
(a) If the
(b) More experienced workers typically have higher incomes than less experienced workers.
(c) Whatever is the temperature outside, people consume the same number of hot dogs per day.
(d) Consumers buy more frozen yogurt when the price of ice cream goes up.
(e) Research finds no relationship between the number of diet books purchased and the number of pounds lost by the average dieter.
(f) Regardless of its price, people buy the same quantity of salt.
Concept Introduction
The slope of a line:
The slope of a line represents the change in the value of y-axis per unit value on the x-axis. The slope of a line is a measure of the steepness of the line.
Explanation of Solution
(a) If the price of movies increases, fewer consumers go to see movies.
- Panel (a) matches the given statements because as the price of the movies will increase, the number of fans going to movies will decrease.
- The variable ‘price of movies’ shall appear on the vertical axis and the variable ‘number of fans’ will appear on the horizontal axis.
- As the variable on the vertical axis increases, the variable on the horizontal axis will decrease. Thus, there is a negative relationship between the two variables indicating the slope is negative. The curve is Concave or decreasing.
Conclusion:
Thus, the slope is negative.
(b) More experienced workers typically have higher incomes than less experienced workers.
- Panel (c) matches the given statements because as the experience of a worker increases, the income will also increase.
- The variable ‘experience of workers’ shall appear on the vertical axis and the variable ‘income of workers’ will appear on the horizontal axis.
- As the variable on the vertical axis increases, the variable on the horizontal axis will also increase. Thus, there is a positive relationship between the two variables indicating that the slope is positive. It is a convex curve or increasing.
Conclusion:
Thus, the slope is positive.
(c) Whatever is the temperature outside, people consume the same number of hot dogs per day.
- Panel (d) matches the given statements because whatever is the outside temperature, the hot dog consumption remains the same.
- The variable ‘temperature’ shall appear on the horizontal axis and the variable ‘consumption of hot dogs’ shall appear on the vertical axis.
- Even if the variable on the horizontal axis increases, the variable on the vertical axis will remain the same. Thus, there is no relationship between the two variables indicating that the slope is zero.
Conclusion:
Thus, the slope is zero.
(d) Consumers buy more frozen yogurt when the price of ice cream goes up.
- Panel (c) matches the given statement because as the price of ice cream increases, the sale of frozen yogurt also increases.
- The variable ‘price of ice cream’ shall appear on the vertical axis and the variable ‘sale of frozen yogurt’ will appear on the horizontal axis.
- As the variable on the vertical axis increases, the variable on the horizontal axis will also increase. Thus, there is a positive relationship between the two variables indicating that the slope is positive.
Conclusion:
Thus, the slope is positive.
(e) Research finds no relationship between the number of diet books purchased and the number of pounds lost by the average dieter.
- Panel (d) matches the given statements because whatever is the number of diet books purchased, the number of pounds lost by the average dieter does not change.
- The variable ‘number of diet books purchased’ shall appear on the horizontal axis and the variable ‘number of pounds lost by average dieter’ shall appear on the vertical axis.
- Even if the variable on the horizontal axis increases, the variable on the vertical axis will remain unchanged. Thus, there is no relationship between the two variables indicating that the slope is zero.
Conclusion:
Thus, the slope is zero.
(f) Regardless of its price, people buy the same quantity of salt.
- Panel (b) matches the given statements because whatever is the price of salt, the quantity of salt purchased remains the same.
- The variable ‘quantity of salt’ shall appear on the horizontal axis and the variable ‘price of salt’ shall appear on the vertical axis.
- Even if the variable on the vertical axis increases, the variable on the horizontal axis will remain unchanged. Thus, the slope shall be:
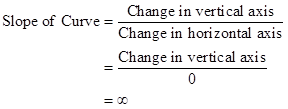
Conclusion:
Thus, the slope is infinity.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2A Solutions
Essentials of Economics
- Critically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forwardCritically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forwardOutline the nine (9) consumer rights as specified in the Consumer Rights Act in South Africa.arrow_forward
- In what ways could you show the attractiveness of Philippines in the form of videos/campaigns to foreign investors? Cite 10 examples.arrow_forwardExplain the following terms and provide an example for each term: • Corruption • Fraud • Briberyarrow_forwardIn what ways could you show the attractiveness of a country in the form of videos/campaigns?arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





