
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
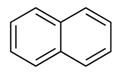
A model of naphthalene is given. The position of multiple bonds in it is to be shown. The number of possible resonance structures for naphthalene is to be stated and their structures are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Hydrogen is monovalent. Carbon is tetravalent and it can form four bonds. The position of double bonds can be identified by looking for carbons in the model having only three bonds. Resonance forms differ only in the placement of their π and nonbonding valence electrons. Neither the position nor the hybridization of any atom changes from one resonance form to another. The shift of electrons to give another resonance structure is represented by a curved arrow.
To determine:
The position of multiple bonds in the given model of naphthalene, C10H8. The number and structures of possible resonance structures for naphthalene are to be drawn
Answer to Problem 20VC
The positions of multiple bonds in naphthalene are shown in the structure given below.
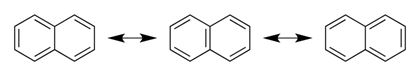
Naphthalene has three resonance forms as shown.
Explanation of Solution
In the model of naphthalene shown all the carbons have formed only three bonds and all the carbons require one more bond to satisfy their fourth valence. This fourth valence of each carbon can be satisfied by placing five double bonds between adjacent carbons as shown.
By shifting the position of double bonds, in total, three resonance structures can be drawn.
The positions of multiple bonds in naphthalene are shown in the structure given below.

Naphthalene has three resonance forms as shown.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Construct a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for BeH2. Sketch the MO pictures (schematic representation) for the HOMO and LUMO of BeH2 [Orbital Potential Energies, H (1s): -13.6 eV; Be (2s): -9.3 eV, Be (2p): -6.0 eV]arrow_forwardIndicate the isomers of the A(H2O)6Cl3 complex. State the type of isomerism they exhibit and explain it briefly.arrow_forwardState the formula of the compound potassium μ-dihydroxydicobaltate (III) tetraoxalate.arrow_forward
- Consider the reaction of the cyclopentanone derivative shown below. i) NaOCH2CH3 CH3CH2OH, 25°C ii) CH3!arrow_forwardWhat constitutes a 'reference material', and why does its utilization play a critical role in the chemical analysis of food products? Provide examples.arrow_forwardExplain what calibration is and why it is essential in relation to food analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forward
- The cobalt mu-hydroxide complex cobaltate(III) of potassium is a dinuclear complex. Correct?arrow_forwardThe cobalt mi-hydroxide complex cobaltate(III) of potassium is a dinuclear complex. Correct?arrow_forward3. Arrange the different acids in Exercise B # 2 from the strongest (1) to the weakest acid (10). 1. 2. (strongest) 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10 10. (weakest)arrow_forward
- Name Section Score Date EXERCISE B pH, pOH, pка, AND PKD CALCULATIONS 1. Complete the following table. Solution [H+] [OH-] PH РОН Nature of Solution A 2 x 10-8 M B 1 x 10-7 M C D 12.3 6.8 2. The following table contains the names, formulas, ka or pka for some common acids. Fill in the blanks in the table. (17 Points) Acid Name Formula Dissociation reaction Ka pka Phosphoric acid H₂PO₁ H3PO4 H++ H₂PO 7.08 x 10-3 Dihydrogen H₂PO H₂PO H+ HPO 6.31 x 10-6 phosphate Hydrogen HPO₁ 12.4 phosphate Carbonic acid H2CO3 Hydrogen HCO 6.35 10.3 carbonate or bicarbonate Acetic acid CH,COOH 4.76 Lactic acid CH₂CHOH- COOH 1.38 x 10 Ammonium NH 5.63 x 10-10 Phenol CH₂OH 1 x 10-10 Protonated form CH3NH3* 3.16 x 10-11 of methylaminearrow_forwardIndicate whether it is true that Co(III) complexes are very stable.arrow_forwardMnO2 acts as an oxidant in the chlorine synthesis reaction.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

