
Concept explainers
To review:
The time and the geological period when the last common ancestor of the seed plants as well as ferns lived.
Given:
The fFigure 1 shows the geological timescale of the origin of various embryophytes (land plants) including ferns and seed plants.
Figure 1: The geological timescale of the origin of various embryophytes.
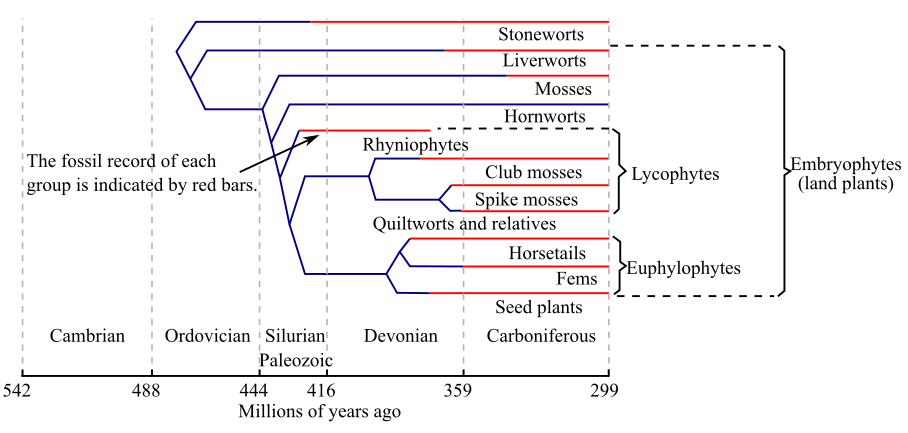
Introduction:
Horsetails, ferns, and seed plants form a clade commonly referred as euphyllophytes. These are the true leaf plants. Another important characteristic feature of these plants is overtopping. It is a growth pattern, where one branch of the plant gets differentiated from the other and grows beyond that other branch. This feature gives an advantage to the plants in competition for light.
Explanation of Solution
It can be clearly observed from Figure 1 that the common ancestor of ferns as well as the seed plants originated about 390 million years ago in the mid-Devonian period of the Paleozoic era. Today, the ferns comprise of more than 12,000 species whereas there are about 15 known species of horsetails. The species of horsetails lie in a single genus, Equisetum. It can be noticed that horsetail species are more closely linked to ferns as compared to the seed plants.
Therefore, it can be concluded that common ancestor of ferns and seed plants arose in mid-Devonian about 390 million years ago.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- please draw in the answers, thank youarrow_forwarda. On this first grid, assume that the DNA and RNA templates are read left to right. DNA DNA mRNA codon tRNA anticodon polypeptide _strand strand C с A T G A U G C A TRP b. Now do this AGAIN assuming that the DNA and RNA templates are read right to left. DNA DNA strand strand C mRNA codon tRNA anticodon polypeptide 0 A T G A U G с A TRParrow_forwardplease answer all question below with the following answer choice, thank you!arrow_forward
- please draw in the answeres, thank youarrow_forwardA) What is being shown here?B) What is indicated by the RED arrow?C) What is indicated by the BLUE arrow?arrow_forwardPlease identify the curve shown below. What does this curve represent? Please identify A, B, C, D, and E (the orange oval). What is occurring in these regions?arrow_forward
- Please identify the test shown here. 1) What is the test? 2) What does the test indicate? How is it performed? What is CX? 3) Why might the test be performed in a clinical setting? GEN CZ CX CPZ PTZ CACarrow_forwardDetermine how much ATP would a cell produce when using fermentation of a 50 mM glucose solution?arrow_forwardDetermine how much ATP would a cell produce when using aerobic respiration of a 7 mM glucose solution?arrow_forward
- Determine how much ATP would a cell produce when using aerobic respiration to degrade one small protein molecule into 12 molecules of malic acid, how many ATP would that cell make? Malic acid is an intermediate in the Krebs cycle. Assume there is no other carbon source and no acetyl-CoA.arrow_forwardIdentify each of the major endocrine glandsarrow_forwardCome up with a few questions and answers for umbrella species, keystone species, redunant species, and aquatic keystone speciesarrow_forward
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College





