
Concept explainers
Convert each ball-and-stick model to a Fischer projection.
a.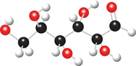 b.
b. 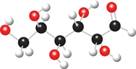
(a)
Interpretation: The given ball-and-stick model is to be converted into Fischer projection.
Concept introduction: In Fischer projection formula, the horizontal and vertical line represents the bonds that are present above and below the plane, respectively. The verticals bonds are represented as dashed wedge and horizontal bonds as dark wedge.
Answer to Problem 36P
The Fischer projection of given ball and stick model is shown below.
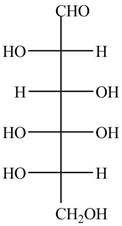
Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
The ball and stick model of given compound is,
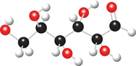
Figure 2
Black colored atoms have four bonds. So, these are the carbon atoms. The grey colored balls have one bond. So, these are the hydrogen atoms. The red colored atoms have two bonds. So, these are oxygen atoms. The molecular structure of given compound is,
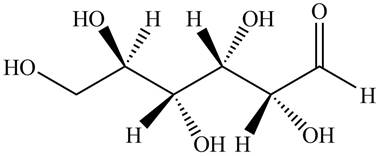
Figure 3
The conversion of given compound into Fisher projection is as follows:
The structure
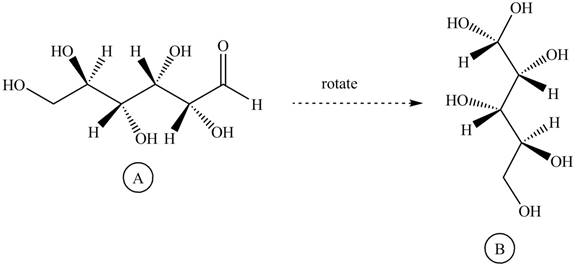
Figure 4
Rotate all the bonds around the carbon atom in such way that all staggered form converted into the eclipsed form in structure
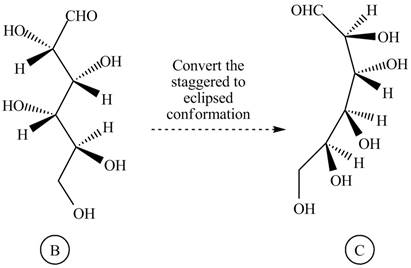
Figure 5
The structure
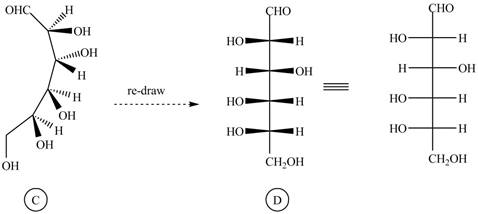
Figure 6
The Fischer projection of given ball and stick model is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The products of given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: In Fischer projection formula, the horizontal and vertical line represents the bonds that are present above and below the plane, respectively. The verticals bonds are represented as dashed wedge and horizontal bonds as dark wedge.
Answer to Problem 36P
The Fischer projection of given ball and stick model is shown below.
