
Mastering Physics with Pearson eText -- Standalone Access Card -- for University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133978216
Author: Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 28, Problem 28.4E
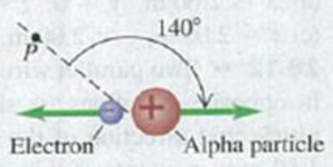
An alpha particle (charge +2e) and an electron move in opposite directions from the same point, each with the speed of 2.50 × 105 m/s (Fig. E28.4). Find the magnitude and direction of the total magnetic field these charges produce at point P, which is 8.65 nm from each charge.
Figure E28.4
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Lab 8 Part 3 PHET Wave Interface simulation.
I am having trouble with this part of the lab.
Mick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?
Hi,
I have canceled, why did you charge me again?
Chapter 28 Solutions
Mastering Physics with Pearson eText -- Standalone Access Card -- for University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
Ch. 28.1 - (a) If two protons are traveling parallel to each...Ch. 28.2 - An infinitesimal current element located at the...Ch. 28.3 - The accompanying figure shows a circuit that lies...Ch. 28.4 - A solenoid is a wire wound into a helical coil....Ch. 28.5 - Prob. 28.5TYUCh. 28.6 - The accompanying figure shows magnetic field lines...Ch. 28.7 - Prob. 28.7TYUCh. 28.8 - Which of the following materials are attracted to...Ch. 28 - A topic of current interest in physics research is...Ch. 28 - Streams of charged particles emitted from the sun...
Ch. 28 - The text discussed the magnetic field of an...Ch. 28 - Prob. 28.4DQCh. 28 - Pairs of conductors carrying current into or out...Ch. 28 - Suppose you have three long, parallel wires...Ch. 28 - In deriving the force on one of the long,...Ch. 28 - Two concentric, coplanar, circular loops of wire...Ch. 28 - A current was sent through a helical coil spring....Ch. 28 - Prob. 28.10DQCh. 28 - Prob. 28.11DQCh. 28 - Two very long, parallel wires carry equal currents...Ch. 28 - In the circuit shown in Fig. Q28.13, when switch S...Ch. 28 - A metal ring carries a current that causes a...Ch. 28 - Prob. 28.15DQCh. 28 - Prob. 28.16DQCh. 28 - If a magnet is suspended over a container of...Ch. 28 - Prob. 28.18DQCh. 28 - Prob. 28.19DQCh. 28 - A cylinder of iron is placed so that it is free to...Ch. 28 - Prob. 28.1ECh. 28 - Prob. 28.2ECh. 28 - An electron moves at 0.100c as shown in Fig....Ch. 28 - An alpha particle (charge +2e) and an electron...Ch. 28 - A 4.80-C charge is moving at a constant speed of...Ch. 28 - Positive point charges q = +8.00 C and q' = +3.00...Ch. 28 - A negative charge q = 3.60 106 C is located at...Ch. 28 - An electron and a proton are each moving at 735...Ch. 28 - A straight wire carries a 10.0-A current (Fig....Ch. 28 - A short current element dl = (0.500 mm) carries a...Ch. 28 - A long, straight wire lies along the z-axis and...Ch. 28 - Two parallel wires are 5.00 cm apart and carry...Ch. 28 - Prob. 28.13ECh. 28 - A square wire loop 10.0 cm on each side carries a...Ch. 28 - The Magnetic Field from a Lightning Bolt....Ch. 28 - A very long, straight horizontal wire carries a...Ch. 28 - Prob. 28.17ECh. 28 - BIO Bacteria Navigation. Certain bacteria (such as...Ch. 28 - (a) How large a current would a very long,...Ch. 28 - Two long, straight wires, one above the other, are...Ch. 28 - A long, straight wire lies along the y-axis and...Ch. 28 - BIO Transmission Lines and Health. Currents in dc...Ch. 28 - Two long, straight, parallel wires, 10.0 cm apart,...Ch. 28 - A rectangular loop with dimensions 4.20 cm by 9.50...Ch. 28 - Four, long, parallel power lines each carry 100-A...Ch. 28 - Four very long, current-carrying wires in the same...Ch. 28 - Two very long insulated wires perpendicular to...Ch. 28 - Three very long parallel wires each carry current...Ch. 28 - Two long, parallel wires arc separated by a...Ch. 28 - Prob. 28.30ECh. 28 - Lamp Cord Wires. The wires in a household lamp...Ch. 28 - Prob. 28.32ECh. 28 - BIO Currents in the Brain. The magnetic field...Ch. 28 - Calculate the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 28 - Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic field at...Ch. 28 - A closely wound, circular coil with radius 2.40 cm...Ch. 28 - A single circular current loop 10.0 cm in diameter...Ch. 28 - A closely wound coil has a radius of 6.00 cm and...Ch. 28 - Two concentric circular loops of wire lie on a...Ch. 28 - Figure E28.40 shows, in cross section, several...Ch. 28 - A closed curve encircles several conductors. The...Ch. 28 - As a new electrical technician, you are designing...Ch. 28 - Prob. 28.43ECh. 28 - Prob. 28.44ECh. 28 - A solenoid that is 35 cm long and contains 450...Ch. 28 - A 15.0-cm-long solenoid with radius 0.750 cm is...Ch. 28 - A solenoid is designed to produce a magnetic field...Ch. 28 - A toroidal solenoid has an inner radius of 12.0 cm...Ch. 28 - A magnetic field of 37.2 T has been achieved at...Ch. 28 - An ideal toroidal solenoid (see Example 28.10) has...Ch. 28 - A wooden ring whose mean diameter is 14.0 cm is...Ch. 28 - A toroidal solenoid with 400 turns of wire and a...Ch. 28 - A long solenoid with 60 turns of wire per...Ch. 28 - The current in the windings of a toroidal solenoid...Ch. 28 - A pair of point charges, q = +8.00 C and q' = 5.00...Ch. 28 - At a particular instant, charge q1 = +4.80 106C...Ch. 28 - Two long, parallel transmission lines, 40.0 cm...Ch. 28 - A long, straight wire carries a current of 8.60 A....Ch. 28 - Prob. 28.59PCh. 28 - Prob. 28.60PCh. 28 - An electric bus operates by drawing direct current...Ch. 28 - Figure P28.62 shows an end view of two long,...Ch. 28 - Prob. 28.63PCh. 28 - The long, straight wire AB shown in Fig. P28.64...Ch. 28 - CP Two long, parallel wires hang by 4.00-cm-long...Ch. 28 - The wire semicircles shown in Fig. P28.66 have...Ch. 28 - CALC Helmholtz Coils. Figure P28.67 is a sectional...Ch. 28 - Prob. 28.68PCh. 28 - CALC A long, straight wire with a circular cross...Ch. 28 - CALC The wire shown in Fig. P28.70 is infinitely...Ch. 28 - Prob. 28.71PCh. 28 - Prob. 28.72PCh. 28 - An Infinite Current Sheet. Long, straight...Ch. 28 - Long, straight conductors with square cross...Ch. 28 - A long, straight, solid cylinder, oriented with...Ch. 28 - Prob. 28.76PCh. 28 - DATA You use a teslameter (a Hall-effect device)...Ch. 28 - DATA A pair of long, rigid metal rods, each of...Ch. 28 - CP Two long, straight conducting wires with linear...Ch. 28 - Prob. 28.80CPCh. 28 - BIO STUDYING MAGNETIC BACTERIA. Some types of...Ch. 28 - Prob. 28.82PPCh. 28 - The solenoid is removed from the enclosure and...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. The event that triggered the change in...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
1. Which is a function of the skeletal system? (a) support, (b) hematopoietic site, (c) storage, (d) providing ...
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
53. This reaction was monitored as a function of time:
A plot of In[A] versus time yields a straight ...
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
WRITE ABOUT A THEME: INTERACTIONS In a short essay (100-150 words), identify the factor or factors in Figure 53...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
16. Monica stands at the edge of a circular platform that is slowly rotating on a frictionless axle. She then w...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
How do food chains and food webs differ? Which is the more accurate representation of feeding relationships in ...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You are standing a distance x = 1.75 m away from this mirror. The object you are looking at is y = 0.29 m from the mirror. The angle of incidence is θ = 30°. What is the exact distance from you to the image?arrow_forwardFor each of the actions depicted below, a magnet and/or metal loop moves with velocity v→ (v→ is constant and has the same magnitude in all parts). Determine whether a current is induced in the metal loop. If so, indicate the direction of the current in the loop, either clockwise or counterclockwise when seen from the right of the loop. The axis of the magnet is lined up with the center of the loop. For the action depicted in (Figure 5), indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop (clockwise, counterclockwise or zero, when seen from the right of the loop). I know that the current is clockwise, I just dont understand why. Please fully explain why it's clockwise, Thank youarrow_forwardA planar double pendulum consists of two point masses \[m_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}, \qquad m_2 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}\]connected by massless, rigid rods of lengths \[L_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{m}, \qquad L_2 = 1.20~\mathrm{m}.\]The upper rod is hinged to a fixed pivot; gravity acts vertically downward with\[g = 9.81~\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}.\]Define the generalized coordinates \(\theta_1,\theta_2\) as the angles each rod makes with thedownward vertical (positive anticlockwise, measured in radians unless stated otherwise).At \(t=0\) the system is released from rest with \[\theta_1(0)=120^{\circ}, \qquad\theta_2(0)=-10^{\circ}, \qquad\dot{\theta}_1(0)=\dot{\theta}_2(0)=0 .\]Using the exact nonlinear equations of motion (no small-angle or planar-pendulumapproximations) and assuming the rods never stretch or slip, determine the angle\(\theta_2\) at the instant\[t = 10.0~\mathrm{s}.\]Give the result in degrees, in the interval \((-180^{\circ},180^{\circ}]\).arrow_forward
- What are the expected readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the circuit in the figure below? (R = 5.60 Ω, ΔV = 6.30 V) ammeter I =arrow_forwardsimple diagram to illustrate the setup for each law- coulombs law and biot savart lawarrow_forwardA circular coil with 100 turns and a radius of 0.05 m is placed in a magnetic field that changes at auniform rate from 0.2 T to 0.8 T in 0.1 seconds. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field.• Calculate the induced electric field in the coil.• Calculate the current density in the coil given its conductivity σ.arrow_forward
- An L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forwardA long, straight wire carries a current of 10 A along what we’ll define to the be x-axis. A square loopin the x-y plane with side length 0.1 m is placed near the wire such that its closest side is parallel tothe wire and 0.05 m away.• Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop using Ampere’s law.arrow_forwardDescribe the motion of a charged particle entering a uniform magnetic field at an angle to the fieldlines. Include a diagram showing the velocity vector, magnetic field lines, and the path of the particle.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Magnets and Magnetic Fields; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IgtIdttfGVw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY