
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781337026345
Author: Katz
Publisher: Cengage
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 26, Problem 68PQ
Figure P26.68 shows three small spheres with identical charges of −3.00 nC placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle with side d = 2.50 cm.
- a. Is the electric potential due to the three spheres zero anywhere in the plane that contains the triangle, other than at infinity?
- b. What is the electric potential at the location of each sphere due to the other two spheres?
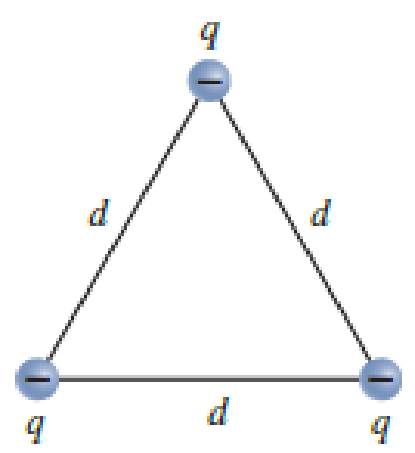
FIGURE P26.68
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
If a force does zero net work on an object over a closed loop, does that guarantee the force is conservative? Explain with an example or counterexample
A futuristic amusement ride spins riders in a horizontal circle of radius 5 m at a constant speed. Thefloor drops away, leaving riders pinned to the wall by friction (coefficient µ = 0.4). What minimum speedensures they don’t slip, given g = 10 m/s²? Draw diagram (or a few) showing all forces, thevelocity of the rider, and their acceleration
Your RL circuit has a characteristic time constant of 19.5 ns, and a resistance of 4.60 MQ.
(a) What is the inductance (in H) of the circuit?
0.00897
× H
(b) What resistance (in MQ) should you use (instead of the 4.60 MQ resistor) to obtain a 1.00 ns time constant, perhaps needed for quick response in an oscilloscope?
8.97
* ΜΩ
Chapter 26 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
Ch. 26.2 - Complete the analogies by filling in the blanks,...Ch. 26.3 - Prob. 26.2CECh. 26.3 - A water molecule is made up of two hydrogen atoms...Ch. 26.4 - Match the topographical maps in Figure 26.15 with...Ch. 26.5 - Which term or phrase is a synonym for electric...Ch. 26.7 - If the contours in Figure 26.26 represent the...Ch. 26.9 - Prob. 26.7CECh. 26 - What does it mean when a force is negative? What...Ch. 26 - Review Return to Chapter 8 and the potential...Ch. 26 - Review A system consists of a planet and a star,...
Ch. 26 - Try to complete Table P26.4 from memory. If you...Ch. 26 - Try to complete Table P26.5 from memory. If you...Ch. 26 - Can you associate electric potential energy with...Ch. 26 - Consider the final arrangement of charged...Ch. 26 - Using the usual convention that the electric...Ch. 26 - FIGURE P26.8 A Find an expression for the electric...Ch. 26 - A hydrogen atom consists of an electron and a...Ch. 26 - What is the work that a generator must do to move...Ch. 26 - How far should a +3.0-C charged panicle be from a...Ch. 26 - A proton is fired from very far away directly at a...Ch. 26 - Four charged particles are at rest at the corners...Ch. 26 - FIGURE P26.14 Problems 14, 15, and 16. Four...Ch. 26 - Four charged particles are at rest at the corners...Ch. 26 - Eight identical charged particles with q = 1.00 nC...Ch. 26 - A conducting sphere with a radius of 0.25 m has a...Ch. 26 - The speed of an electron moving along the y axis...Ch. 26 - Figure P26.20 is a topographic map. a. Rank A, B,...Ch. 26 - At a point in space, the electric potential due to...Ch. 26 - Explain the difference between UE(r) = kQq/r and...Ch. 26 - Suppose a single electron moves through an...Ch. 26 - Two point charges, q1 = 2.0 C and q2 = 2.0 C, are...Ch. 26 - Separating the electron from the proton in a...Ch. 26 - Can a contour map help you visualize the electric...Ch. 26 - Prob. 27PQCh. 26 - Find the electric potential at the origin given...Ch. 26 - Prob. 29PQCh. 26 - Prob. 30PQCh. 26 - Prob. 31PQCh. 26 - Prob. 32PQCh. 26 - A source consists of three charged particles...Ch. 26 - Two identical metal balls of radii 2.50 cm are at...Ch. 26 - Figure P26.35 shows four particles with identical...Ch. 26 - Two charged particles with qA = 9.75 C and qB =...Ch. 26 - Two charged particles with q1 = 5.00 C and q2 =...Ch. 26 - Prob. 38PQCh. 26 - Prob. 39PQCh. 26 - A uniformly charged ring with total charge q =...Ch. 26 - A line of charge with uniform charge density lies...Ch. 26 - A line of charge with uniform charge density =...Ch. 26 - A Consider a thin rod of total charge Q and length...Ch. 26 - Figure P26.44 shows a rod of length = 1.00 m...Ch. 26 - The charge density on a disk of radius R = 12.0 cm...Ch. 26 - Prob. 46PQCh. 26 - In some region of space, the electric field is...Ch. 26 - A particle with charge 1.60 1019 C enters midway...Ch. 26 - Prob. 49PQCh. 26 - Prob. 50PQCh. 26 - Prob. 51PQCh. 26 - Prob. 52PQCh. 26 - Prob. 53PQCh. 26 - According to Problem 43, the electric potential at...Ch. 26 - The electric potential is given by V = 4x2z + 2xy2...Ch. 26 - The electric potential V(x, y, z) in a region of...Ch. 26 - Prob. 57PQCh. 26 - In three regions of space, the electric potential...Ch. 26 - Prob. 59PQCh. 26 - Prob. 60PQCh. 26 - The distance between two small charged spheres...Ch. 26 - Prob. 62PQCh. 26 - A glass sphere with radius 4.00 mm, mass 85.0 g,...Ch. 26 - Prob. 64PQCh. 26 - Two 5.00-nC charged particles are in a uniform...Ch. 26 - A 5.00-nC charged particle is at point B in a...Ch. 26 - A charged particle is moved in a uniform electric...Ch. 26 - Figure P26.68 shows three small spheres with...Ch. 26 - What is the work required to charge a spherical...Ch. 26 - For a system consisting of two identical...Ch. 26 - Figure P26.71 shows three charged particles...Ch. 26 - Problems 72, 73, and 74 are grouped. 72. A Figure...Ch. 26 - A Start with V=2k[(R2+x2)x] for the electric...Ch. 26 - A Review Consider the charged disks in Problem 72...Ch. 26 - A long thin wire is used in laser printers to...Ch. 26 - An electric potential exists in a region of space...Ch. 26 - A disk with a nonuniform charge density =ar2 has...Ch. 26 - An infinite number of charges with q = 2.0 C are...Ch. 26 - An infinite number of charges with |q| =2.0 C are...Ch. 26 - Figure P26.80 shows a wire with uniform charge per...Ch. 26 - Prob. 81PQ
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Your RL circuit has a characteristic time constant of 19.5 ns, and a resistance of 4.60 MQ. (a) What is the inductance (in H) of the circuit? H (b) What resistance (in MQ) should you use (instead of the 4.60 MQ resistor) to obtain a 1.00 ns time constant, perhaps needed for quick response in an oscilloscope? ΜΩarrow_forwardAt a distance of 0.212 cm from the center of a charged conducting sphere with radius 0.100cm, the electric field is 485 N/C . What is the electric field 0.598 cm from the center of the sphere? At a distance of 0.196 cmcm from the axis of a very long charged conducting cylinder with radius 0.100cm, the electric field is 485 N/C . What is the electric field 0.620 cm from the axis of the cylinder? At a distance of 0.202 cm from a large uniform sheet of charge, the electric field is 485 N/C . What is the electric field 1.21 cm from the sheet?arrow_forwardA hollow, conducting sphere with an outer radius of 0.260 m and an inner radius of 0.200 m has a uniform surface charge density of +6.67 × 10−6 C/m2. A charge of -0.800 μC is now introduced into the cavity inside the sphere. What is the new charge density on the outside of the sphere? Calculate the strength of the electric field just outside the sphere. What is the electric flux through a spherical surface just inside the inner surface of the sphere?arrow_forward
- A point charge of -3.00 μC is located in the center of a spherical cavity of radius 6.60 cm inside an insulating spherical charged solid. The charge density in the solid is 7.35 × 10−4 C/m3. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field inside the solid at a distance of 9.10 cm from the center of the cavity. Find the direction of this electric field.arrow_forwardAn infinitely long conducting cylindrical rod with a positive charge λ per unit length is surrounded by a conducting cylindrical shell (which is also infinitely long) with a charge per unit length of −2λ and radius r1, as shown in the figure. What is E(r), the radial component of the electric field between the rod and cylindrical shell as a function of the distance r from the axis of the cylindrical rod? Express your answer in terms of λ, r, and ϵ0, the permittivity of free space. What is σinner, the surface charge density (charge per unit area) on the inner surface of the conducting shell? What is σouterσouter, the surface charge density on the outside of the conducting shell? (Recall from the problem statement that the conducting shell has a total charge per unit length given by −2λ.) What is the radial component of the electric field, E(r), outside the shell?arrow_forwardA very long conducting tube (hollow cylinder) has inner radius aa and outer radius b. It carries charge per unit length +α, where αα is a positive constant with units of C/m. A line of charge lies along the axis of the tube. The line of charge has charge per unit length +α. Calculate the electric field in terms of α and the distance r from the axis of the tube for r<a. Calculate the electric field in terms of α and the distance rr from the axis of the tube for a<r<b. Calculate the electric field in terms of αα and the distance r from the axis of the tube for r>b. What is the charge per unit length on the inner surface of the tube? What is the charge per unit length on the outer surface of the tube?arrow_forward
- Two small insulating spheres with radius 9.00×10−2 m are separated by a large center-to-center distance of 0.545 m . One sphere is negatively charged, with net charge -1.75 μC , and the other sphere is positively charged, with net charge 3.70 μC . The charge is uniformly distributed within the volume of each sphere. What is the magnitude E of the electric field midway between the spheres? Take the permittivity of free space to be ϵ0 = 8.85×10−12 C2/(N⋅m2) . What is the direction of the electric field midway between the spheres?arrow_forwardA conducting spherical shell with inner radius aa and outer radius bb has a positive point charge Q located at its center. The total charge on the shell is -3Q, and it is insulated from its surroundings. Derive the expression for the electric field magnitude in terms of the distance r from the center for the region r<a. Express your answer in terms of some or all of the variables Q, a, b, and appropriate constants. Derive the expression for the electric field magnitude in terms of the distance rr from the center for the region a<r<b. Derive the expression for the electric field magnitude in terms of the distance rr from the center for the region r>b. What is the surface charge density on the inner surface of the conducting shell? What is the surface charge density on the outer surface of the conducting shell?arrow_forwardA small sphere with a mass of 3.00×10−3 g and carrying a charge of 4.80×10−8 C hangs from a thread near a very large, charged insulating sheet, as shown in the figure (Figure 1). The charge density on the sheet is −2.20×10−9 C/m2 . Find the angle of the thread.arrow_forward
- A small conducting spherical shell with inner radius aa and outer radius bb is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and outer radius d (Figure 1). The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge −2q. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field in terms of q and the distance rr from the common center of the two shells for r<a. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field for a<r<b. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field for b<r<c.arrow_forwardA cube has sides of length L = 0.800 m . It is placed with one corner at the origin as shown in the figure. The electric field is not uniform but is given by E→=αxi^+βzk^, where α=−3.90 and β= 7.10. What is the sum of the flux through the surface S5 and S6? What is the sum of the flux through the surface S2 and S4? Find the total electric charge inside the cube.arrow_forwardIn the figure, a proton is projected horizontally midway between two parallel plates that are separated by 0.6 cm. The electrical field due to the plates has magnitude 450000 N/C between the plates away from the edges. If the plates are 3 cm long, find the minimum speed of the proton if it just misses the lower plate as it emerges from the field.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY