
Concept explainers
1 and 2
Prepare a 10 column worksheet for the given account balances, and prepare the
1 and 2
Explanation of Solution
Worksheet:
A spreadsheet is a worksheet. It is used while preparing a financial statement. It is a type of form having multiple columns and it is used in the adjustment process. The use of a worksheet is optional for any organization. A worksheet can neither be considered as a journal nor a part of the general ledger.
Prepare 10 column worksheet for the given account balances, and trial balance as follows:
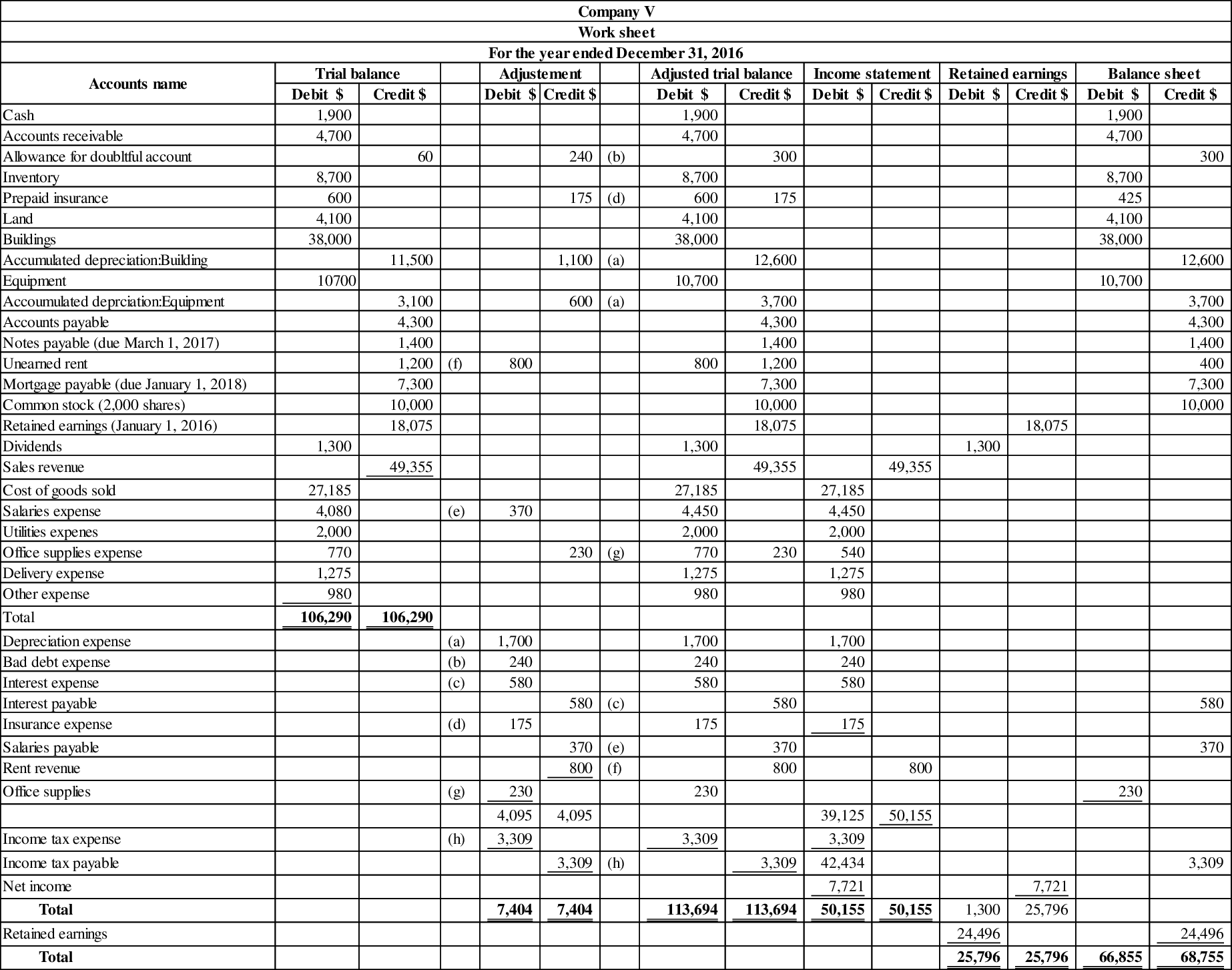
Figure (1)
Adjusting entry:
| Date | Account Title & Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit($) |
| December 31, 2016 | 1,700 | ||
| 1,100 | |||
| Accumulated depreciation - Equipment | 600 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | |||
| December 31, 2016 | 240 | ||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts | 240 | ||
| (To record the bad debts expense estimated at the end of the accounting year) | |||
| December 31, 2016 | Interest expense | 580 | |
| Interest payable | 580 | ||
| (To record the interest expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | |||
| December 31, 2016 | Insurance expense | 175 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 175 | ||
| (To record the insurance expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | |||
| December 31, 2016 | Salaries expense | 370 | |
| Salaries payable | 370 | ||
| (To record the salaries expense accrued at the end of the accounting year) | |||
| December 31, 2016 | Unearned rent | 800 | |
| Rent revenue | 800 | ||
| (To record the rent revenue recognized) | |||
| December 31, 2016 | Office supplies expense | 230 | |
| Office supplies | 230 | ||
| (To record the supplies used during the year) | |||
| December 31, 2016 | Income tax expense (1) | 3,309 | |
| Income tax payable | 3,309 | ||
| (To record the income tax expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) |
Table (1)
Working note (1):
Calculate the value of income tax expense.
3.
Prepare income statement,
3.
