
Concept explainers
(a)
Country with
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The absolute advantage is the ability to produce more quantity than the opponent countries in the economy. In this case, France can produce 2kg of cheese, whereas Germany can only produce 1 kg, which means that France has absolute advantage in producing cheese. In the case of cars, France can produce 0.25 cars per hour, whereas Germany can produce 0.50 per hour, which means that the output per hour is higher in Germany. This indicates that Germany has absolute advantage in the production of cars.
Absolute advantage: Absolute advantage is the ability to produce more quantity than the competent economies in the market.
(b)
Relative
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The output per hour in France is 2kg of cheese or 0.25 cars. Thus, dividing the quantity of cars with cheese can provide the relative price of cheese in France. This means that when France does not trade cheese, the relative price of the absolute advantaged product will be one-eighth of that of the car. In the case of Germany, the output is either 1 kg of cheese or 0.5 cars, which means that the relative price of cheese will be half of that of the car.
(c)
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The opportunity cost is the next best alternative that is foregone while making the decision between the available choices in the economy. The opportunity cost can be calculated by dividing the output of the car lost with the output of cheese gained. This will be similar to the relative price of cheese, which means one-eighth of the cars in France and half of cars in Germany.
(d)
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Comparative advantage is the ability of the economy to produce the output at the least opportunity cost of production. The opportunity cost of producing cheese is lower in France as it has an opportunity cost of one-eighth of the cars compared to half in Germany. The opportunity cost of a car can be calculated by dividing the units of cheese lost with the units of cars gained. It is 2 in Germany, whereas it is 8 in France, which means that Germany has the lowest opportunity cost of producing cars.
(e)
Upper and lower bounds of trade prices for cheese.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The relative prices of the two countries act as the upper and lower bounds of the trade price of cheese. The relative price of cheese is one-eighth in France and one-half in Germany, which means that the upper bound will be one-half and the lower bound will be one-eighth. The actual price for cheese will settle between these two values.
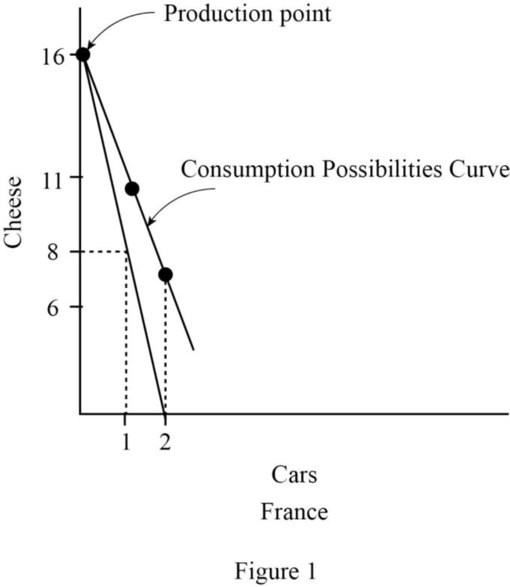
(f)
PPC curve for France.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
PPC is the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
EBK INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS
- Critically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forwardCritically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forwardOutline the nine (9) consumer rights as specified in the Consumer Rights Act in South Africa.arrow_forward
- In what ways could you show the attractiveness of Philippines in the form of videos/campaigns to foreign investors? Cite 10 examples.arrow_forwardExplain the following terms and provide an example for each term: • Corruption • Fraud • Briberyarrow_forwardIn what ways could you show the attractiveness of a country in the form of videos/campaigns?arrow_forward

 Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506756Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Macroeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506756Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning





