
Using Figure 3.1, determine
a. the number of grams of
b. the number of grams of water required to dissolve
c. the number of grams of water required to dissolve
d. the number of grams of water required to dissolve a mixture containing
(a)
Interpretation:
The number of grams of
Concept introduction:
Solution is a homogenous mixture of two or more components. A sample taken from any part of the solution will have the same composition as the rest of the solution. Many chemical reactions occur in water solutions.
Answer to Problem 1ASA
The number of grams of
Explanation of Solution
The given illustration of the graph is shown below.
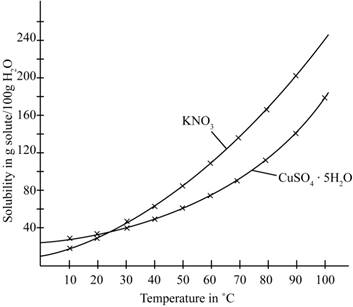
Figure 1
According to the above graph, the number of grams of
The number of grams of
(b)
Interpretation:
The number of grams of water required to dissolve
Concept introduction:
Solution is a homogenous mixture of two or more components. A sample taken from any part of the solution will have the same composition as the rest of the solution. Many chemical reactions occur in water solutions.
Answer to Problem 1ASA
The number of grams of water required to dissolve
Explanation of Solution
The given illustration of the graph is shown below.
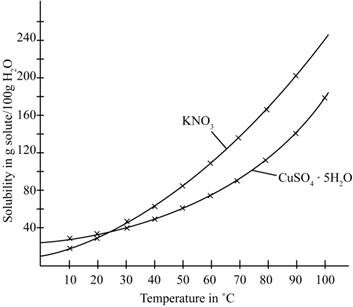
Figure 1
According to the above graph, the number of grams of
Thus, water required to dissolve
The number of grams of water required to dissolve
(c)
Interpretation:
The number of grams of water required to dissolve
Concept introduction:
Solution is a homogenous mixture of two or more components. A sample taken from any part of the solution will have the same composition as the rest of the solution. Many chemical reactions occur in water solutions.
Answer to Problem 1ASA
The number of grams of water required to dissolve
Explanation of Solution
The given illustration of the graph is shown below.
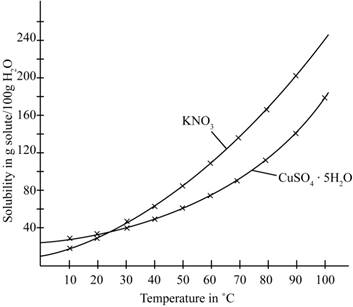
Figure 1
According to the above graph, the number of grams of
Thus, the water required to dissolve
The number of grams of water required to dissolve
(d)
Interpretation:
The number of grams of water required to dissolve a mixture containing
Concept introduction:
Solution is a homogenous mixture of two or more components. A sample taken from any part of the solution will have the same composition as the rest of the solution. Many chemical reactions occur in water solutions.
Answer to Problem 1ASA
The number of grams of water required to dissolve a mixture containing
Explanation of Solution
The given illustration of the graph is shown below.
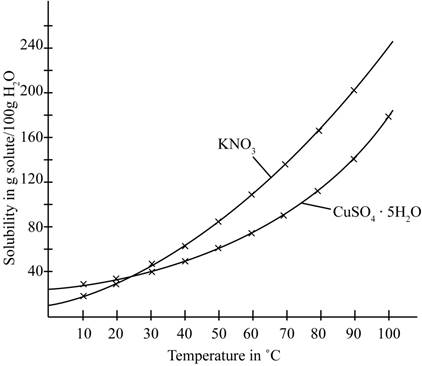
Figure 1
The amount of water required to dissolve
The amount of water required to dissolve
Therefore, the total amount of water required to dissolve a mixture containing
The number of grams of water required to dissolve a mixture containing
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
CHM 111/112 LAB MANUAL >C<
- At a metal-solution interface, an electron is exchanged, and the symmetry factor beta < 0.5 is found in the Butler-Volmer equation. What does this indicate?arrow_forwardTopic: Photochemistry and Photophysics of Supramoleculesarrow_forwardTopic: Photochemistry and Photophysics of Supramoleculesarrow_forward
- How to name hydrocarbonsarrow_forwardPlease do these questions within the SCH4U course please with full steps since I am still unsure how to format my answers! Thank you so much.arrow_forwardWhen two solutions, one of 0.1 M KCl (I) and the other of 0.1 M MCl (II), are brought into contact by a membrane. The cation M cannot cross the membrane. At equilibrium, x moles of K+ will have passed from solution (I) to (II). To maintain the neutrality of the two solutions, x moles of Cl- will also have to pass from I to II. Explain this equality: (0.1 - x)/x = (0.1 + x)/(0.1 - x)arrow_forward
- Calculate the variation in the potential of the Pt/MnO4-, Mn2+ pair with pH, indicating the value of the standard potential. Data: E0 = 1.12.arrow_forwardGiven the cell: Pt l H2(g) l dis X:KCl (sat) l Hg2Cl2(s) l Hg l Pt. Calculate the emf of the cell as a function of pH.arrow_forwardThe decimolar calomel electrode has a potential of 0.3335 V at 25°C compared to the standard hydrogen electrode. If the standard reduction potential of Hg22+ is 0.7973 V and the solubility product of Hg2Cl2 is 1.2x 10-18, find the activity of the chlorine ion at this electrode.Data: R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1, F = 96485 C mol-1, T = 298.15 K.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning





