
To describe:
The normal anatomy and physiology of the renal system.
Introduction:
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
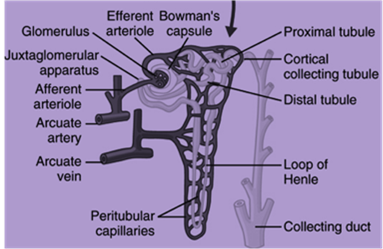
The normal anatomy and physiology of the renal system are described below:
The principal system that is involved in the excretion of waste is the urinary system. From the blood, the metabolic waste is removed by the kidney. The kidney plays an important role in regulating blood pressure and blood volume. The back of the abdominal cavity is the place where the kidney (bean shaped) is located. Vertebrae T12 to L3 is the level where the kidney lies. The left kidney is located slightly higher than the right kidney (lower). This is due to the large right lobe of the liver that occupies the space above the right kidney. The middle part of the left kidney is nearly crossed by Rib 12. The kidneys are retroperitoneal, along with the renal artery, vein, ureters, adrenal glands, and the urinary bladder.
The structural unit of the kidney is referred to as nephron. One million nephrons are present in each kidney. The filtering process takes in the glomerulus. The glomerulus is a bunch of capillaries that is encapsulated by the glomerular capsule. The time taken for filtering the blood is called as glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
The glomerular filtration rate is controlled by the afferent arterioles (approaching the glomerulus) and the efferent arterioles (exiting the glomerulus). The proximal tubule or proximal convoluted tubule plays an important role in returning 60% - 70% of water and sodium from the filtered fluid into the blood. The nephron is surrounded by the blood vessels that permit the reabsorbed substances directly to reach the blood stream. This process (one of the active transport) needs the adenosine triphosphate molecule as an energy source. The active transportation of potassium and sodium ions returns back into the bloodstream, which is known as passive reabsorption (water and chloride). The water and chloride ions follow (passively) the potassium and sodium ions by means of osmosis. The loop of Henle (ascending) is the area where 20% - 25% of sodium ion is reabsorbed back into the blood. In the loop of Henle, sodium is passively reabsorbed, and chloride is actively reabsorbed.
In the distal convoluted tubule or distal tubule, the remaining (5%-10%) sodium is reabsorbed. The sodium ion is actively filtered in the distal tubule. This process is controlled by aldosterone. The final pathway (common) for the remains that begin in the glomerulus is called as collecting duct. The antidiuretic hormone plays an important role to raise water absorption (into the blood). Hence, excess water is prevented from being excreted in the urine.
The glomerular filtration rate’s measurement is used in the detection of some kidney diseases. Yet, the quantity of NaCl could not be assumed by the glomerular filtration rate; there are two causes to explain this reason. (1) The glomerulus is not able to filter the NaCl in urine that is produced by the renal tubule. (2) The tubule reabsorbs all the NaCl that the glomerulus has filtered.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 28 Solutions
Pharmacology and the Nursing Process, 8e
- true or false dark skinned infants should be screened for vitamin D levelsarrow_forwardtrue or false any practice employee is authorized to and should communicate collection guidelines with practice?arrow_forwardrtrue or false equesting a listing of specific creditreferences during patient intake os an acceptable business practice?arrow_forward
- give an overview on the respiratory assessmentarrow_forwardexplain an abdominal exam?arrow_forwardDiscuss β -Lactam antibiotics under the following subheadings Classifications of penicillins Classification of Cephalosporins General Mechanism of Actions Clinical Indications of penicillins and cephalosporins Adverse effects of β-lactamsarrow_forward
- a. Define neoplasm b. Differentiate between benign and malignant tumours c. Describe the molecular basis of cancerarrow_forwarddifferentiate the extra heart sounds S3,S4, murmurs and gallopsarrow_forward• Define shock and list types of shock • Discuss pathogenesis of septic shock. • Enumerate the stages of shock. • Define oedema and describe the pathophysiologic mechanisms of oedema with examples.arrow_forward
- Discuss Hypertension under the following headings: Definition Diagnosis Non-pharmacological intervention Drugs Classification Management of a Hypertensive emergencyarrow_forwardExplain how the answer could be 2 or 1.8 WITHOUT changing the questionarrow_forwardoverview of the neurological system, cranial nerves and what part of the body it innervatesarrow_forward
 Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC.
Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC. Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders
Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer,
Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer, Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science
Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders
Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning





