
Concept explainers
Explain the process how 230/460-volt motor is used as a part winding motor.
Explanation of Solution
Part winding motor:
The part winding motor has two sets of identical windings which are connected in parallel with each other. The two identical windings are energized in a sequence to produce the reduced starting current and the reduced starting torque.
Dual voltage motor:
The dual voltage motor has two sets of windings (not identical) which are connected either in parallel or in series. When the 230/460-volt motor operates with the part winding starter, it is intended to connect the two sets of windings in parallel (voltage ratio is 1:2). An each set of windings is connected either in Y or delta connection.
The dual voltage motor can operate with different power supply voltages. When the dual voltage motor’s two sets of windings are connected in parallel, the motor can operate with low voltage connection. When the windings are connected in series, the motor can operate with high voltage.
230/460-volt motor as a part winding motor:
230/460-volt dual voltage motor can be used as a part winding motor with low voltage connection. At the starting of the motor, the low voltage supply is connected to the one set of winding. As soon as the motor reaches to the normal speed, apply the power to the other set of winding (the other winding from the parallel windings) in the running conditions for the normal running operation of the motor. The motor runs with reduced starting current and the reduced starting torque after both the windings are energized in a sequence.
The part winding starter is a reduced voltage starter and used in the starting process of the 230/460-volt part winding motor.
Refer to Figure 28.3 in textbook where the 230/460-volt motor can be used as a part winding motor with low voltage connection. One set of winding terminals
Figure 1 shows the low voltage connection of a part winding motor.
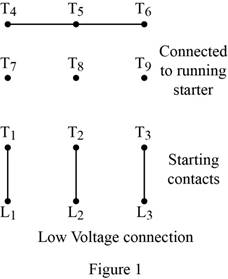
Conclusion:
Thus, the 230/460-volt motor can be used as a part winding motor.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 28 Solutions
Electric Motor Control
- Q5B. Find the type of the controller in the following figures and use real values to find the transfer function of three of them[ Hint Pi,Pd and Lead,lag are found so put the controller with its corresponding compensator]. R₁ R₂ Rz HE C2 RA HE R₁ R2 RA とarrow_forwardQ1// Sketch the root locus for the unity feedback system. Where G(s)=)= K S3+252 +25 and find the following a. Sketch the asymptotes b. The exact point and gain where the locus crosses the jo-axis c. The breakaway point on the real axis d. The range of K within which the system is stable e. Angles of departure and arrival.arrow_forwardDetermine X(w) for the given function shown in Figure (1) by applying the differentiation property of the Fourier Transform. Figure (1) -1 x(t)arrow_forward
- Can you solve a question with a drawing Determine X(w) for the given function shown in Figure (1) by applying the differentiation property of the Fourier Transform. Figure (1) -1 x(t)arrow_forwardAn inductor has a current flow of 3 A when connected to a 240 V, 60 Hz power line. The inductor has a wire resistance of 15 Find the Q of the inductorarrow_forwardصورة من s94850121arrow_forward
- The joint density function of two continuous random variables X and Yis: p(x, y) = {Keós (x + y) Find (i) the constant K 0 2 0arrow_forwardShow all the steps please, Solve for the current through R2 if E2 is replaced by a current source of 10mA using superposition theorem. R5=470Ω R2=1000Ω R6=820Ωarrow_forwardPlease solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forwardPlease solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam today, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forwardIf C is the circle |z|=4 evaluate f f (z)dz for each of the following functions using residue. 1 f(z) = z(z²+6z+4)arrow_forwardIf C is the circle |z|=4 evaluate ff(z)dz for each of the following functions using residue. f(z) z(z²+6z+4)arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios

 Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Electricity for Refrigeration, Heating, and Air C...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337399128Author:Russell E. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Electricity for Refrigeration, Heating, and Air C...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337399128Author:Russell E. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning


