
Concept explainers
(a)
Country with
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The absolute advantage is the ability to produce more quantity than the opponent countries in the economy. In this case, France can produce 2kg of cheese, whereas Germany can only produce 1 kg, which means that France has absolute advantage in producing cheese. In the case of cars, France can produce 0.25 cars per hour, whereas Germany can produce 0.50 per hour, which means that the output per hour is higher in Germany. This indicates that Germany has absolute advantage in the production of cars.
Absolute advantage: Absolute advantage is the ability to produce more quantity than the competent economies in the market.
(b)
Relative price of cheese in two countries.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The output per hour in France is 2kg of cheese or 0.25 cars. Thus, dividing the quantity of cars with cheese can provide the relative price of cheese in France. This means that when France does not trade cheese, the relative price of the absolute advantaged product will be one-eighth of that of the car. In the case of Germany, the output is either 1 kg of cheese or 0.5 cars, which means that the relative price of cheese will be half of that of the car.
(c)
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The opportunity cost is the next best alternative that is foregone while making the decision between the available choices in the economy. The opportunity cost can be calculated by dividing the output of the car lost with the output of cheese gained. This will be similar to the relative price of cheese, which means one-eighth of the cars in France and half of cars in Germany.
(d)
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Comparative advantage is the ability of the economy to produce the output at the least opportunity cost of production. The opportunity cost of producing cheese is lower in France as it has an opportunity cost of one-eighth of the cars compared to half in Germany. The opportunity cost of a car can be calculated by dividing the units of cheese lost with the units of cars gained. It is 2 in Germany, whereas it is 8 in France, which means that Germany has the lowest opportunity cost of producing cars.
(e)
Upper and lower bounds of trade prices for cheese.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The relative prices of the two countries act as the upper and lower bounds of the trade price of cheese. The relative price of cheese is one-eighth in France and one-half in Germany, which means that the upper bound will be one-half and the lower bound will be one-eighth. The actual price for cheese will settle between these two values.
(f)
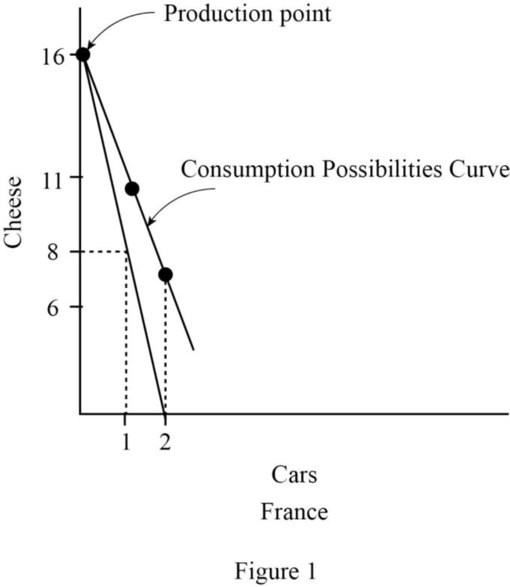
PPC curve for France.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
PPC is the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
EBK INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS
- Explain poverty experienced in a friend or family.arrow_forwardExplain how much of emotional, mental and physical toll makes it so difficult to break the cycle of poverty.arrow_forwardCase Study: The Impact of Ebola on Tax Revenue in the DRC Background: The Democratic Republic of the Congo has experienced mulitiple outbreaks, with the 2018-2020 outbreak being one of the most severe. The outbreak had profound effects on public health, the economy and government operations. The DRC's economy already fragile due to policital instability and conflict, faced additional stain as the Ebola virus spread across several provinces. Economic disruption: The Ebola outbreak led to significant disruptions in the affected regions. Businesses were forced to close or reduce operations due to quarantine measures and the fear of contagion. this resulted in a sharp decline in economic activities, particularly in sectors such as agriculute, mining and trade. reduced consumer spending and interruptions in supply chains further exacerbated the economic downturn. Impact on Tax Revenue: the economic…arrow_forward
- Key shortcomings of the Human Capital approach to measuring the monetary value of benefits of new treatments are that it Will generate lower benefits for male lives on average Will generate higher benefits for female lives on average Will tend to OVERVALUE improvements in quality of life Will tend to UNDERVALUE improved survival for people out of labour forcearrow_forwardOne of the key concepts in economics that underpins the necessity of making tough choices and confronting difficult tradeoffs through some form of collective decision-making is called Production Consumption Exchange Equity Scarcityarrow_forwardAllocative efficiency WITHIN the health care sector refers to What mix of nonmedical and medical goods and services should be produced in the macro-economy What mix of medical goods and services should be produced in the health economy What specific health care resources should be used to produce the chosen medical goods and services Who should receive the medical goods and services that are producedarrow_forward
- Production efficiency is most concerned with Choice of inputs in production process Quantity of outputs resulting from the production process The technological process of production All of the abovearrow_forwardChoose all of the following that are assumed to be constant while constructing the production possibilities curve Technology Precise mix of inputs Institutional arrangements like judicial protection of business contracts Outputsarrow_forwardA point that lies OUTSIDE of the PPC can be achieved if A major technological innovation increases production efficiency A sudden influx of resources e.g., massive immigration of trained nurses Economic reform resulting in greater protection of intellectual property rights All of the above Only options 1 and 2arrow_forward
- The marginal benefit from each successive unit of medical care consumed declines BECAUSE each successive unit is more expensive to produce True Falsearrow_forwardIn the Human Capital approach, estimated monetary worth of life is MOST SENSITIVE to which key indicator Discount rate Social security payroll taxes Labour market earnings Workplace injury compensationarrow_forwardOver the last few decades out-of-pocket costs have formed a DECLINING proportion of total consumer expenditure on medical care True Falsearrow_forward

 Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506756Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Macroeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506756Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning





