
coli to cause cystitis. Do the same for pyelonephritis. Diagram the pathway taken by Neisseria gonorrhoeae to cause PID.
To draw:
Pathway taken by E. coli to cause cystitis and pyelonephritis. Pathway taken by Neisseria gonorrhoeae to cause PID
Pictorial representation:
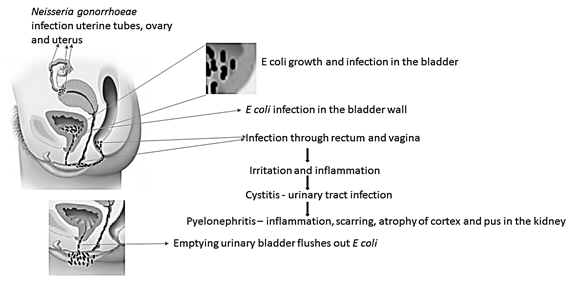
Concept introduction:
Cystitis is a urinary tract infection, mostly caused by E coli. Bacterial growth in the urothelium of the bladder through rectum, urethra, perineum and vagina causes cystitis. Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory disease of kidneys, mostly caused by E coli. Bacteria can reach kidney through lower urinary tract and bloodstream. Pelvic inflammatory disease or PID is a severe bacterial infection of pelvic organs of women, mostly caused by N gonorrhoeae.
Explanation of Solution
Cystitis is a common urinary tract infection, caused by Escherichia coli (E coli) bacteria. Nearly 70-95% of the urinary tract infections are caused by E coli. It is a gram-negative, anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria. It is commonly found in environment, skin and intestines of animal and human. Mostly they are harmless and help in digestion, and sometimes they can cause serious health problems like diarrhea, cystitis (urinary tract infections), respiratory problem, pneumonia, food poison and others. Cystitis is primarily caused by Escherichia coli and also by Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Klebsiella species, Proteus species and Enterobacter species. E coli covers the lining of the bladder and causes irritation and inflammation which leads to cystitis. Cystitis affects people in all age groups, however, it is more common in women than men due to the short urethra, which is less than 2 inches. The female urethra is very close to anal opening, hence it may lead to intestinal bacterial contamination. It can be prevented by drinking plenty of water which can flush bacteria and also with personal hygiene. Cystitis can be treated with antibiotics such as nitrofurantoin, trimethoprim - sulfamethoxazole, fluoroquinolone and ampicillin.
Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory disease of kidneys, caused by bacterial infection. It is a life-threatening disease which severely damages one or both kidneys and causes renal scarring. More than 70% of pyelonephritis is caused by E coli and rarely by Enterococcus faecalis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella species. Bacteria can reach kidney through lower urinary tract and bloodstream. Initially, it infects bladder and move to kidney and severely damage one or both kidneys. Lower urinary tract infection is very vulnerable for kidney damage and pyelonephritis. Pyelonephritis is more common in women than men due to short urethra, which is less than 2 inches. The female urethra is very close to anal opening, hence it may lead to intestinal bacterial contaminations. Second or third generation cephalosporin is used to treat pyelonephritis.
Pelvic inflammatory disease or PID is a severe bacterial infection of pelvic organs such as uterus, cervix, uterine tubes or ovaries in female. N gonorrhoeae and C trachomatis are common microorganisms mostly responsible for PID. Uterine tubes infection or salpingitis by N gonorrhoeae leads to scarring which blocks ovary. The uterine block may cause ectopic pregnancy. Salpingitis causes10-15% infertility in women. PID can be treated with doxycycline and cefoxitin.
Cystitis is a urinary tract infection, majorly caused by E. coli leads to irritation and inflammation of the urinary bladder. Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory disease of the kidney caused by E coli. PID is an inflammatory diseases of female pelvic organ caused by N gonorrhoeae.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction (13th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physical Universe
HUMAN ANATOMY
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
- Explain down bellow what happens to the cell in pictures not in words: Decreased pH in mitochondria Increased ATP Decreased pH in cytosol Increased hydrolysis Decreasing glycogen and triglycerides Increased MAP kinase activity Poor ion transport → For each one:→ What normally happens?→ What is wrong now?→ How does it mess up the cell?arrow_forward1.) Community Diversity: The brown and orange line represent two different plant communities. a. Which color represents the community with a higher species richness? b. Which color represents the community with a higher species evenness? Relative abundance 0.1 0.04 0.001 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Rank abundance c. What is the maximum value of the Simpson's diversity index (remember, Simpson's index is D = p², Simpson's diversity index is 1-D)? d. If the Simpson's diversity index equals 1, what does that mean about the number of species and their relative abundance within community being assessed?arrow_forward1.) Community Diversity: The brown and orange line represent two different plant communities. a. Which color represents the community with a higher species richness? b. Which color represents the community with a higher species evenness? Relative abundance 0.1 0.04 0.001 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Rank abundance c. What is the maximum value of the Simpson's diversity index (remember, Simpson's index is D = p², Simpson's diversity index is 1-D)? d. If the Simpson's diversity index equals 1, what does that mean about the number of species and their relative abundance within community being assessed?arrow_forward
- what measures can a mother to take to improve the produce of her to milk to her newborn baby ?arrow_forward1. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Eastern white pine tree green (but only the ancestral line NOT shared with other organisms) 2. Oncle the last common ancestor of the Colorado blue spruce tree and Eastern white pine tree. 3. Put a box around the last common ancestor of the sugar maple tree and the dogwood tree. 4. Put a triangle around the last common ancestor of the red pine tree and the american holly bush. 5. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Ponderosa pine tree red (including all shared ancestors). 6. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the American elm tree blue (including all shared ancestors). 7 Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Sabal palm tree purple (including all shared ancestors) 8. Using a yellow highlighter or colored pencil, circle the clade that includes all pine trees. 9. Using a orange highlighter or colored pencil, circle the clade that includes all gymnosperms 10. Can you tell…arrow_forwardYou have been hired as a public relations specialist to give invertebrates a good name. After all, they are much more than just creepy crawly bugs! Your first task though is to convince yourself that is true. The best way to do that is to start close to home. Find something in your house that is a product obtained directly from an invertebrate or only due to an invertebrate’s actions. Describe the product, its function and utility, as well as any human manufactured alternatives. Be sure to highlight the advantages of obtaining this directly from nature. Keep in mind, a product can be something you use, wear, eat, or enjoy for its visual appeal.arrow_forward
- Use the following tree diagram to answer Questions #8-10. 8) Which of the following two animals are the most closely related based on the tree to the left? a) Pig and camel b) Hippo and pig c) Deer and cow 9) CIRCLE on the tree diagram where the common ancestor between a hippo and a cow is. 10) Put a SQUARE on the tree diagram where the common ancestor between a pig and a peccary is.arrow_forwardExplain: Healthy Cell Function Overview→ Briefly describe how a healthy cell usually works: metabolism (ATP production), pH balance, glycogen storage, ion transport, enzymes, etc. Gene Mutation and Genetics Part→ Focus on the autosomal recessive mutation and explain: How gene mutation affects the cell. How autosomal inheritance works. Compare the normal and mutated gene sequences simply. → Talk about possible consequences of a faulty hydrolytic enzyme.arrow_forwardCan you fill out those termsarrow_forward
- Explain down bellow what happens to the cell: Decreased pH in mitochondria Increased ATP Decreased pH in cytosol Increased hydrolysis Decreasing glycogen and triglycerides Increased MAP kinase activity Poor ion transport → For each one:→ What normally happens?→ What is wrong now?→ How does it mess up the cell?arrow_forwardAn 1100 pound equine patient was given 20 mg/kg sucralfate 3 times a day, 2.8 mg/kg famotidine twice a day, and 10mg/kg doxycycline twice a day. Sucralfate comes as a 1 gm tablet, famotidine as 20 mg tablets, and doxycycline as 100mg tablets. All are in bottles of 100 tablets.How many total mg are needed for the patient and how many tablets of each would be needed to provide each dose?How many bottles of each would be needed to have available if this patient were to be on this drug regimen for 5 days?arrow_forwardThe patient needs a solution of 2.5% dextrose in Lactated Ringer’s solution to run at 75 ml/hr for at least the next 12hours. LRS comes in fluid bags of 500 ml, 1 Liter, 3 Liters and 5 Liters. How can a 2.5% solution be made by adding50% dextrose to the LRS?arrow_forward
 Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage LearningEssentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage
Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage LearningEssentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage- Understanding Health Insurance: A Guide to Billin...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337679480Author:GREENPublisher:CengageSurgical Tech For Surgical Tech Pos CareHealth & NutritionISBN:9781337648868Author:AssociationPublisher:Cengage