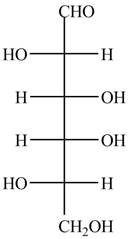
Figure 7
Explanation of Solution
The ball and stick model of given compound is,
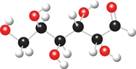
Figure 8
Black colored atoms have four bonds. So, these are the carbon atoms. The grey colored balls have one bond. So, these are the hydrogen atoms. The red colored atoms have two bonds. So, these are oxygen atoms. The molecular structure of given compound is,
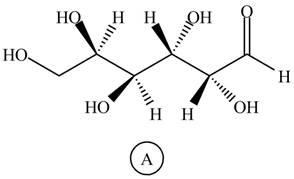
Figure 9
The conversion of given compound into Fisher projection is follow:
The structure
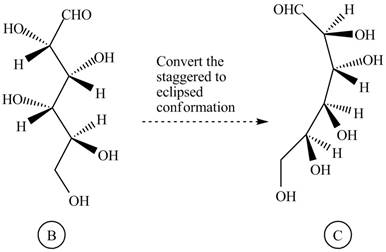
Figure 10
Rotate all the bonds around the carbon atom in such way that all staggered form converts into the eclipsed form in structure
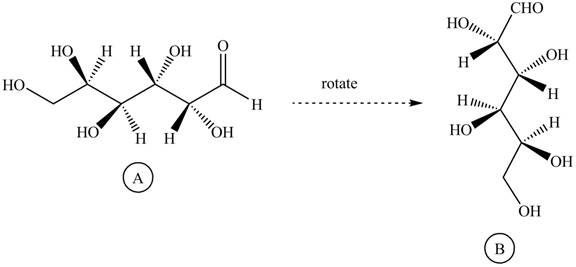
Figure 11
The structure
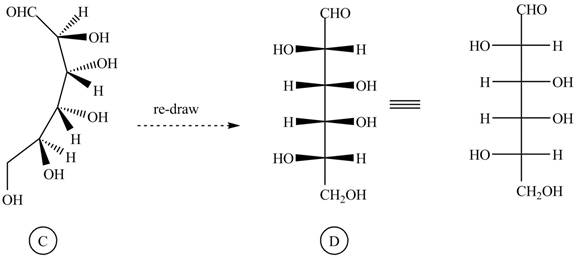
Figure 12
The Fischer projection of given ball and stick model is shown in Figure 7.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - LOOSELEAF W/CONNECT
- 8. (16 pts) Provide the stepwise mechanism for the synthesis of the following compound via an enaminearrow_forwardDraw the titration curve of (i) weak acid vs. strong base; (ii) weak acid vs. weakbase; (iii) diprotic acid with strong base (iii) triprotic acid with strong base.arrow_forwardComplete the reaction in the drawing area below by adding the major products to the right-hand side. If there won't be any products, because nothing will happen under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead. Note: if the products contain one or more pairs of enantiomers, don't worry about drawing each enantiomer with dash and wedge bonds. Just draw one molecule to represent each pair of enantiomers, using line bonds at the chiral center. More... No reaction. my ㄖˋ + 1. Na O Me Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2. H +arrow_forward
- Predict the intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this organic reaction: NaOMe H+ + 1 2 H H work up You can draw 1 and 2 in any arrangement you like. Note: if either 1 or 2 consists of a pair of enantiomers, just draw one structure using line bonds instead of 3D (dash and wedge) bonds at the chiral center. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X $ dmarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: 1. NaH (20°C) 2. CH3Br ? Some notes: • Draw only the major product, or products. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds where necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • If there are no products, just check the box under the drawing area. No reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. G Crarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: 1. LDA (-78°C) ? 2. Br Some notes: • Draw only the major product, or products. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. . • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds where necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • If there are no products, just check the box under the drawing area. No reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forward
- Please draw the structuresarrow_forwardDraw the missing intermediates 1 and 2, plus the final product 3, of this synthesis: 0 1. Eto 1. Eto- 1 2 2. MeBr 2. EtBr H3O+ A 3 You can draw the three structures in any arrangement you like. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardDraw the missing intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this synthesis: 1. MeO- H3O+ 1 2 2. PrBr Δ You can draw the two structures in any arrangement you like. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- What is the differences between: Glyceride and phosphoglyceride Wax and Fat Soap and Fatty acid HDL and LDL cholesterol Phospho lipids and sphingosine What are the types of lipids? What are the main lipid components of membrane structures? How could lipids play important rules as signaling molecules and building units? The structure variety of lipids makes them to play significant rules in our body, conclude breifly on this statement.arrow_forwardWhat is the differences between DNA and RNA for the following: - structure - function - type What is the meaning of: - replication - transcription - translation show the base pair connection(hydrogen bond) in DNA and RNAarrow_forwardWhat is the IP for a amino acid- give an example what are the types of amino acids What are the structures of proteins The N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Try-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val- Tyr- Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
