
Interpretation:
The position of the three hydroxyl groups present in cholic acid are to be located and whether they are axial or equatorial are to be identified. Further whether cholic acid is a A-B trans or a A-B cis steroid is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
If the two cyclohexane rings are fused in trans manner the two hydrogens at the ring junction will be diaxial. If the ring fusion is cis, then hydrogen at one ring junction is axial while that in the other junction is equatorial.
Among the disubstituted cyclohexanes, 1,2-cis, 1,3-trans and 1,4-cis substituents will have axial and equatorial arrangements. 1,2-trans, 1,3-cis and 1,4-trans substituents will have either diequatorial or diaxial arrangements.
To locate:
The position of the three hydroxyl groups present in cholic acid.
To identify:
Whether they are axial or equatorial.
To state:
Whether cholic acid is A-B trans or a A-B cis steroid.
Answer to Problem 11VC
The three hydroxyl groups are on C3, C6 and C12. The hydroxyl group on C3 is equatorial while those at C6 and C12 are axial. Cholic acid is A-B cis steroid.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of cholic acid represented by the model is
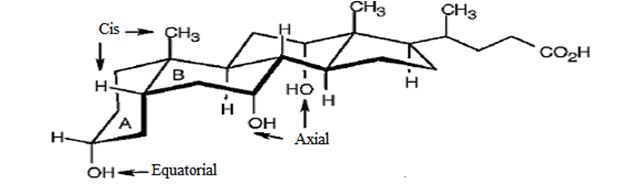
Since lithocholic acid has the rings A and B fused in cis manner, the methyl group on C9 has to be equatorial and the H C10 has to be axial for ring A. In lithocholic acid, the -OH on C3 (in ring A), is in 1,4 trans relationship with the methyl on C9. Hence the –OH on C3 occupies the equatorial position.
For ring B the methyl group on C9 is axial and the H C10 is equatorial. The OH group on C6 has 1,4 trans relationship with methyl on C9 it has to occupy the axial position.
The rings C and D are trans fused. The methyl on C13 and H on C14 has diaxial arrangement. Since the OH group on C12 has 1,2 trans relationship with methyl on C13 it has to occupy the axial position.
The H on C7 is axial for ring C. Since the OH group on C12 is three carbons away from C7 it has to occupy the axial position.
The three hydroxyl groups are on C3, C6 and C12. The hydroxyl group on C3 is equatorial while those at C6 and C12 are axial. Cholic acid is A-B cis steroid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 27 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - With Access (Custom)
- Consider the reaction of the cyclopentanone derivative shown below. i) NaOCH2CH3 CH3CH2OH, 25°C ii) CH3!arrow_forwardWhat constitutes a 'reference material', and why does its utilization play a critical role in the chemical analysis of food products? Provide examples.arrow_forwardExplain what calibration is and why it is essential in relation to food analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forward
- The cobalt mu-hydroxide complex cobaltate(III) of potassium is a dinuclear complex. Correct?arrow_forwardThe cobalt mi-hydroxide complex cobaltate(III) of potassium is a dinuclear complex. Correct?arrow_forward3. Arrange the different acids in Exercise B # 2 from the strongest (1) to the weakest acid (10). 1. 2. (strongest) 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10 10. (weakest)arrow_forward
- Name Section Score Date EXERCISE B pH, pOH, pка, AND PKD CALCULATIONS 1. Complete the following table. Solution [H+] [OH-] PH РОН Nature of Solution A 2 x 10-8 M B 1 x 10-7 M C D 12.3 6.8 2. The following table contains the names, formulas, ka or pka for some common acids. Fill in the blanks in the table. (17 Points) Acid Name Formula Dissociation reaction Ka pka Phosphoric acid H₂PO₁ H3PO4 H++ H₂PO 7.08 x 10-3 Dihydrogen H₂PO H₂PO H+ HPO 6.31 x 10-6 phosphate Hydrogen HPO₁ 12.4 phosphate Carbonic acid H2CO3 Hydrogen HCO 6.35 10.3 carbonate or bicarbonate Acetic acid CH,COOH 4.76 Lactic acid CH₂CHOH- COOH 1.38 x 10 Ammonium NH 5.63 x 10-10 Phenol CH₂OH 1 x 10-10 Protonated form CH3NH3* 3.16 x 10-11 of methylaminearrow_forwardIndicate whether it is true that Co(III) complexes are very stable.arrow_forwardMnO2 acts as an oxidant in the chlorine synthesis reaction.arrow_forward
- In Potassium mu-dihydroxydicobaltate (III) tetraoxalate K4[Co2(C2O4)4(OH)2], indicate whether the OH ligand type is bidentate.arrow_forwardImagine an electrochemical cell based on these two half reactions with electrolyte concentrations as given below: Oxidation: Pb(s) → Pb2+(aq, 0.10 M) + 2 e– Reduction: MnO4–(aq, 1.50 M) + 4 H+(aq, 2.0 M) + 3 e– → MnO2(s) + 2 H2O(l) Calculate Ecell (assuming temperature is standard 25 °C).arrow_forward: ☐ + Draw the Fischer projection of the most common naturally-occurring form of aspartate, with the acid group at the top and the side chain at the bottom. Important: be sure your structure shows the molecule as it would exist at physiological pH. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ✓arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





