
(a)
To explain:
The effect of an increase in government purchase in the short run on the given two diagrams.
Answer to Problem 1P
The effect of an increase in government purchase is shown on the diagrams below:
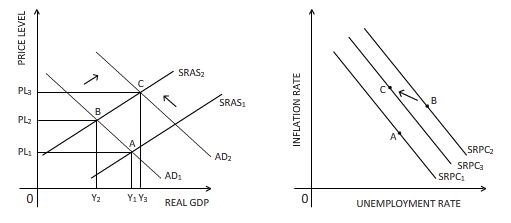
Explanation of Solution
Government purchase is a part of aggregate
Government purchase:
The goods and services bought by the government to undertake infrastructural developments and other developmental activities is referred as government purchase.
(b)
To explain:
The effect of reduced growth rate of money supply in the short run on the given two diagrams.
Answer to Problem 1P
The effect of decrease in growth rate of money supply is shown on the diagrams below:
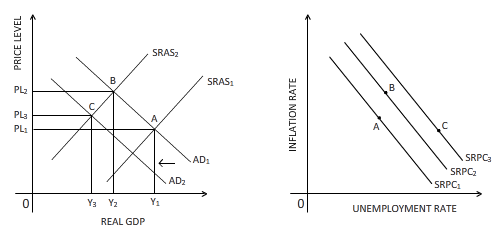
Explanation of Solution
A reduction in the growth rate of money supply affects the aggregate demand negatively through the real balance effect. This leads to a leftward shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2. The new equilibrium point is established at point C, where both real GDP and price level are lower than that of the equilibrium point at B. Due to fall in real GDP, there will be rise in unemployment, and hence the SRPC line shifts rightward from SRPC2 to SRPC3. The new equilibrium point C is shown on the SRPC3 in the right-hand side diagram.
Money supply:
The amount of money in the form of currency and other financial liquid instruments supplied in an economy over a specific time period is referred as money supply.
(c)
To explain:
The effect of an expected higher inflation in the short run on the given two diagrams.
Answer to Problem 1P
The effect of an expected higher inflation is shown on the diagrams below:
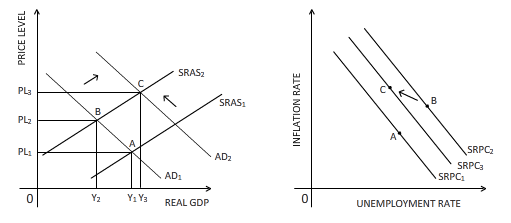
Explanation of Solution
If people expect that higher inflation is approaching, they will increase their consumption expenditure to ward off the high inflation. Therefore, the aggregate demand will rise in the short run. This is reflected in the rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 in the above diagram. This results in a new equilibrium point C in the diagram where both real GDP and price level are higher than that of point B. On the right-hand side diagram, the SRPC line shifts from SRPC2 to SRPC3 because as real GDP grows at each level of inflation rate, unemployment falls. The new equilibrium point C is marked on SRPC3 line.
Inflation rate:
The rate at which the price level of an economy rises is termed as the rate of inflation. An increased inflation rate decreases the
(d)
To explain:
The effect of a favorable supply shock on the given two diagrams.
Answer to Problem 1P
The effect of supply shock is shown on the diagrams below:
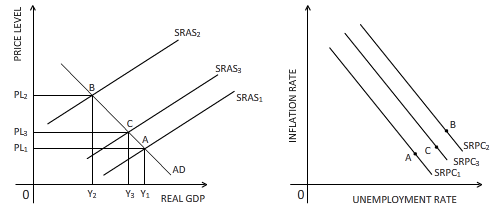
Explanation of Solution
A favorable supply shock will push the supply of the economy upward, causing the
Supply shock:
An event which leads to a sudden rise or fall in the supply of goods and services is referred as supply shock.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- Can you please help with this one. Some economists argue that taxing consumption is more efficient than taxing income. Following the same argument, the minister of finance of a country introduced a new tax for sugar based products “sugar tax” to promote healthy eating in the economy. Please use relevant diagrams to explain the impact of the tax on consumers, producers and the tax revenue when sugar is elastic and inelastic.arrow_forwardprofit maximizing and loss minamization fire dragon co mindtaparrow_forwardProblem 3 You are given the following demand for European luxury automobiles: Q=1,000 P-0.5.2/1.6 where P-Price of European luxury cars PA = Price of American luxury cars P, Price of Japanese luxury cars I= Annual income of car buyers Assume that each of the coefficients is statistically significant (i.e., that they passed the t-test). On the basis of the information given, answer the following questions 1. Comment on the degree of substitutability between European and American luxury cars and between European and Japanese luxury cars. Explain some possible reasons for the results in the equation. 2. Comment on the coefficient for the income variable. Is this result what you would expect? Explain. 3. Comment on the coefficient of the European car price variable. Is that what you would expect? Explain.arrow_forward
- Problem 2: A manufacturer of computer workstations gathered average monthly sales figures from its 56 branch offices and dealerships across the country and estimated the following demand for its product: Q=+15,000-2.80P+150A+0.3P+0.35Pm+0.2Pc (5,234) (1.29) (175) (0.12) (0.17) (0.13) R²=0.68 SER 786 F=21.25 The variables and their assumed values are P = Price of basic model = 7,000 Q==Quantity A = Advertising expenditures (in thousands) = 52 P = Average price of a personal computer = 4,000 P. Average price of a minicomputer = 15,000 Pe Average price of a leading competitor's workstation = 8,000 1. Compute the elasticities for each variable. On this basis, discuss the relative impact that each variable has on the demand. What implications do these results have for the firm's marketing and pricing policies? 2. Conduct a t-test for the statistical significance of each variable. In each case, state whether a one-tail or two-tail test is required. What difference, if any, does it make to…arrow_forwardYou are the manager of a large automobile dealership who wants to learn more about the effective- ness of various discounts offered to customers over the past 14 months. Following are the average negotiated prices for each month and the quantities sold of a basic model (adjusted for various options) over this period of time. 1. Graph this information on a scatter plot. Estimate the demand equation. What do the regression results indicate about the desirability of discounting the price? Explain. Month Price Quantity Jan. 12,500 15 Feb. 12,200 17 Mar. 11,900 16 Apr. 12,000 18 May 11,800 20 June 12,500 18 July 11,700 22 Aug. 12,100 15 Sept. 11,400 22 Oct. 11,400 25 Nov. 11,200 24 Dec. 11,000 30 Jan. 10,800 25 Feb. 10,000 28 2. What other factors besides price might be included in this equation? Do you foresee any difficulty in obtaining these additional data or incorporating them in the regression analysis?arrow_forwardsimple steps on how it should look like on excelarrow_forward
- Consider options on a stock that does not pay dividends.The stock price is $100 per share, and the risk-free interest rate is 10%.Thestock moves randomly with u=1.25and d=1/u Use Excel to calculate the premium of a10-year call with a strike of $100.arrow_forwardCompute the Fourier sine and cosine transforms of f(x) = e.arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward

 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning

 Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning





