
1.
Analyze the effects of the January transaction on the
1.
Explanation of Solution
The effects of the accounting equation for the September events using a table are indicated as follows:
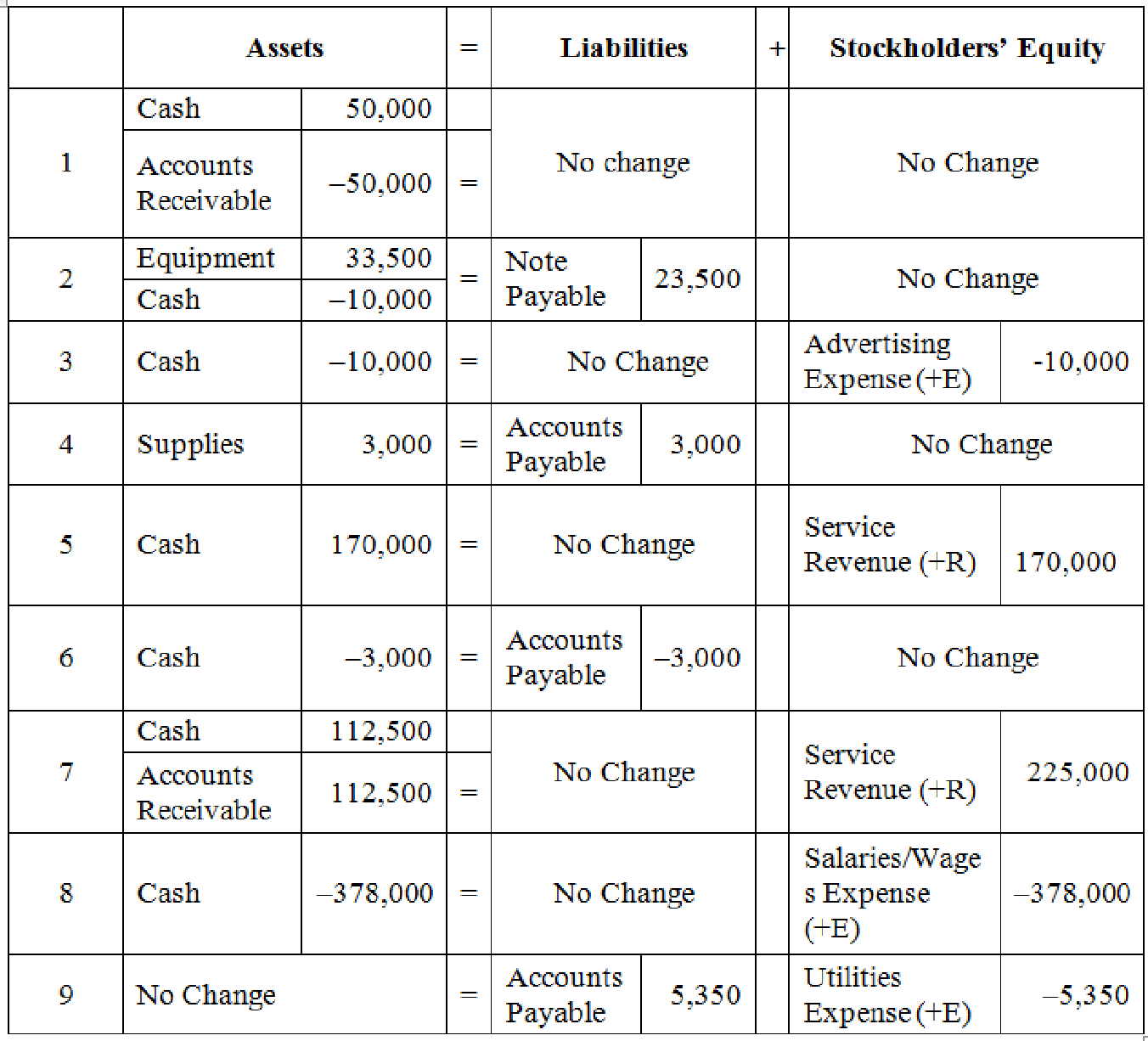
Table (1)
Note:
SE refers to Stockholder’s equity.
E refers to Expenses.
R refers to Revenues.
2.
Prepare
2.
Explanation of Solution
Journal: Journal is the book of original entry. Journal consists of the day today financial transactions in a chronological order. The journal has two aspects; they are debit aspect and the credit aspect.
Journal entries for September events are prepared as follows:
|
Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 1. | Cash (A+) | 50,000 | ||
| 50,000 | ||||
| (To record the cash receipt from customer for the service rendered already) | ||||
| 2. | Equipment (A+) | 33,500 | ||
| Cash (A–) | 10,000 | |||
| Notes Payable (L+) | 23,500 | |||
| (To record the purchase of equipment partly for cash and partly by signing a note) | ||||
| 3. | Advertising Expense | 10,000 | ||
| Cash (A–) | 10,000 | |||
| (To record the payment made for advertising expenses) | ||||
| 4. | Supplies (A+) | 3,000 | ||
| Accounts Payable (L+) | 3,000 | |||
| (To record the supplies purchased on accounts) | ||||
| 5. | Cash (A+) | 170,000 | ||
| Service Revenue (R+, SE+) | 170,000 | |||
| (To record the cash receipt for the service provide) | ||||
| 6. | Accounts Payable (L–) | 3,000 | ||
| Cash (A–) | 3,000 | |||
| (To record the payment made for the supplies purchased on account) | ||||
| 7. | Cash (A+) | 112,500 | ||
| Accounts Receivable (A+) | 112,500 | |||
| Service Revenue (R+, SE+) | 225,000 | |||
| (To record the sales made partly for cash and partly on account ) | ||||
| 8. | Salaries and Wages Expense (E+, SE–) | 378,000 | ||
| Cash (A–) | 378,000 | |||
| (To record the payment of wages expenses to employees) | ||||
| 9. | Utilities Expense (E+, SE–) | 5.350 | ||
| Accounts Payable (L+) | 5.350 | |||
| (To record the utilities expenses incurred which are to be paid later) | ||||
Table (2)
3.
Create T accounts for the
3.
Explanation of Solution
T-account: An account is referred to as a T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’. An account consists of the three main components which are as follows:
- The title of the account
- The left or debit side
- The right or credit side
The posting of the journal entries to the T accounts are as follows:
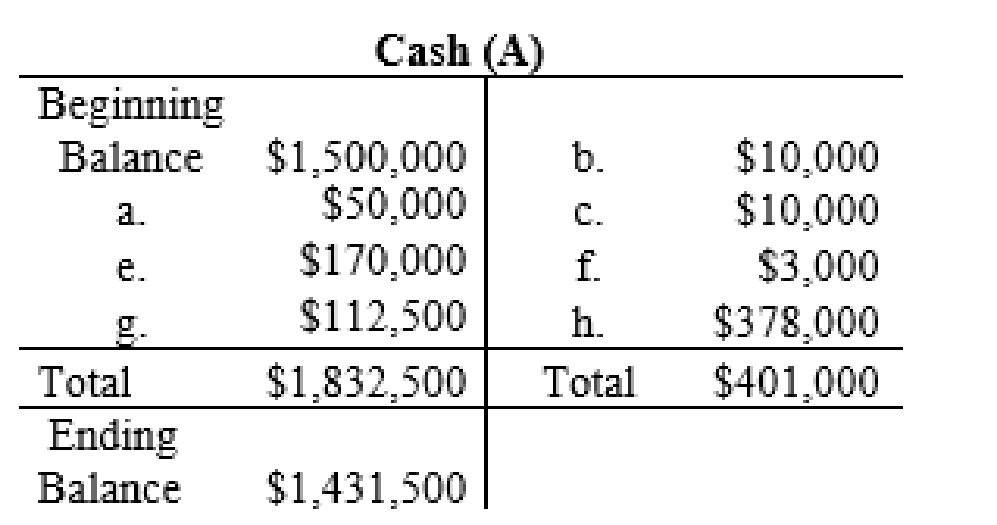