Explanation of Solution
Financial statements: Financial statements are condensed summary of transactions communicated in the form of reports for the purpose of decision making. The financial statements are balance sheet, income statement, statement of retained earnings, and the cash flow statement.
Prepare income statement, retained earnings, and balance sheet of Company V as follows:
| Company V | ||
| Income statement | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2016 | ||
| Particulars | Amount($) | Amount ($) |
| Service revenue | 49,355 | |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | (27,185) | |
| Gross profit | 22,170 | |
| Less: Operating expense | ||
| Salaries expense | 4,450 | |
| Utilities expense | 2,000 | |
| Office supplies expense | 540 | |
| Delivery expense | 1,275 | |
| Depreciation expense | 1,700 | |
| Bad debt expense | 240 | |
| Insurance expense | 175 | |
| Other expense | 980 | |
| Total operating expense | 11,360 | |
| Income from operations | 10,810 | |
| Other items: | ||
| Rent revenue | 800 | |
| Interest expense | (580) | 220 |
| Income before income taxes | 11,030 | |
| Income tax expense | (3,309) | |
| Net income (A) | 14,339 | |
| Number of shares (B) | 2,000 shares | |
| Earnings per share | $3.86 | |
Table (2)
| Company V | |
| Statement of retained earnings | |
| For the year end December 31, 2016 | |
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Retained earnings on January 1, 2016 | 18,075 |
| Add: Net income | 7,721 |
| 25,796 | |
| Less: Dividend for 2016 | (1,300) |
| Retained earnings on December 31, 2016 | 24,496 |
Table (3)
| Company V | ||
| Balance sheet | ||
| As at December 31, 2016 | ||
| Assets | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Current assets: | ||
| Cash | 1,900 | |
| Accounts receivable | 4,700 | |
| Less: Allowance for doubtful accounts | (300) | 4,400 |
| Inventory | 8,700 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 425 | |
| Office supplies | 230 | |
| Total current assets (C) | 15,655 | |
| Property, plant and equipment: | ||
| Land | 4,100 | |
| Buildings | 38,000 | |
| Less: Accumulated depreciation | (12,600) | 25,400 |
| Equipment | 10,700 | |
| Less: Accumulated depreciation | (3,700) | 7,000 |
| Total property, plant and equipment (D) | 36,500 | |
| Total assets | 52,155 | |
| Liabilities | ||
| Current liabilities: | ||
| Accounts payable | 4,300 | |
| Notes payable (due March 1, 2017) | 1,400 | |
| Interest payable | 580 | |
| Salaries payable | 370 | |
| Unearned rent | 400 | |
| Income tax payable | 3,309 | |
| Total current liabilities | 10,359 | |
| Long-term liabilities: | ||
| Mortgage payable (due January 1, 2018) | 7,300 | |
| Total liabilities | 17,659 | |
| Shareholders' equity | ||
| Contributed capital: | ||
| Common stock | 10,000 | |
| Retained earnings | 24,496 | 34,496 |
| Total shareholder's equity | 52,155 | |
Table (4)
4.
Prepare closing entries of Company V for the current year.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries: The journal entries prepared to close the temporary accounts to Retained Earnings account are referred to as closing entries. The revenue, expense, and dividends accounts are referred to as temporary accounts because the information and figures in these accounts is held temporarily and consequently transferred to permanent account at the end of accounting year.
Prepare closing entries of Company V for the current year as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2016 | Sales revenue | 49,355 | |
| Rent revenue | 800 | ||
| Income summary | 50,155 | ||
| (To close the sales revenue and rent revenue account) | |||
| December 31, 2016 | Income summary | 42,434 | |
| Cost of goods sold | 27,185 | ||
| Salaries expense | 4,450 | ||
| Utilities expense | 2,000 | ||
| Office supplies expense | 540 | ||
| Delivery expense | 1,275 | ||
| Other expense | 980 | ||
| Depreciation expense | 1,700 | ||
| Bad debt expense | 240 | ||
| Interest expense | 580 | ||
| Insurance expense | 175 | ||
| Income tax expense | 3,309 | ||
| (To close all expenses account) | |||
| December 31, 2016 | Income summary | 7,721 | |
| Retained earnings (2) | 7,721 | ||
| (To close the income summary account) | |||
| December 31, 2016 | Retained Earnings | 1,300 | |
| Dividends | 1,300 | ||
| (To close the dividends account.) |
Table (5)
Closing entry for revenue account:
In this closing entry, the sales revenue and rent revenue account is closed by transferring the amount of revenue to the income summary account in order to bring the revenue accounts balance to zero. Hence, debit all revenue account for $50,155, and credit the income summary account for $50,155.
Closing entry for expenses account:
In this closing entry, cost of goods sold, operating expense, and income tax expense are closed by transferring the amount of all expenses to the income summary account in order to bring all the expense accounts balance to zero. Hence, debit the income summary account for $42,434, and credit all the expenses account for $42,434.
Closing entry for income summary account:
In this closing entry, the income summary account is closed by transferring the amount of net income to the retained earnings account in order to bring the income summary balance to zero. Hence, debit the income summary account for $7,721, and credit the retained earnings for $7,721.
Closing entry for dividends account:
The dividends are paid to the shareholders out of the retained earnings. Thus, retained earnings are debited since the earnings are decreased on payment of dividend. Dividends are a component of shareholders’ equity account. It is credited because dividends are transferred to retained earnings account.
Working note (2):
Calculate the value of retained earnings.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting and Analysis
- If a country can give up one unit of future consumption and as result increase its current consumption by 0.94 units, its real rate of interest must be: (a) 1.4% (b) 3.4% (c) 6.4% (d) 9.4%arrow_forwardWhat is the total contribution margin??arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution to this general accounting question with accurate financial calculations.arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
