
Concept explainers
Determine the angle θ between the force and the line AO.
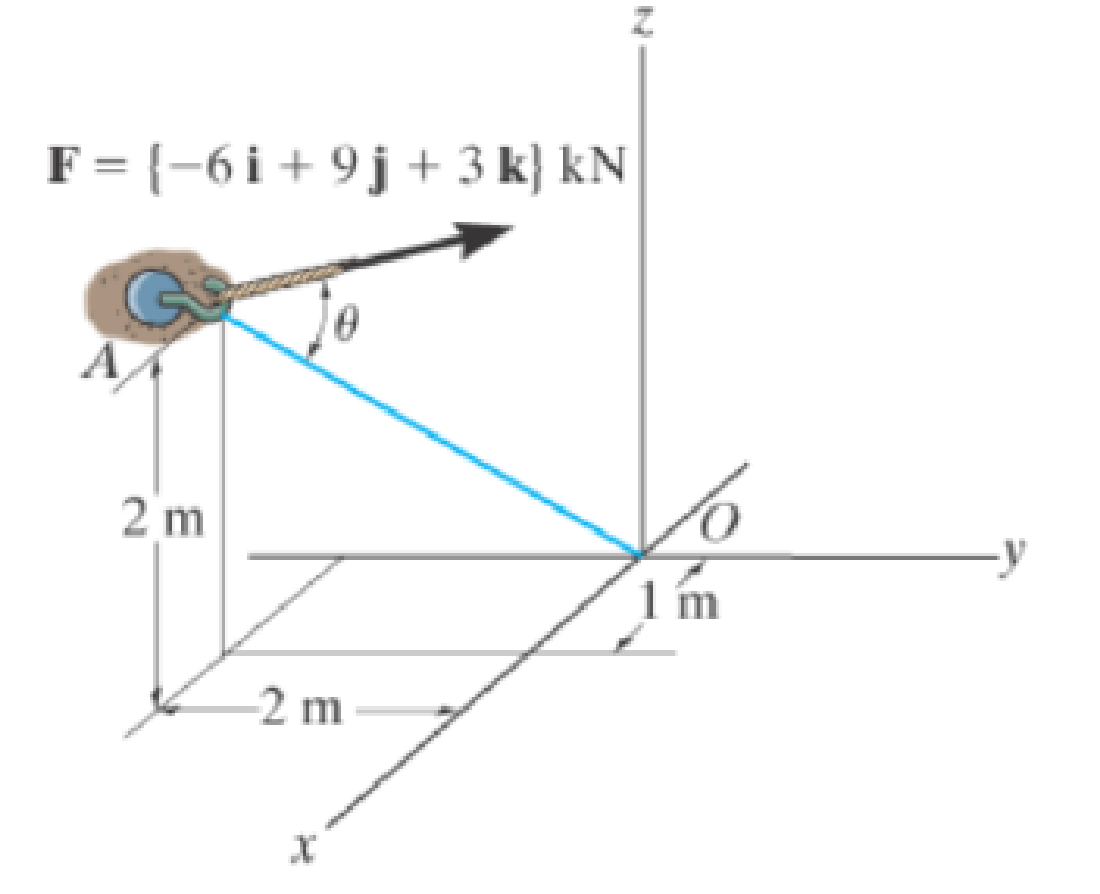
Prob. F2-25
Answer to Problem 25FP
The angle
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The force in the form of Cartesian vector,
Explanation:
Draw the free body diagram of forces F and line AO as in Figure (1).
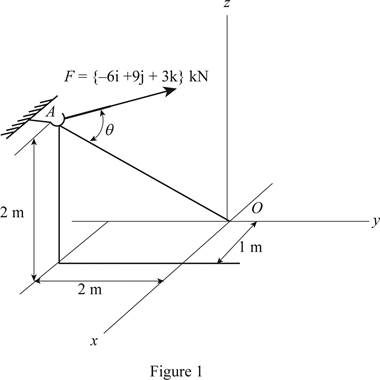
Let us establish a position vector for points A and O. The coordinate points
Express the position vector r in the direction of AO using Figure (1).
Here, the coordinates of A and O are
Express the magnitude of the direction of AO.
Express the force in Cartesian vector form.
Express the magnitude of the direction of F.
Determine the unit vector of AO.
Apply the dot product to find the angle between F and line AO.
Conclusion:
Substitute 1 m for
Substitute 1 m for
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the angle
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Modern Database Management
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
- Please find the torsional yield strength, the yield strength, the spring index, and the mean diameter. Use: E = 28.6 Mpsi, G = 11.5 Mpsi, A = 140 kpsi·in, m = 0.190, and relative cost= 1.arrow_forwardA viscoelastic column is made of a material with a creep compliance of D(t)= 0.75+0.5log10t+0.18(log10t)^2 GPA^-1 for t in s. If a constant compressive stress of σ0 = –100 MPa is applied at t = 0, how long will it take (= t1/2) for the height of the column to decrease to ½ its original value? Note: You will obtain multiple answers for this problem! One makes sense physically and one does not.arrow_forwardA group of 23 power transistors, dissipating 2 W each, are to be cooled by attaching them to a black-anodized square aluminum plate and mounting the plate on the wall of a room at 30°C. The emissivity of the transistor and the plate surfaces is 0.9. Assuming the heat transfer from the back side of the plate to be negligible and the temperature of the surrounding surfaces to be the same as the air temperature of the room, determine the length of the square plate if the average surface temperature of the plate is not to exceed 50°C. Start the iteration process with an initial guess of the size of the plate as 43 cm. The properties of air at 1 atm and the film temperature of (Ts + T)/2 = (50 + 30)/2 = 40°C are k = 0.02662 W/m·°C, ν = 1.702 × 10–5 m2 /s, Pr = 0.7255, and β = 0.003195 K–1. Multiple Choice 0.473 m 0.284 m 0.513 m 0.671 marrow_forward
- A 40-cm-diameter, 127-cm-high cylindrical hot water tank is located in the bathroom of a house maintained at 20°C. The surface temperature of the tank is measured to be 44°C and its emissivity is 0.4. Taking the surrounding surface temperature to be also 20°C, determine the rate of heat loss from all surfaces of the tank by natural convection and radiation. The properties of air at 32°C are k=0.02603 W/m-K, v=1.627 x 10-5 m²/s, Pr = 0.7276, and ẞ = 0.003279 K-1 The rate of heat loss from all surfaces of the tank by natural convection is The rate of heat loss from all surfaces of the tank by radiation is W. W.arrow_forwardA 2.5-m-long thin vertical plate is subjected to uniform heat flux on one side, while the other side is exposed to cool air at 5°C. The plate surface has an emissivity of 0.73, and its midpoint temperature is 55°C. Determine the heat flux subjected on the plate surface. Uniform heat flux -Plate, € = 0.73 Cool air 5°C 7 TSUIT Given: The properties of water at Tf,c= 30°C. k=0.02588 W/m.K, v=1.608 x 10-5 m²/s Pr = 0.7282 The heat flux subjected on the plate surface is W/m²arrow_forwardHot water is flowing at an average velocity of 5.82 ft/s through a cast iron pipe (k=30 Btu/h-ft-°F) whose inner and outer diameters are 1.0 in and 1.2 in, respectively. The pipe passes through a 50-ft-long section of a basement whose temperature is 60°F. The emissivity of the outer surface of the pipe is 0.5, and the walls of the basement are also at about 60°F. If the inlet temperature of the water is 150°F and the heat transfer coefficient on the inner surface of the pipe is 30 Btu/h-ft².°F, determine the temperature drop of water as it passes through the basement. Evaluate air properties at a film temperature of 105°C and 1 atm pressure. The properties of air at 1 atm and the film temperature of (Ts+ T∞)/2 = (150+60)/2 = 105°F are k=0.01541 Btu/h-ft-°F. v=0.1838 × 10-3 ft2/s, Pr = 0.7253, and ẞ = 0.00177R-1arrow_forward
- hand-written solutions only, please. correct answers upvoted!arrow_forwardhand-written solutions only, please. correct answers upvoted!arrow_forward! Required information Consider a flat-plate solar collector placed horizontally on the flat roof of a house. The collector is 1.3 m wide and 2.8 m long, and the average temperature of the exposed surface of the collector is 42°C. The properties of air at 1 atm and the film temperature are k=0.02551 W/m-°C, v = 1.562 × 10-5 m²/s, Pr = 0.7286, and ẞ= 0.003356 K-1 Determine the rate of heat loss from the collector by natural convection during a calm day when the ambient air temperature is 8°C. The rate of heat loss from the collector by natural convection is W.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





