
Sub part (a):
Diminishing marginal utility .
Sub part (a):
Explanation of Solution
The utility function is
Figure 1 illustrates the diminishing marginal utility.
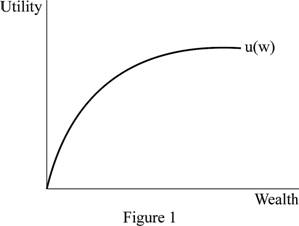
In Figure 1, the horizontal axis measures the quantity of wealth and the vertical axis measures the utility. When the quantity of wealth increases then the additional utility decreases.
Concept introduction:
Marginal utility: Marginal utility refers to the additional units of satisfaction derived from one more additional unit of goods and services.
Diminishing marginal utility: Diminishing marginal utility refers to a decrease in the additional satisfaction as a result of increasing the consumption.
Sub Part (b):
Expected value.
Sub Part (b):
Explanation of Solution
Since the value is sure, the probability is 1. Expected value of A can be calculated as follows:
Expected value of A is $4,000,000.
Expected value of B can be calculated as follows.
Expected value of B is $4,200,000. Thus, B offers higher value.
Concept introduction:
Risk is the future uncertainty about deviation from expected earnings or expected outcome. Risk measures the uncertainty situation that an investor is willing to take to realize a gain from an investment.
Risk aversion: Risk aversion can be defined as it is a dislike of an uncertainty.
Marginal utility: Marginal utility refers to the additional units of satisfaction derived from one more additional unit of goods and services.
Diminishing marginal utility: Diminishing marginal utility refers to a decrease in the additional satisfaction as a result of increasing the consumption.
Sub part (c):
Expected utility.
Sub part (c):
Explanation of Solution
Expected utility of A can be calculated as follows:
Expected utility of A is $2,000.
Expected utility of B can be calculated as follows.
Expected utility of B is $1,800.
Concept introduction:
Risk is the future uncertainty about deviation from expected earnings or expected outcome. Risk measures the uncertainty situation that an investor is willing to take to realize a gain from an investment.
Risk aversion: Risk aversion can be defined as it is a dislike of an uncertainty.
Marginal utility: Marginal utility refers to the additional units of satisfaction derived from one more additional unit of goods and services.
Diminishing marginal utility: Diminishing marginal utility refers to a decrease in the additional satisfaction as a result of increasing the consumption.
Sub part (d):
greaterExpected utility.
Sub part (d):
Explanation of Solution
Since the expected utility from B is greater than A, the person should select A.
Concept introduction:
Risk is the future uncertainty about deviation from expected earnings or expected outcome. Risk measures the uncertainty situation that an investor is willing to take to realize a gain from an investment.
Risk aversion: Risk aversion can be defined as it is a dislike of an uncertainty.
Marginal utility: Marginal utility refers to the additional units of satisfaction derived from one more additional unit of goods and services.
Diminishing marginal utility: Diminishing marginal utility refers to a decrease in the additional satisfaction as a result of increasing the consumption.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 27 Solutions
Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Course List)
- How Command Economics Relate to Principle Of Economics?arrow_forwardhow commond economies relate to principle Of Economics ?arrow_forwardCritically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forward
- Critically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forwardOutline the nine (9) consumer rights as specified in the Consumer Rights Act in South Africa.arrow_forwardIn what ways could you show the attractiveness of Philippines in the form of videos/campaigns to foreign investors? Cite 10 examples.arrow_forward
- Explain the following terms and provide an example for each term: • Corruption • Fraud • Briberyarrow_forwardIn what ways could you show the attractiveness of a country in the form of videos/campaigns?arrow_forwardWith the VBS scenario in mind, debate with your own words the view that stakeholders are the primary reason why business ethics must be implemented.arrow_forward
- The unethical decisions taken by the VBS management affected the lives of many of their clients who trusted their business and services You are appointed as an ethics officer at Tyme Bank. Advise the management regarding the role of legislation in South Africa in providing the legal framework for business operations.arrow_forwardTyme Bank is a developing bank in South Africa and could potentially encounter challenges similar to those faced by VBS in the future. Explain five (5) benefits of applying business ethics at Tyme Bank to prevent similar ethical scandals.arrow_forward1.3. Explain the five (5) ethical challenges that can be associated with the implementation of the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forward
 Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning





