
Draw the four water molecules that can hydrogen-bond to this water molecule. Label the bonds and the partial negative and positive charges that account for the formation of these hydrogen bonds.
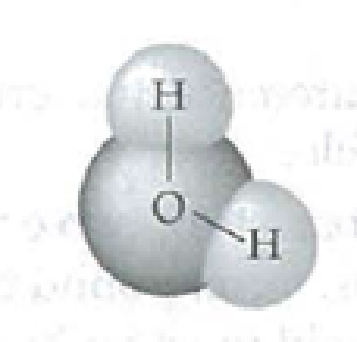
To draw: The four water molecules that can form hydrogen-bond to the given water molecule and label the bonds and the partial negative and positive charges that account for the formation of these hydrogen bonds.
Introduction: A water molecule is shaped like a ‘V’ that consists of an oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms. Oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen. Thus, the shared electrons in the O-H covalent bond are more attracted by the oxygen atom.
Answer to Problem 1IQ
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 represents the four water molecules that can form hydrogen-bond for the given water molecule and label the bonds and the partial negative and positive charges that account for the formation of these hydrogen bonds.
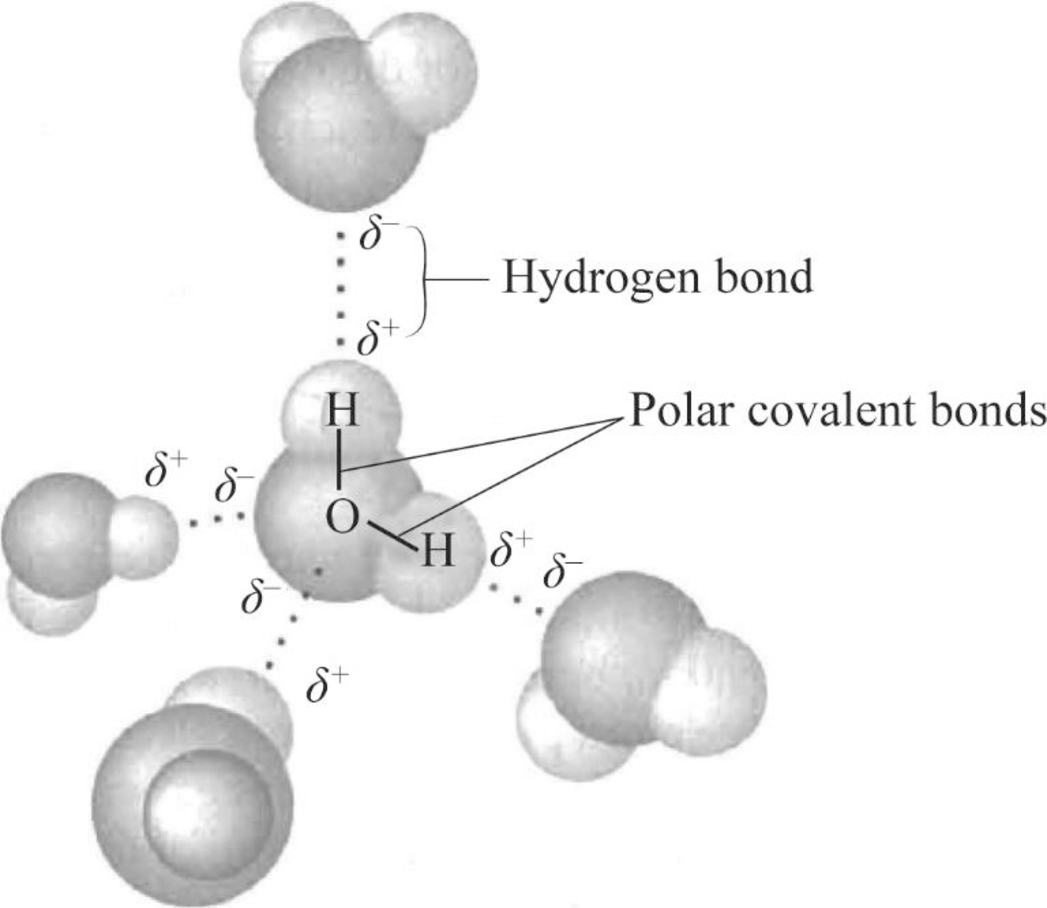
Fig.1: Four water molecules bind with one water molecule
Explanation of Solution
Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons shared in a covalent bond. If one atom is more electronegative, the electrons would be more on the side of that atom. Oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen. In a water molecule, there are two polar covalent bonds between oxygen and hydrogen. Hence, there are two regions of partial negative charge on oxygen and a partial positive charge on each hydrogen atom.
The partial negatively charged oxygen atom of a water molecule is attracted to the partial positively charged hydrogen of the other water molecule. As per Fig.1, atoms on the partial charged regions can bind to oppositely charged regions on other adjoining water molecules. There are four regions of partial charge in a water molecule. Thus, the central water molecule can form a hydrogen bonds with four other water molecules.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Study Guide for Campbell Biology
- Not part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forwardNoggin mutation: The mouse, one of the phenotypic consequences of Noggin mutationis mispatterning of the spinal cord, in the posterior region of the mouse embryo, suchthat in the hindlimb region the more ventral fates are lost, and the dorsal Pax3 domain isexpanded. (this experiment is not in the lectures).a. Hypothesis for why: What would be your hypothesis for why the ventral fatesare lost and dorsal fates expanded? Include in your answer the words notochord,BMP, SHH and either (or both of) surface ectoderm or lateral plate mesodermarrow_forwardNot part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forward
- Explain in a flowcharts organazing the words down below: genetics Chromosomes Inheritance DNA & Genes Mutations Proteinsarrow_forwardplease helparrow_forwardWhat does the heavy dark line along collecting duct tell us about water reabsorption in this individual at this time? What does the heavy dark line along collecting duct tell us about ADH secretion in this individual at this time?arrow_forward
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning





