
Concept explainers
Muzzle Velocity The following data represent the muzzle velocity (in meters per second) of rounds fired from a 155-mm gun.

- a. Compute the sample
mean andmedian muzzle velocity. - b. Compute the
range , sample variance, and sample standard deviation.
(a)
To compute: The sample mean and median muzzle velocity.
Answer to Problem 1RE
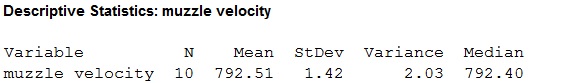
The sample mean and median is 795.21 and 792.40 meter per seconds.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The data represent the muzzle velocity (in meter per second) round-fired gun from 155mm.
Calculation:
Software procedure:
A step-by-step procedure for obtaining summary statistics, the mean, median, range, sample variance, and standard deviation for the data of muzzle velocity is given as follows:
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > Display Descriptive Statistics.
- In Variables enter the columns Variable.
- Click OK.
The Minitab output for muzzle velocity:
(b)
To compute: The range, sample variance, and standard deviation
Answer to Problem 1RE
The range is 4.80 m/sec,
The sample variance is 2.03 m/sec,
The standard deviation is 1.42 m/sec.
Explanation of Solution
From the Minitab output obtained in part (a), the range is 4.80 m/sec, sample variance is 2.03 m/sec, and the standard deviation is 1.42 m/sec.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
MyLab Statistics with Pearson eText -- Standalone Access Card -- for Fundamentals of Statistics
- A company found that the daily sales revenue of its flagship product follows a normal distribution with a mean of $4500 and a standard deviation of $450. The company defines a "high-sales day" that is, any day with sales exceeding $4800. please provide a step by step on how to get the answers in excel Q: What percentage of days can the company expect to have "high-sales days" or sales greater than $4800? Q: What is the sales revenue threshold for the bottom 10% of days? (please note that 10% refers to the probability/area under bell curve towards the lower tail of bell curve) Provide answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forwardFind the critical value for a left-tailed test using the F distribution with a 0.025, degrees of freedom in the numerator=12, and degrees of freedom in the denominator = 50. A portion of the table of critical values of the F-distribution is provided. Click the icon to view the partial table of critical values of the F-distribution. What is the critical value? (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardA retail store manager claims that the average daily sales of the store are $1,500. You aim to test whether the actual average daily sales differ significantly from this claimed value. You can provide your answer by inserting a text box and the answer must include: Null hypothesis, Alternative hypothesis, Show answer (output table/summary table), and Conclusion based on the P value. Showing the calculation is a must. If calculation is missing,so please provide a step by step on the answers Numerical answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forward
 Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill

