
Sub part (a):
Diminishing marginal utility .
Sub part (a):
Explanation of Solution
The utility function is
Figure 1 illustrates the diminishing marginal utility.
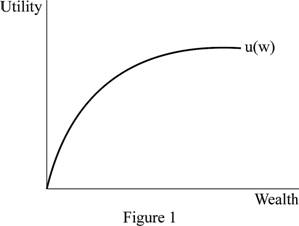
In Figure 1, the horizontal axis measures the quantity of wealth and the vertical axis measures the utility. When the quantity of wealth increases then the additional utility decreases.
Concept introduction:
Marginal utility: Marginal utility refers to the additional units of satisfaction derived from one more additional unit of goods and services.
Diminishing marginal utility: Diminishing marginal utility refers to a decrease in the additional satisfaction as a result of increasing the consumption.
Sub Part (b):
Expected value.
Sub Part (b):
Explanation of Solution
Since the value is sure, the probability is 1. Expected value of A can be calculated as follows:
Expected value of A is $4,000,000.
Expected value of B can be calculated as follows.
Expected value of B is $4,200,000. Thus, B offers higher value.
Concept introduction:
Risk is the future uncertainty about deviation from expected earnings or expected outcome. Risk measures the uncertainty situation that an investor is willing to take to realize a gain from an investment.
Risk aversion: Risk aversion can be defined as it is a dislike of an uncertainty.
Marginal utility: Marginal utility refers to the additional units of satisfaction derived from one more additional unit of goods and services.
Diminishing marginal utility: Diminishing marginal utility refers to a decrease in the additional satisfaction as a result of increasing the consumption.
Sub part (c):
Expected utility.
Sub part (c):
Explanation of Solution
Expected utility of A can be calculated as follows:
Expected utility of A is $2,000.
Expected utility of B can be calculated as follows.
Expected utility of B is $1,800.
Concept introduction:
Risk is the future uncertainty about deviation from expected earnings or expected outcome. Risk measures the uncertainty situation that an investor is willing to take to realize a gain from an investment.
Risk aversion: Risk aversion can be defined as it is a dislike of an uncertainty.
Marginal utility: Marginal utility refers to the additional units of satisfaction derived from one more additional unit of goods and services.
Diminishing marginal utility: Diminishing marginal utility refers to a decrease in the additional satisfaction as a result of increasing the consumption.
Sub part (d):
greaterExpected utility.
Sub part (d):
Explanation of Solution
Since the expected utility from B is greater than A, the person should select A.
Concept introduction:
Risk is the future uncertainty about deviation from expected earnings or expected outcome. Risk measures the uncertainty situation that an investor is willing to take to realize a gain from an investment.
Risk aversion: Risk aversion can be defined as it is a dislike of an uncertainty.
Marginal utility: Marginal utility refers to the additional units of satisfaction derived from one more additional unit of goods and services.
Diminishing marginal utility: Diminishing marginal utility refers to a decrease in the additional satisfaction as a result of increasing the consumption.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 27 Solutions
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
- Problem 2: At a raffle, 2000 tickets are sold at $5 each for five prizes of $2000, $1000, $500, $250, and $100. You buy one ticket. What is the expected value of your gain? 1. Find the gain for each prize. 2. Write a probability distribution for the possible gains. 3. Find the expected value. 4. Interpret the results.arrow_forwardThis activity focuses on developing direct and supported opinions using various sources of information on the importance of the following topics: non-renewable and renewable energies, economic factors and obstacles that can affect the relationship between international trade and economic growth, devaluation of the currency in countries, and the imbalance of economic equity. In this context, it is essential that, when studying and developing these topics, students understand the concepts of the value of currencies and that leads to devaluation, non-renewable and renewable energy resources, economic development and obstacles, distribution of wealth, economic growth and external and internal constraints, and about international trade as a growth factor. Thus, the objectives that are intended to be achieved are the following: Acquire knowledge about the concepts mentioned above. Determine relationships between economic growth and international trade. Understand what some limitations that…arrow_forwardConsider a firm facing conventional production technology. The short run Production Function has a small range of increasing marginal product (increasing marginal returns) and then is subject to the Law of Diminishing Marginal Product (diminishing marginal returns). A. Putting quantity on the horizontal axis and dollars on the vertical axis, depict three important curves: Fixed Cost (FC), Variable Cost (VC), and Total Cost (TC). (Note that we are not asking you to depict average cost functions!) B. Please clearly indicate on this graph the range of quantities where the firm is experiencing (1) increasing marginal product and (2) diminishing marginal product. C. In a few sentences, please justify why you've made this specific classification of increasing/diminishing marginal product in part (b).arrow_forward
- please answer the following questions: What is money, and why does anyone want it? Explain the concept of the opportunity cost of holding money . Explain why an increase in U.S. interest rates relative to UK interest rates would affect the U.S.-UK exchange rate. Suppose that a person’s wealth is $50,000 and that her yearlyincome is $60,000. Also suppose that her money demand functionis given by Md = $Y10.35 - i2Derive the demand for bonds. Suppose the interest rate increases by 10 percentage points. What is the effect on her demand for bonds?b. What are the effects of an increase in income on her demand for money and her demand for bonds? Explain in wordsarrow_forwardDriving Quiz X My Course G city place w x D2L Login - Univ X D2L Login - Univ x D2L Login - U acmillanlearning.com/ihub/assessment/f188d950-dd73-11e0-9572-0800200c9a66/4db68a5e-69bb-4767-8d6c-a12d +1687 pts /1800 © Macmillan Learning Question 6 of 18 > The graph shows the average total cost (ATC) curve, the marginal cost (MC) curve, the average variable cost (AVC) curve, and the marginal revenue (MR) curve (which is also the market price) for a perfectly competitive firm that produces terrible towels. Answer the three questions, assuming that the firm is profit-maximizing and does not shut down in the short run. What is the firm's total revenue? S What is the firm's total cost? $ What is the firm's profit? (Enter a negative number for a loss.) $ Price $320 $300 $200 $150 205 260 336 365 Quantity MC ATC AVC MR=Parrow_forward1. Suppose that the two nations face the following benefits of pollution, B, and costs of abatement, C: BN = 10, Bs = 7; CN = 5, Cs = 4. Further assume that if the nation chooses to abate pollution, it still receives the benefits of pollution but now must pay the cost of abatement as well. a. Identify the payoffs that accrue to each nation under the four different possible outcomes of the game and present these payoffs in the normal form of the game. b. Recall that the term dominant strategy defines the condition that a player in a game would prefer to play that strategy (in this case either pollute or abate) regardless of the strategy chosen by the other player in the game. Does either nation have a dominant strategy in this game? If so, what is it? c. Identify the Nash equilibria, or non-cooperative equilibria, of this game.arrow_forward
- agrody calming Inted 001 and me 2. A homeowner is concerned about the various air pollutants (e.g., benzene and methane) released in her house when she cooks with natural gas. She is considering replacing her gas oven and stove with an electric stove comprising an induction cooktop and convection oven. The new appliance costs $900 to purchase and install. Capping the old gas line costs an additional $150 (a one-time fee). The old line must be inspected for leaks each year after capping, at a cost of $35 for each inspection. a. If the homeowner plans to remain in the house for four more years and the discount rate is 4%, what is the minimum present value of the benefits that the homeowner would need to experience for this purchase to be justified based on its private net sub present value? b. While trying to understand how she might express the value of reduced exposure to indoor air pollutants in dollar terms, the homeowner consulted the EPA website and found estimates provided by…arrow_forwardAfter the ban is imposed, Joe’s firm switches to the more expensive biodegradable disposable cups. This increases the cost associated with each cup of coffee it produces. Which cost curve(s) will be impacted by the use of the more expensive biodegradable disposable cups? Why? Which cost curve(s) will not shift, and why not? Please use the table below to answer this question. For the second column (“Impacted? If so, how?”), please use one of the following three choices: No shift; Shifts up (i.e., increases: at nearly any given quantity, the cost goes up); or Shifts down (i.e., decreases: at nearly any given quantity, the cost goes down). $ Cost Curve Impacted? If so, how? Explanation of the Shift: Why or Why Not AFC No shift. Fix costs stay the same, regardless of quantity. Fixed cost is calculated as Fixed Cost/Quantity. Since fixed costs remain unchanged, AFC stays the same for each quantity. MC Shifts up. Since the biodegradable cups are more expensive, the…arrow_forwardStyrofoam is non-biodegradable and is not easily recyclable. Many cities and at least one state have enacted laws that ban the use of polystyrene containers. These locales understand that banning these containers will force many businesses to turn to other more expensive forms of packaging and cups, but argue the ban is environmentally important. Shane owns a firm with a conventional production function resulting in U-shaped ATC, AVC, and MC curves. Shane's business sells takeout food and drinks that are currently packaged in styrofoam containers and cups. Graph the short-run AFC0, AVC0, ATC0, and MC0 curves for Shane's firm before the ban on using styrofoam containers.arrow_forward
 Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning





