
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
In conjugated triene,
Concept introduction:
The molecular orbital is a combination of two atomic orbitals. It is used to represent the regions in a molecule where the electron is likely to be present in an orbital. It represents the wave-like nature of an electron in a molecule. It may be symmetric or antisymmetric. It may be bonding, antibonding or non-bonding. It may be HOMO or LUMO.
Answer to Problem 28.2P
In
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
The electron configuration of carbon atom is
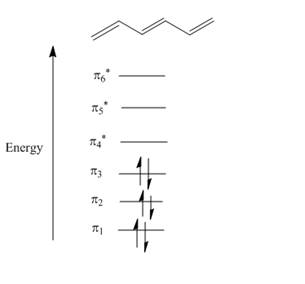
Figure 1
The atomic p orbital of carbon atom overlapped together to form molecular orbital. A total of six molecular orbitals are formed due to six carbon atomic orbital overlapping in
(b)
Interpretation:
Each molecular orbital is to be classified as symmetric and antisymmetric.
Concept introduction:
The molecular orbital is a combination of two atomic orbitals. It is used to represent the regions in a molecule where the electron is likely to be present in an orbital. It represents the wave-like nature of an electron in a molecule. It may be symmetric or antisymmetric. It may be bonding, antibonding or non-bonding. It may be HOMO or LUMO.
Answer to Problem 28.2P
The molecular orbitals
Explanation of Solution
In molecular orbital theory, the MO is said to be symmetric or anti-symmetric is depend on the relative phase of the two terminal carbons. In symmetric MO, the peaks reflect across the reference plane into the peaks and troughs reflect into troughs. On the other hand, in antisymmetric MO, the peaks reflect into troughs and vice versa. According to the general principle, the even number molecular orbitals are antisymmetric and odd number molecular orbitals are symmetric. Therefore, the molecular orbitals
The odd number of molecular orbitals is symmetric molecular orbitals that are
(c)
Interpretation:
Bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals are to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The molecular orbital is a combination of two atomic orbitals. It is used to represent the regions in a molecule where the electron is likely to be present in an orbital. It represents the wave-like nature of an electron in a molecule. It may be symmetric or antisymmetric. It may be bonding, antibonding or non-bonding. It may be HOMO or LUMO.
Answer to Problem 28.2P
The molecular orbital
Explanation of Solution
In
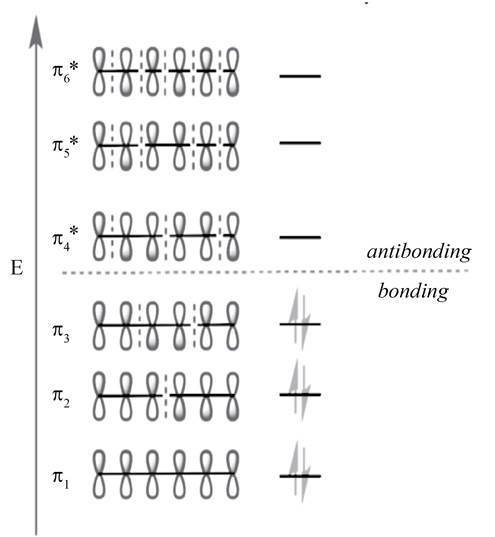
Figure 2
The molecular orbital with lower energy are bonding MO
(d)
Interpretation:
Among the molecular orbitals, the frontier molecular orbital is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The molecular orbital is a combination of two atomic orbitals. It is used to represent the regions in a molecule where the electron is likely to be present in an orbital. It represents the wave-like nature of an electron in a molecule. It may be symmetric or antisymmetric. It may be bonding, antibonding or non-bonding. It may be HOMO or LUMO.
Answer to Problem 28.2P
The molecular orbital
Explanation of Solution
The highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) is known as frontier molecular orbitals. In
The molecular orbital
(e)
Interpretation:
Whether the phase at terminal carbons in HOMO orbitals is the same or different is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The molecular orbital is a combination of two atomic orbitals. It is used to represent the regions in a molecule where the electron is likely to be present in an orbital. It represents the wave-like nature of an electron in a molecule. It may be symmetric or antisymmetric. It may be bonding, antibonding or non-bonding. It may be HOMO or LUMO.
Answer to Problem 28.2P
The HOMO orbital that is
Explanation of Solution
According to the general principle, the even number molecular orbitals are antisymmetric or its phase terminal carbons are different and odd number molecular orbitals are symmetric or its phase terminal carbons are same. The HOMO orbital is
The HOMO orbital is
(f)
Interpretation:
Whether the phase at terminal carbons in LUMO orbitals is the same or different is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The molecular orbital is a combination of two atomic orbitals. It is used to represent the regions in a molecule where the electron is likely to be present in an orbital. It represents the wave-like nature of an electron in a molecule. It may be symmetric or antisymmetric. It may be bonding, antibonding or non-bonding. It may be HOMO or LUMO.
Answer to Problem 28.2P
The LUMO orbital that is
Explanation of Solution
According to the general principle, the even number molecular orbitals are antisymmetric or its phase terminal carbons are different and odd number molecular orbitals are symmetric or its phase terminal carbons are same. The LUMO orbital is
The LUMO orbital is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 28 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Ebook And Single-course Homework Access
- Polymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. Draw three repeat units (trimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. Assume there are hydrogen atoms there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the trimer. Ignore inorganic byproducts please.arrow_forwardi need help with the folarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP NOW! URGENT!arrow_forward
- a. Determine whether each of the Followery Molecules is in the R- On the y- Configuration 1-01"/ 1-6-4 Br 4 I el Br b. Draw The Fisher projection For all the Meso compounds that can exist FOR The Following molenlearrow_forward1- Refer to the monosaccharides below to answer each of the following question(s): CH₂OH CHO CH₂OH CH₂OH 0 H- OH 0 0 HO- H H- -OH HO H HO H H OH HO- H CH₂OH H. OH HO H HO- H CH₂OH CH₂OH CH3 a. Sorbose b. Rhamnose c. Erythrulose d. Xylulose Classify each sugar by type; for example, glucose is an aldohexose. a. Xylulose is .. b. Erythrulose is . c. Sorbose is .. d. Rhamnose is .. 2- Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s). CHO H OH CH₂OH CH₂OH HO- H HO HO + H. -OH HO OH HO. H OH OH H -OH H OH CH₂OH Q Z a. Refer to Exhibit 25-11. Place a triangle around the anomeric carbon in compound Q. Compound Z is: b. 1. the D-anomer. 2. the a-anomer. 3. the ẞ-anomer. 4. the L-anomer. c. Which anomer is the LEAST stable? d. Q and Z are cyclic examples of: a. acetals b. hemiacetals c. alditols d. hemialditolsarrow_forwardi need help identifying the four carbon oxygen bonds in the following:arrow_forward
- Imagine each of the molecules shown below was found in an aqueous solution. Can you tell whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral? molecule HO H3N + The solution is... X O acidic OH O basic H3N-CH-C-O O neutral ○ (unknown) O acidic ○ basic CH2 CH 3-S-CH2 O neutral ○ (unknown) H3N O OH O acidic O basic Oneutral O (unknown) 0 H3N-CH-C-O CH3 CH CH3 O acidic O basic O neutral ○ (unknown) ? olo Ar BHarrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughs need other product (product in picture is wrong dont submit the same thing)arrow_forwardHow to solve this!arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning