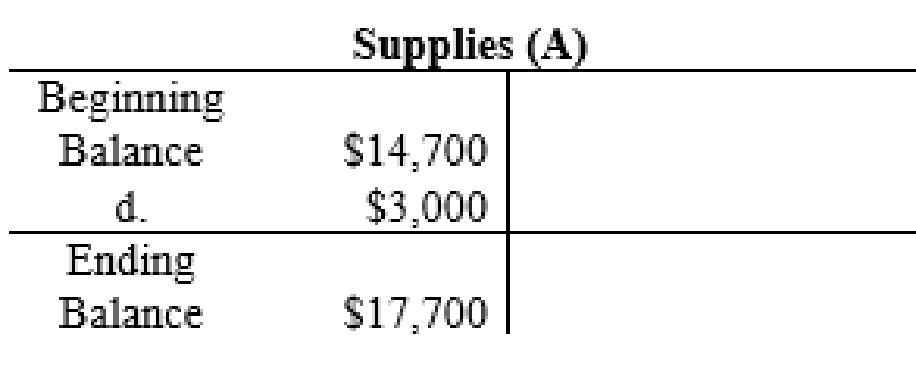
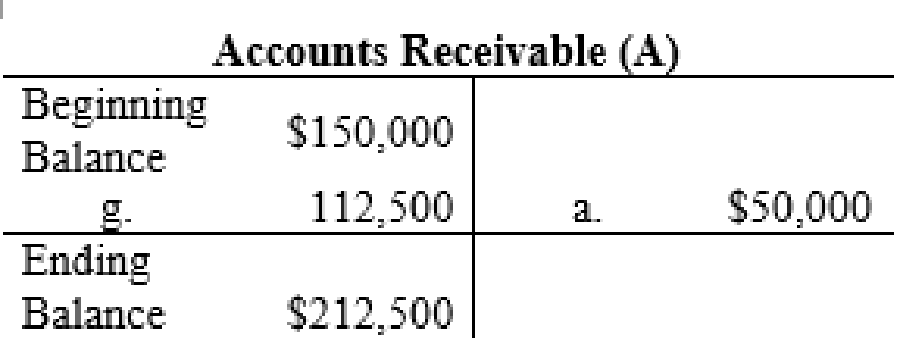
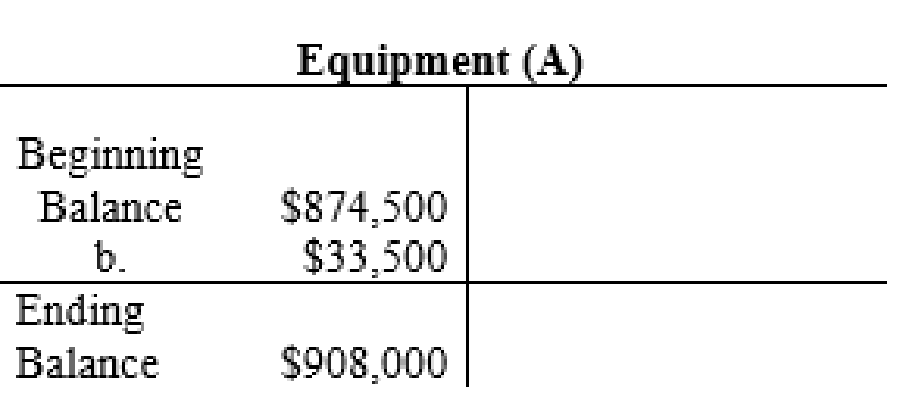
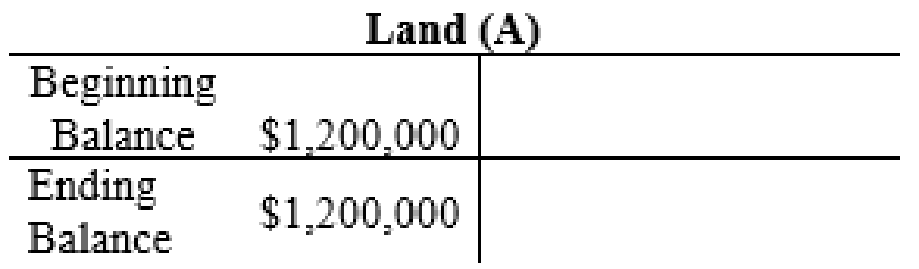
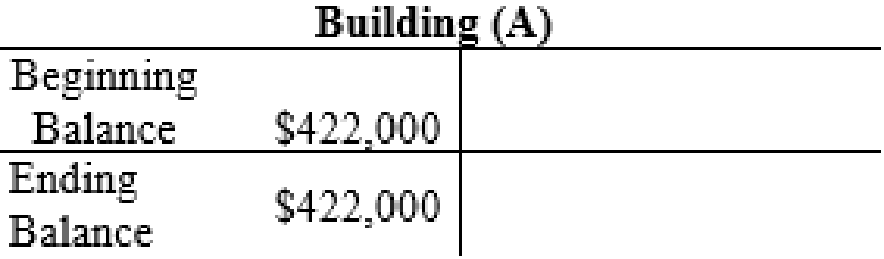
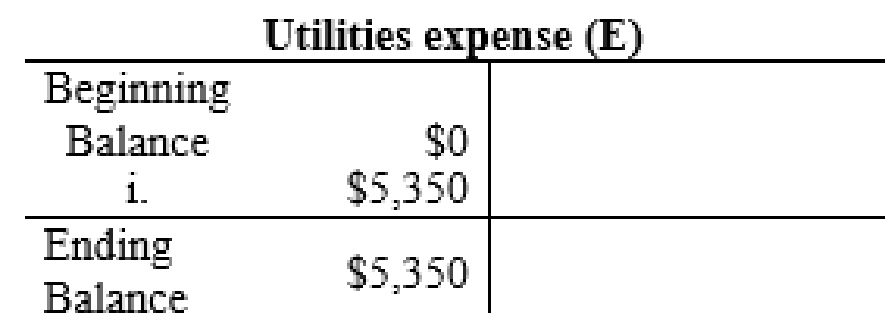

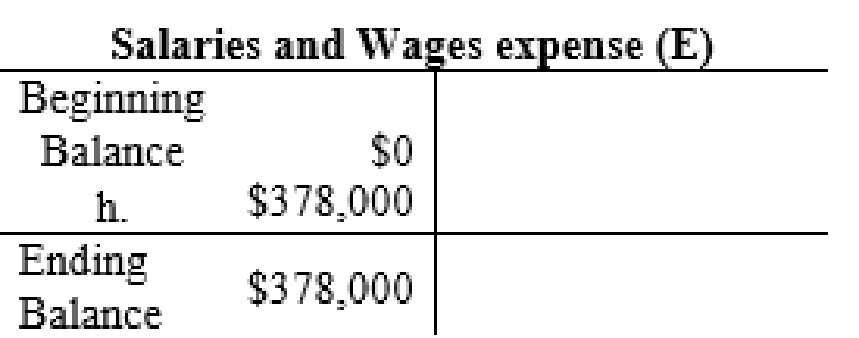
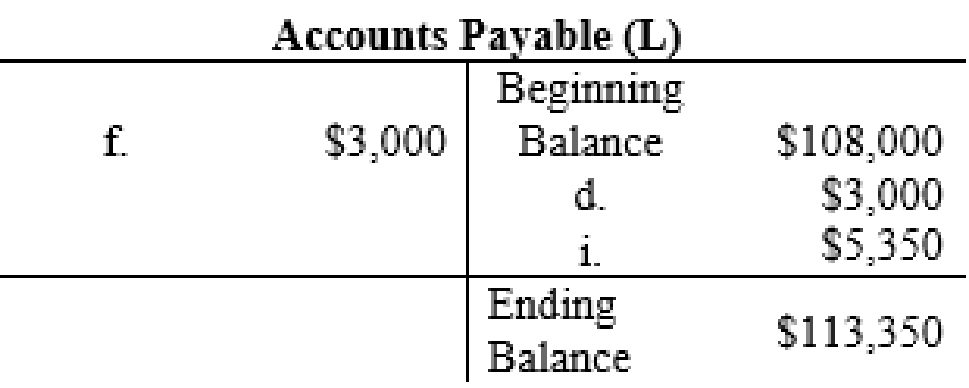

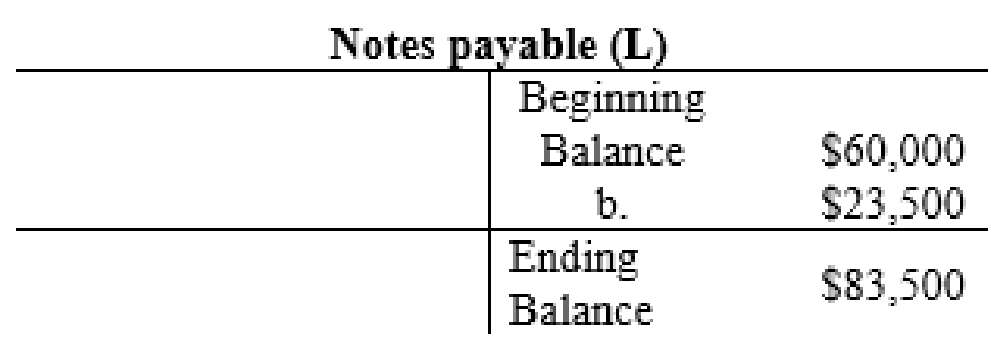
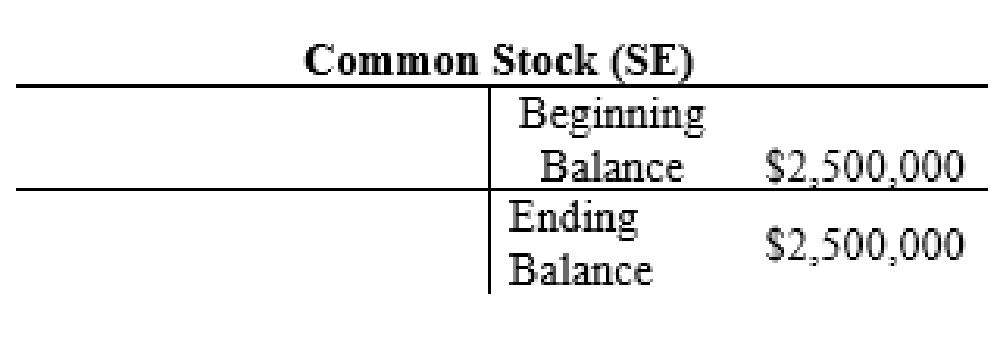
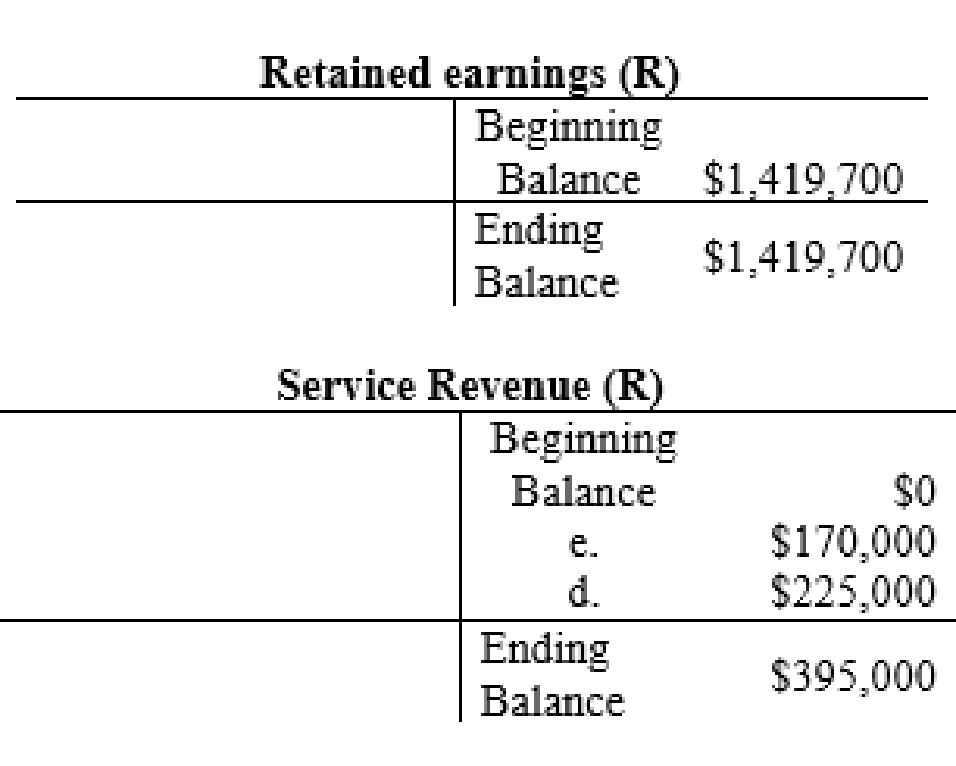
4.
Prepare an unadjusted
4.
Explanation of Solution
Unadjusted trial balance: Unadjusted trial balance is that statement which contains complete list of accounts with their unadjusted balances. This statement is prepared at the end of every financial period.
An unadjusted trial balance of corporation V for the month ended January 31, 2018 is prepared as follows:
| Corporation V | ||
| Unadjusted Trial Balance | ||
| At January 31, 2018 | ||
| Particulars | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | $1,431,500 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 212,500 | |
| Supplies | 17,700 | |
| Equipment | 908,000 | |
| Building | 422,000 | |
| Land | 1,200,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | $113,350 | |
| Deferred Revenue | 73,500 | |
| Notes Payable | 83,500 | |
| Common Stock | 2,500,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | 1,419,700 | |
| Service Revenue | 395,000 | |
| Salaries and Wages Expense | 378,000 | |
| Advertising Expense | 10,000 | |
| Utilities Expense | 5,350 | |
| Total | $4,585,050 | $4,585,050 |
Table (3)
The debit column and credit column of the unadjusted trial balance are agreed, both having balance of $4,585,050.
5.
Prepare an income statement of corporation V for the year ended January 31, 2018.
5.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
An income statement of corporation V for the year ended December 31is prepared as follows:
|
Corporation V Income Statement For the year Ended January 31, 2018 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenues: | ||
| Service Revenue | $395,000 | |
| Total Revenues | 395,000 | |
|
Less: Expenses: | ||
| Salaries and Wages Expense | 378,000 | |
| Advertising Expense | 10,000 | |
| Utilities Expense | 5,350 | |
| Total Expenses | 393,350 | |
| Net Income | $1,650 | |
Table (4)
6.
Prepare the statement of retained earnings of Corporation V for the year ended January 31, 2018.
6.
Explanation of Solution
Statement of Retained Earnings: Statement of retained earnings shows, the changes in the retained earnings, and the income left in the company after payment of the dividends, for the accounting period.
The statement of retained earnings of Corporation V for the year ended January 31, 2018 is prepared as follows.
| Corporation V | |
| Statement of Retained Earnings | |
| For the Year Ended January 31, 2018 | |
| Particulars | $ |
| Retained Earnings, January 1, 2018 | 1,419,700 |
| Less: Net Loss | 1,650 |
| Dividends | 0 |
| Retained Earnings, December 31 | 1,421,350 |
Table (5)
7.
Prepare a classified balance sheet of Corporation V for the year ended January 31, 2018.
7.
Explanation of Solution
Classified balance sheet: This is the financial statement of a company which shows the grouping of similar assets and liabilities under subheadings.
A classified balance sheet of Corporation V for the year ended January 31, 2018 is prepared as follows:
| Corporation V | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| At January 31, 2018 | ||
| Assets: | $ | $ |
| Current Assets | ||
| Cash | $1,431,500 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 212,500 | |
| Supplies | 17,700 | |
| Total Current Assets | 1,661,700 | |
| Equipment | 908,000 | |
| Building | 422,000 | |
| Land | 1,200,000 | |
| Total Assets | $4,191,700 | |
| Liabilities: | ||
| Current Liabilities | ||
| Accounts Payable | $113,350 | |
| Deferred Revenue | 73,500 | |
| Total Current Liabilities | 186,850 | |
| Notes Payable | 83,500 | |
| Total Liabilities | 270,350 | |
| Stockholders’ Equity | ||
| Common Stock | 2,500,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | 1,421,350 | |
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | 3,921,350 | |
| Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | $4,191,700 | |
Table (6)
8.
Calculate the net profit margin of the company.
8.
Explanation of Solution
Profit Margin Ratio: Profit margin provides an indication of the earnings per dollar of sales, and it represents the net profit as a percentage of the revenues. Use the following formula to calculate the profit margin ratio.
The net profit margin of the Company is determined as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
CONNECT CODE F/FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
- Cypress Ltd.'s contribution margin is $250, after-tax income is $90, and the tax rate is 25%. What are the fixed costs? a. $65 b. $175 c. $130 d. None of the above HELParrow_forwardGeneral accounting question with helparrow_forwardDylan Manufacturing had an estimated 90,000 direct labor hours, $360,000 manufacturing overhead, and 30,000 machine hours. The actual results were 91,200 direct labor hours, 32,500 machine hours, and $415,000 manufacturing overhead. Overhead is applied based on machine hours. Calculate the predetermined overhead rate. Helparrow_forward
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning

