
Concept explainers
Complete the following table to help you review the structures and functions of the four classes of organic molecules.
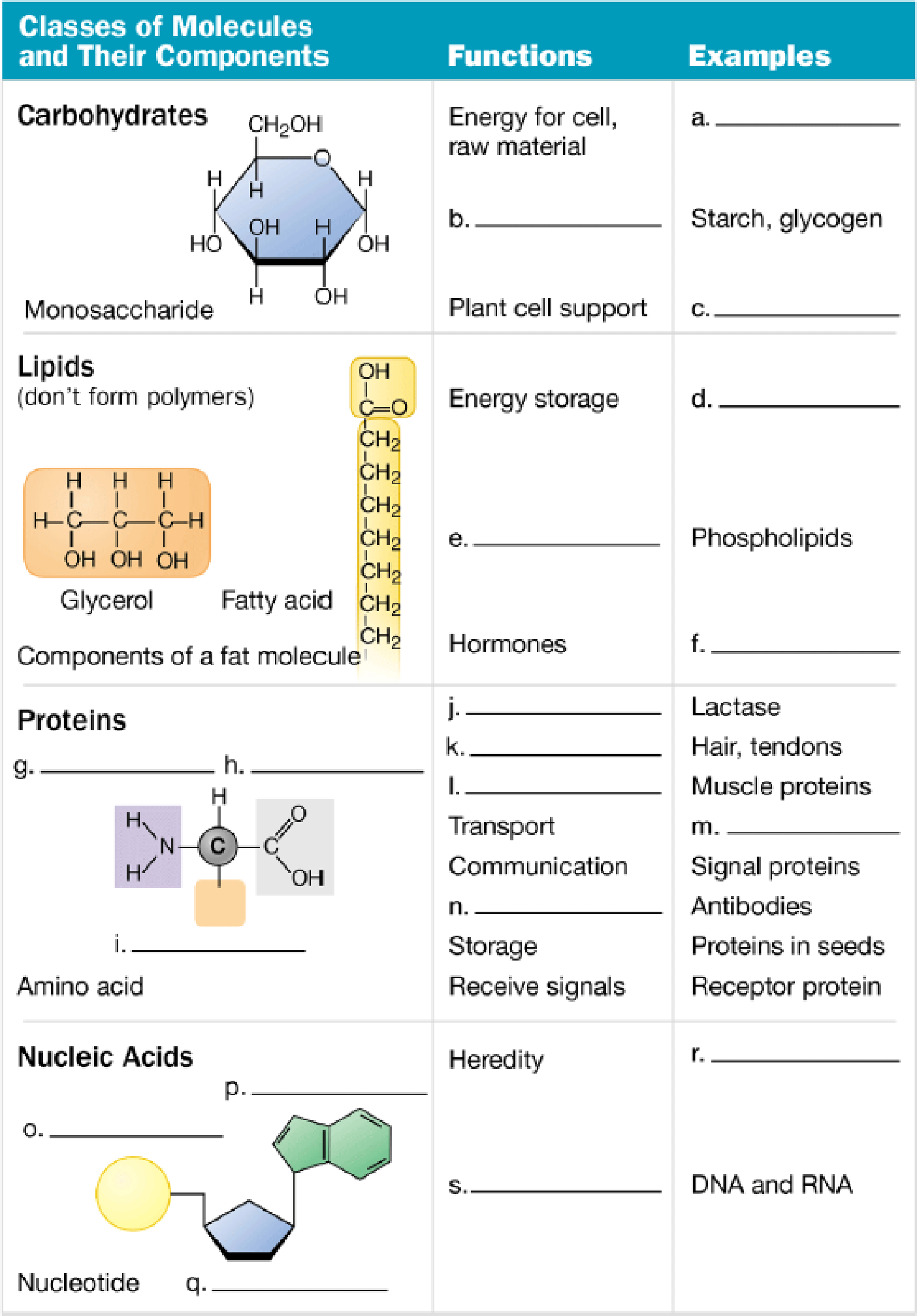
To create: The concept map to review the structures and functions of the four classes of organic molecules.
Introduction: The four classes of molecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids are important to sustain the life. Carbohydrates serve as a fuel and building material for cellsand tissues. Lipid comprises a diverse group of molecules. It does not mix with water. A protein is a polymer of amino acids. It is structurally and functionally most complex and varied. Nucleic acid is the genetic material that consists of a polynucleotide.
Answer to Problem 1CC
Pictorial representation: Fig. 1 shows the completed concept map of structures and functions of the four classes of organic molecules.
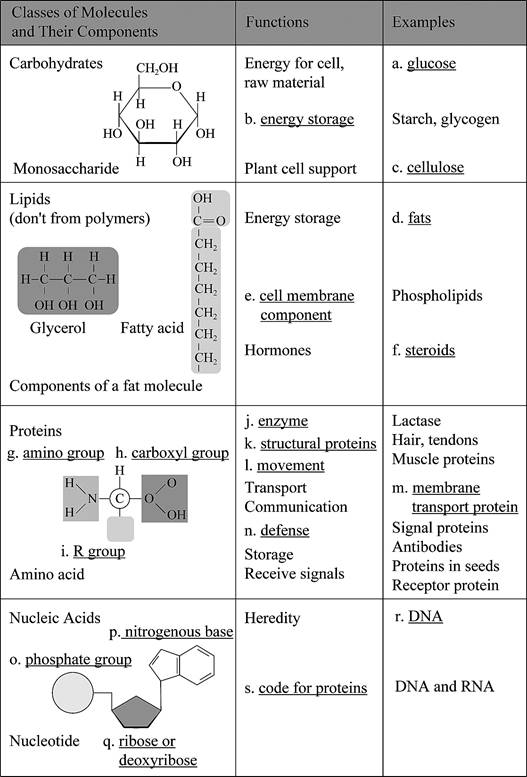
Fig.1: Concept map of the structures and functions of the four classes of organic molecules.
Explanation of Solution
a.
Correct answer: Glucose
Explanation: Glucose is the raw material from which cell will get energy. Hence, the correct answer is Glucose.
b.
Correct answer: Energy storage
Explanation: The starch and glycogen is used as storage material of energy. Hence, the correct answer is energy storage.
c.
Correct answer: Cellulose
Explanation: Cellulose is polysaccharides which is a polymer of glucose molecule. Hence, the correct answer is cellulose.
d.
Correct answer: Fats
Explanation: Fats are a type of lipid. It is composed of glycerol and fatty acids. Hence, the correct answer is fats.
e.
Correct answer: Cell membrane component
Explanation: Cell is the outermost boundary of animal cell. It is made of phospholipid bilayer. Hence, the correct answer is cell membrane component.
f.
Correct answer: Steroids
Explanation: Steroids are hormones such as estrogen. Hence, the correct answer is steroids.
g.
Correct answer: Amino group
Explanation: Protein is made of amino acids. An amino acid contains amino group which is
h.
Correct answer: Carboxylic group
Explanation: Protein is made of amino acids. An amino acid contains carboxylic group which is
i.
Correct answer: R group
Explanation: Protein is made of amino acids. An amino acid contains a side group which is called R group. Hence, the correct answer is R group.
j.
Correct answer: Enzyme
Explanation: Proteins have broad functions such as enzymes, structural proteins, transport, movement, defense, and storage. Lactase is an enzyme used for breakdown of lactose molecule. Hence, the correct answer is Enzyme.
k.
Correct answer: Structural proteins
Explanation: Proteins have broad functions such as enzymes, structural proteins, transport, movement, defense, and storage. Hair and tendons are structural proteins. Hence, the correct answer is structural proteins.
l.
Correct answer: Movement
Explanation: Muscle is a protein that helps in movement. Hence, the correct answer is movement.
m.
Correct answer: Membrane transport protein
Explanation: Membrane transport protein helps in transport of different molecules across the membrane. Hence, the correct answer is Membrane transport protein.
n.
Correct answer: Defense
Explanation: Signal protein helps in communication. Antibodies are immunoglobulin protein that helps in body defense. Hence, the correct answer is defense.
o.
Correct answer: Phosphate group
Explanation: Nucleic acid is a polymer of nucleotides. A nucleotide consists of phosphate group, sugar and nitrogenous base. Hence, the correct answer is phosphate group.
p.
Correct answer: Nitrogenous base
Explanation: Nucleic acid is a polymer of nucleotides. A nucleotide consists of phosphate group, sugar and nitrogenous base. Hence, the correct answer is nitrogenous base.
q.
Correct answer: Ribose or deoxyribose
Explanation: Nucleic acid is a polymer of nucleotides. A nucleotide consists of phosphate group, sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) and nitrogenous base. Hence, the correct answer is ribose or deoxyribose.
r.
Correct answer: DNA
Explanation: Nucleic acid is a polymer of nucleotides. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the hereditary material. Hence, the correct answer is DNA.
s.
Correct answer: Code for protein
Explanation: Nucleic acid is a polymer of nucleotides. DNA and RNA have information to code for protein. Hence, the correct answer is code for protein.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
CAMPBEL BIOLOGY:CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS
- An 1100 pound equine patient was given 20 mg/kg sucralfate 3 times a day, 2.8 mg/kg famotidine twice a day, and 10mg/kg doxycycline twice a day. Sucralfate comes as a 1 gm tablet, famotidine as 20 mg tablets, and doxycycline as 100mg tablets. All are in bottles of 100 tablets.How many total mg are needed for the patient and how many tablets of each would be needed to provide each dose?How many bottles of each would be needed to have available if this patient were to be on this drug regimen for 5 days?arrow_forwardThe patient needs a solution of 2.5% dextrose in Lactated Ringer’s solution to run at 75 ml/hr for at least the next 12hours. LRS comes in fluid bags of 500 ml, 1 Liter, 3 Liters and 5 Liters. How can a 2.5% solution be made by adding50% dextrose to the LRS?arrow_forward“Gretchen” was a 68-pound canine who came to the VMTH as small animal surgery patient. She receivedacepromazine, 0.2 mg/kg from a 10 mg/ml solution and oxymorphone, 0.08 mg/kg from a 1 mg/ml solution before surgery.What are the mechanisms of action of acepromazine and oxymorphone? Why would they be given together?How many mg provide each dose and how many ml of each of these solutions were given?arrow_forward
- After surgery, “Gretchen” was put on carprofen, 1 mg/pound bid (twice a day). The tablets come in 25, 75 and 100 mgsizes. Which size tablet would be appropriate?What is the mechanism of action of carprofen?An outpatient prescription was written for her so she would have enough for 10 days. How many tablets did she need?What information needs to be on her out-patient prescription?arrow_forwardJoden Koepp olor in chickens is due to incomplete dominance. BB = Black chicken, WW = White BLOOD TYPES Arhite chicken is In humans, Rh positive blood is dominant (R) over Rh negative blood (r). A man with type 0, Rh positive blood (whose mother had Rh negative blood), marries a woman with type AB, Rh negative blood. Several children were born. is? R R Genotypes Phenotypes RRR RR Rr Rr 4/16 RR R RR RK Rr Rr 4/16 rr 3/4 Rh posi 1/4 Rh negu 1/2 Rr rr rr rrrr 88 888 75 e genotype of the man? the genotype of the woman? The mother of the man had type AB blood.arrow_forwardPlease indentify the unknown organismarrow_forward
- 5G JA ATTC 3 3 CTIA A1G5 5 GAAT I I3 3 CTIA AA5 Fig. 5-3: The Eco restriction site (left) would be cleaved at the locations indicated by the arrows. However, a SNP in the position shown in gray (right) would prevent cleavage at this site by EcoRI One of the SNPs in B. rapa is found within the Park14 locus and can be detected by RFLP analysis. The CT polymorphism is found in the intron of the Bra013780 gene found on Chromosome 1. The Park14 allele with the "C" in the SNP has two EcoRI sites and thus is cleaved twice by EcoRI If there is a "T" in that SNP, one of the EcoRI sites is altered, so the Park14 allele with the T in the SNP has only one EcoRI site (Fig. 5-3). Park14 allele with SNP(C) Park14 allele with SNPT) 839 EcoRI 1101 EcoRI 839 EcoRI Fig. 5.4: Schematic restriction maps of the two different Park14 alleles (1316 bp long) of B. rapa. Where on these maps is the CT SNP located? 90 The primers used to amplify the DNA at the Park14 locus (see Fig. 5 and Table 3 of Slankster et…arrow_forwardFrom your previous experiment, you found that this enhancer activates stripe 2 of eve expression. When you sequence this enhancer you find several binding sites for the gap gene, Giant. To test how Giant interacts with eve, you decide to remove all of the Giant binding sites from the eve enhancer. What results do you expect to see with respect to eve expression?arrow_forwardWhat experiment could you do to see if the maternal gene, bicoid, is sufficient to form anterior fates?arrow_forward
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College





