
The cross-sectional sequence of different layers of sedimentary rocks depicting the laws of original continuity, superposition, and original horizontality.
Answer to Problem 1QR
The characteristics features, formation and composition of sedimentary rock can be explained through the law of original continuity, the law of superposition, and the law of original horizontality.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 represents, the cross section of a sedimentary rock demonstrating the law of original horizontality. Fig.2 represents the corss section of a sedimentary rock demonstrating the law of superposition. Fig.3 represents the corss section of a sedimentary rock demonstrating the law of original continuity.
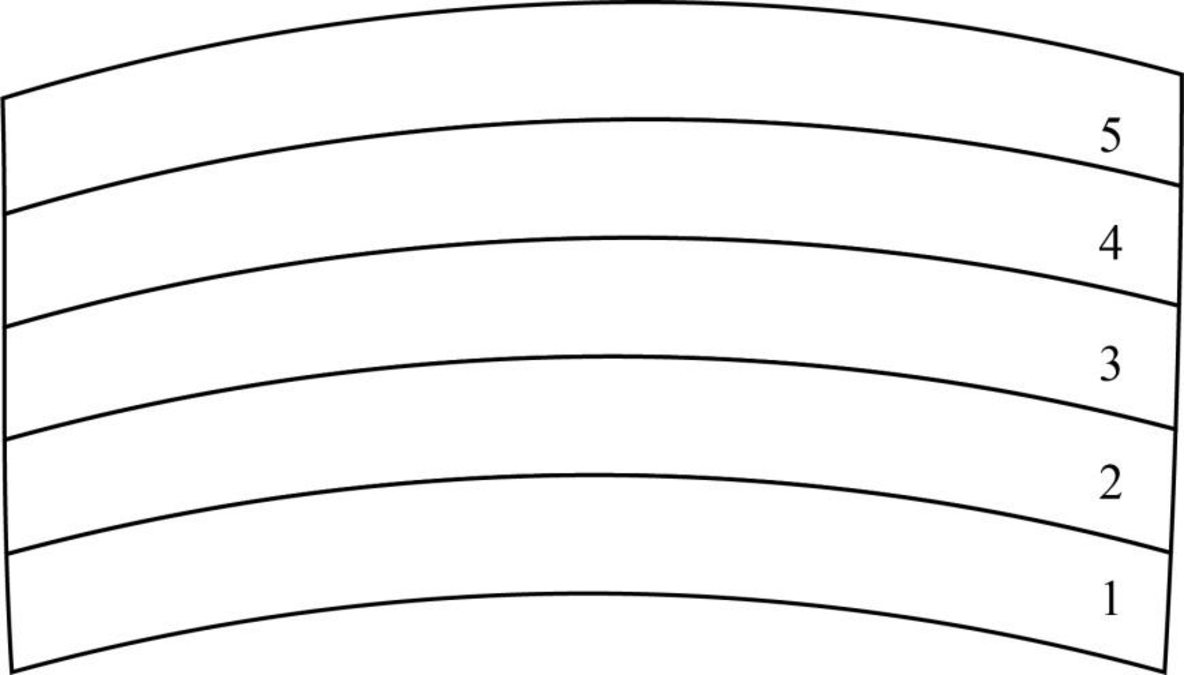
Fig. 1: Cross section of a sedimentary rock (law of original horizontality)
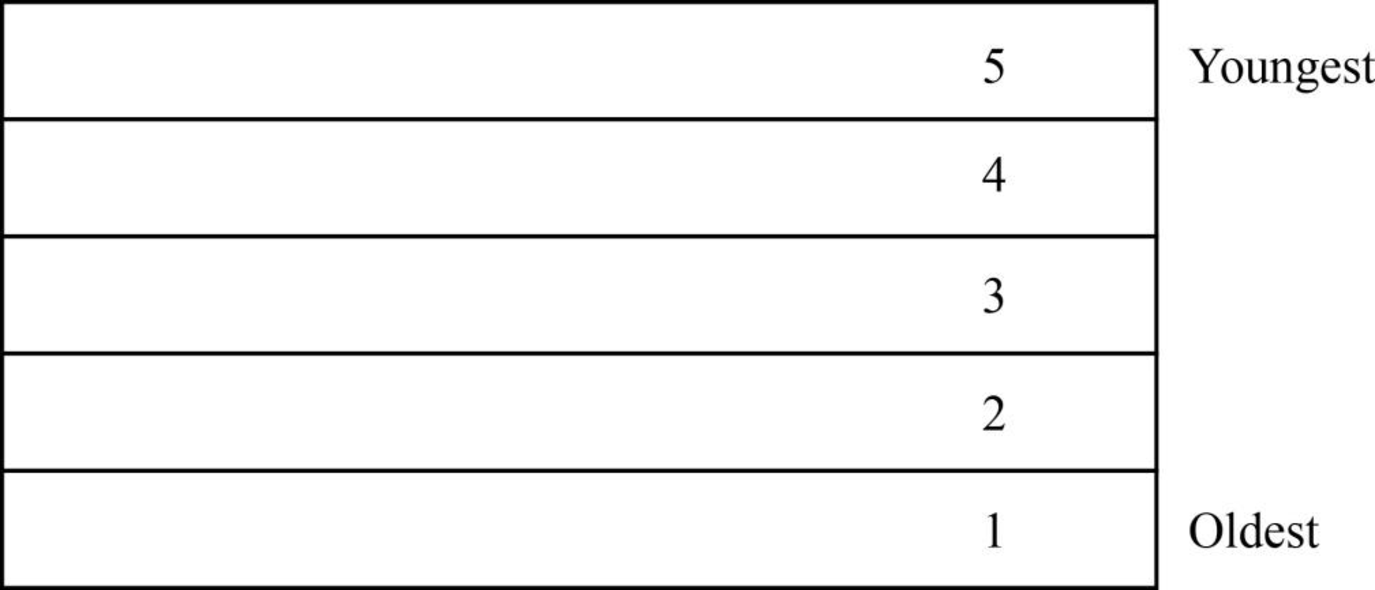

Fig. 2: Cross section of a sedimentary rock (law of superposition)
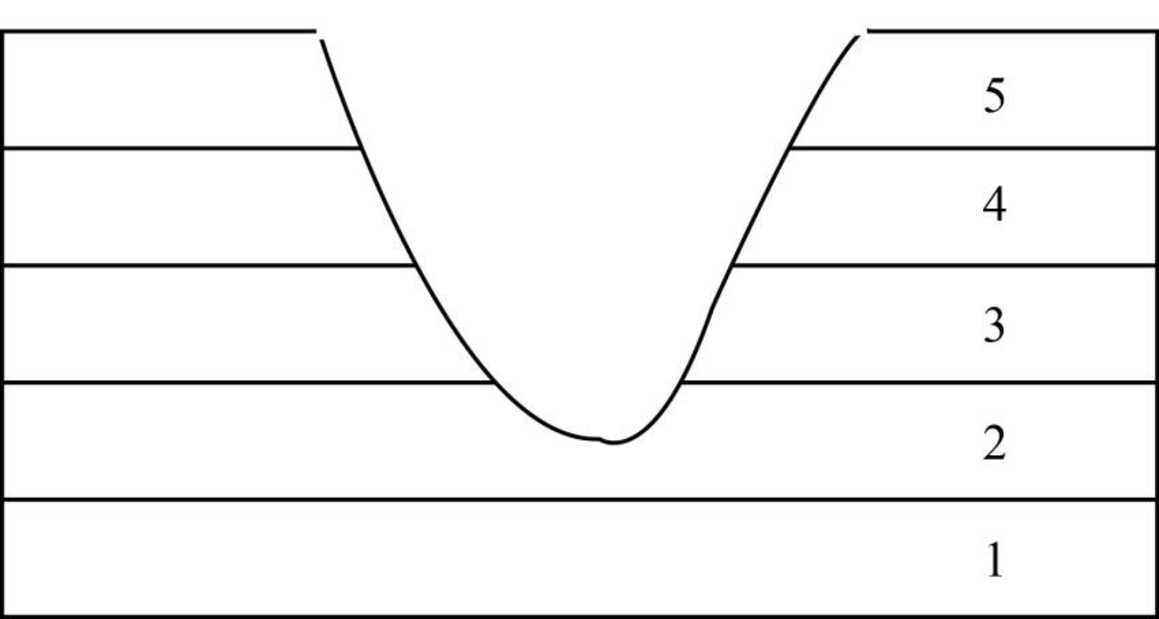
Fig. 3: Cross section of sedimentary rock (law of original continuity).
(i) Law of original horizontality: This law describes the formation of sedimentary rock and involves the sequential deposition of sediments in a horizontal layer. Fig.1 shows a sedimentary rock formed by five layers of sedimentation. The layer 1 represents the oldest sedimentation layer while layer 5 depicts the newest sedimentation layer. Based on the law of original horizontality, it can be ascertained that the deformed layer shown above have been originally formed due to horizontal sedimentation.
(ii) Law of superposition: This law describes that in case the sedimentary rock has not undergone deformation, the sedimentation layers are arranged such that the youngest layer is the topmost while the oldest layer is formed by the bottom sedimentation layers. Fig.2 describes the sedimentary layer arrangement in sedimentary rock. This figure shows five layers in a non-deformed sedimentary rock. The layer 1 (bottom) corresponds to the oldest sedimentation layer while layer 5 (top) depicts the youngest layer.
(iii) Law of original continuity: This law states that the layers of sedimentary rock are continuous only when the sedimentary rock demonstrates a gradual change between successive sedimentation layers. In case a discontinuity is observed in the sedimentary layers, it is primarily due to fault movements. Fig.3 represents a sedimentary rock having five layers. The deformation ranging from layer 2 to layer 5 can be attributed to fault movements.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- 5. Use Figure 9.14 to draw a topographic profile along the X-Y line from Sugar Loaf Mountain to Bear Lake and mark the position of the Lake Fork stream. (Use only index contours.) 6. Describe the shape of Lake Fork Valley, based on your profile. 7. What glacial feature is Lake Fork Valley?arrow_forward7. The streamlined, asymmetrical hills composed of till, labeled B, are what type of feature? 8. Examine the shape of the features labeled B on the map in Figure 9.10. How can these features be used to determine the direction of ice flow in a glaciated area? 9. Using the features labeled B in Figure 9.10 as a guide, draw an arrow on the map to indicate the direction of ice movement that occurred in this region. 10. What is the likely location of the outwash plain on the map? Identify and label the area "outwash plain." (Hint: Refer to Figure 9.7.) 11. Label the area covered by ground moraine. 12. What term is applied to the numerous almost circular depressions designated with the letter C?arrow_forwardRabbit population over time which letter(A,B,or C) shows a growth period for the rabbit populationarrow_forward
- Activity 9.5 Depositional Features Associated with Ice Sheets Pgs 159-1611. After examining the map and stereogram, draw a line on the map to outline the area illustrated on the stereogram. 2. What evidence on the map indicates that portions of the area are poorly drained? On what part of the map are these features located? 3. Use Figure 9.11 to draw a topographic profile of the X-Y line on Figure 9.10. 4. Is the general topography of the land in Sections 7 and 8 in the northwest portion of the region higher or lower in elevation than the land around the letter A located near the center of the map? Is it more or less hilly? 5. Is the area that coincides with Kettle Moraine State Forest higher or lower in elevation than the land to the northwest and southeast? 6. The feature labeled A on the map is a long ridge composed of till. Is this ridge an esker, an end moraine, or a drumlin? 7. The streamlined, asymmetrical hills composed of till, labeled B, are what type of feature?The features…arrow_forwardA prairie has plenty of grass.The soil on the prairie provides all of the following except? A.nutrients that help the grass live and grow B.a place for the roots of the grass to take holdC. Water in pore spaces that the grass can absorb D. Energy that the grass needs to make its foodarrow_forwardtimeters (inches) (11) 25.0 (10) 22.5 (9) 20.0 (8) 17.5 (7) 15.0 (6) 12.5 (5) 10.0 (4) 7.5 (70) 16 (60) 10 (50) 4 (40) 0(32) (30) -18 (3) 5.0 (2) 2.5 (1) 0 25.0 (10) (70) 16 (60) 10 Temperature °C (°F) Temperature °C (°F) — 22.5 (9) (50) 20.0 (8) 17.5 17 15.0 4 (40) 0(32) -1 (30) -7 (6) (20) 12.5 -12 (5) (10) 10.0 -18 (0) (4) (0) -23 7.5 (-10) (3) -23 (-10) -29 5.0 -29 (-20) (2) (-20) -34 2.5 -34 (-30) (-30) -40 0 -40 (-40) J F M A M J JASOND (-40) Month Station: San Francisco, California Lat/long: 37°37' N 122°23' W Avg. Ann. Temp. Total Ann. Precip.: 14°C (57.2°F) 47.5 cm (18.7 in.) Elevation: 5 m (16.4 ft) Population: 777,000 Ann. Temp. Range: 9°C (16.2 F°) Ann. Hr of Sunshine: (a) J F M A M J JASOND Month 2975 Station: Sevilla, Spain Lat/long: 37°22' N 6°00' W Avg. Ann. Temp.: 18°C (64.4°F) Total Ann. Precip.: 55.9 cm (22 in.) (b) Elevation: 13 m (42.6 ft) Population: 683,000 Ann. Temp. Range: 16 C° (28.8 F°) Ann. Hr of Sunshine: 2862 With all graphs, we start with the question,…arrow_forward
- I need help with part A, B and Carrow_forwardDiscussion Question: Atmospheric Water & Weather A+ This chapter beautifully focuses on water from the small molecular scale to large-scale weather patterns. The surplus of heat at the equator and the deficit at the Poles drives our atmospheric instability. Instability is a good thing! Without the unstable conditions, there would not be any atmospheric motion. The overheating of the equator pumps atmospheric uplift. As the air rises into lower pressures, it expands and cools... adiabatic cooling! The air migrates north and south and becomes denser than the surrounding air and sinks. The sinking air enters higher pressures and creates the subtropical high pressures and adiabatic heating...whaaaa-la! We have Hadley Cells! Not to mention, the Rainforests and World's largest deserts too! We now can imagine the Hadley cells in three-dimensions. They more or less "sandwich" the equator during the spring and fall equinoxes. However, what happens in the summer and winter? mP Maritime polar…arrow_forwardUsing the map. Solve part e f garrow_forward
- Answer the below questions in detail using the attached pictures. Please ensure it is all 100% done by human, please do not use AI or chatgpt. using the provided hydraulic head data (attached spreadsheet), plot the values at their corresponding piezometer locations (attached piezometer map), contour the head data to create equipotential lines that allow you to demonstrate the groundwater flow direction, indicate the flow direction with arrows, provide comments/observations about the characteristics of the groundwater flow system, for example, are the equipotential lines equally spaced? If not, can you comment on why there are areas with close spacing and other areas with wide spacing? Are there any areas where the aquifer displays artesian conditions? If so, where?arrow_forwardPlease answer the question in detail. Please ensure it is 100% done by human, please do not use AI or chatgpt. Organize your spreadsheets carefully and make sure they are easy to follow. Make sure that your units are consistent, use SI units and make sure your graphs are clear and well labelled.arrow_forwardPlease answer each question in detail. Please ensure it is 100% done by human, please do not use AI or chatgpt.arrow_forward
 Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...Earth ScienceISBN:9780134746241Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...Earth ScienceISBN:9780134746241Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134041360Author:Greg CarbonePublisher:PEARSON
Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134041360Author:Greg CarbonePublisher:PEARSON Environmental ScienceEarth ScienceISBN:9781260153125Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Environmental ScienceEarth ScienceISBN:9781260153125Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Earth Science (15th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134543536Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON
Earth Science (15th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134543536Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)Earth ScienceISBN:9781337569613Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott SpoolmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)Earth ScienceISBN:9781337569613Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott SpoolmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical GeologyEarth ScienceISBN:9781259916823Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, LisaPublisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Physical GeologyEarth ScienceISBN:9781259916823Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, LisaPublisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





