings in order to bring the expense account balance to zero. Hence, debit the retained earnings for $165,800 and credit supplies account for $165,800.
Closing entry for dividends account:
In this closing entry, the dividends account is closed by transferring the amount of dividends to retained earnings in order to bring the dividends account balance to zero. Hence, debit the retained earnings for $10,000 and credit dividends account for $10,000.
T-account:
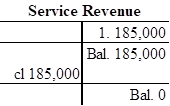
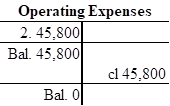
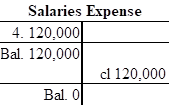
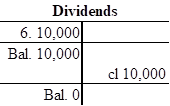
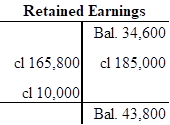
e.
Ascertain the amount of change in retained earnings and also explain the reason for changes in the amount of retained earnings.
e.
Explanation of Solution
Retained earnings:
Retained earnings are the portion of earnings kept by the business for the purpose of reinvestments, payment of debts, or for future growth.
Ascertain the amount of change in retained earnings and also explain the reason for changes in the amount of retained earnings as follows:
The amount of change in the retained earnings is $9,200. Dividend decreases the retained earnings because dividend is a temporary account and dividend account is closed by transferring the amount of dividend to retained earnings. Hence, the dividend account reduces the value of retained earnings, but does not decrease the value net income.
Calculate the amount of change in retained earnings
Therefore, the amount of change in the retained earnings is $9,200.
f.
Prepare post-closing
f.
Explanation of Solution
Post-closing trial balance:
The post-closing trial balance is a summary of all ledger accounts, and it shows the debit and the credit balances after the closing entries are journalized and posted. The post-closing trial balance contains only permanent (
Prepare post-closing trial balance of Company O as follows:
| Company O | ||
| Post-Closing Trial Balance | ||
| Accounts | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 20,600 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 70,000 | 22,800 |
| Accounts Payable | 24,000 | |
| Common Stock | 43,800 | |
| Retained Earnings | 22,450 | |
| Total | 90,600 | 90,600 |
Table (9)
Therefore, the total of debit, and credit columns of post-closing trial balance is $90,600 and agree.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Fundamental Financial Accounting Concepts

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





