
Concept explainers
1.
Prepare general journal entries to record transactions (a) through (k).
1.
Explanation of Solution
Job order costing is one of the methods of cost accounting under which cost is collected and gathered for each job, work order, or project separately. It is a system by which a factory maintains a separate record of each particular quantity of product that passes through the factory. Job order costing is used when the products produced are significantly different from each other.
Prepare
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| a. | Material | 45,000 | |
| Accounts payable | 45,000 | ||
| (To record the purchase of materials on account.) | |||
| b. | Work in process | 10,000 | |
| Work in process | 11,000 | ||
| Work in process | 9,500 | ||
| Work in process | 12,200 | ||
| Materials | 42,700 | ||
| (To record issuance of direct materials for the job: job no.201,202,203,204) | |||
| c. | Factory overhead | 7,500 | |
| Materials | 7,500 | ||
| (To record the issuance of indirect materials) | |||
| d. | Work in process | 18,000 | |
| Work in process | 19,000 | ||
| Work in process | 20,500 | ||
| Work in process | 17,500 | ||
| Wages payable | 75,000 | ||
| (To record direct labor incurred for the job: job no.201,202,203,204) | |||
| e. | Factory overhead | 11,000 | |
| Wages payable | 11,000 | ||
| (To record the indirect labor charged to production) | |||
| f. | Factory overhead | 7,000 | |
| Cash | 7,000 | ||
| (To record the payment of electricity bill, heating oil, and repairs bills for the factory and charge made to production) | |||
| g. | Factory overhead | 40,000 | |
| | 40,000 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expense on factory equipment) | |||
| h. | Work in process | 15,000 | |
| Work in process | 16,500 | ||
| Work in process | 16,500 | ||
| Work in process | 18,000 | ||
| Factory overhead | 66,000 | ||
| (To record applied factory overhead to the job: job no.201,202,203,204) | |||
| i. | Finished goods (Product C) | 43,000 | |
| Work in process | 43,000 | ||
| (To record the transfer of Job no. 201 to Product C) | |||
| Finished goods (Product D) | 46,500 | ||
| Work in process | 46,500 | ||
| (To record the transfer of Job no.202 to Product D) | |||
| Finished goods (Product E) | 46,500 | ||
| Work in process | 46,500 | ||
| (To record the transfer of Job no.203 to Product E) | |||
| j. | Accounts receivable | 47,000 | |
| Sales | 47,000 | ||
| (To record sale of product C) | |||
| Cost of goods sold | 43,000 | ||
| Finished goods (Product C) | 43,000 | ||
| (To record cost of goods sold on finished goods of Product C) | |||
| Accounts receivable | 49,000 | ||
| Sales | 49,000 | ||
| (To record sale of product D) | |||
| Cost of goods sold | 46,500 | ||
| Finished goods (Product D) | 46,500 | ||
| (To record cost of goods sold on finished goods of Product D) | |||
| k. | Factory overhead | 500 | |
| Cost of goods sold (2) | 500 | ||
| (To record cost of goods sold) |
(Table 1)
Working note:
(1) Calculate the actual factory overhead:
(2) Calculate the cost of goods sold:
2.
2.
Explanation of Solution
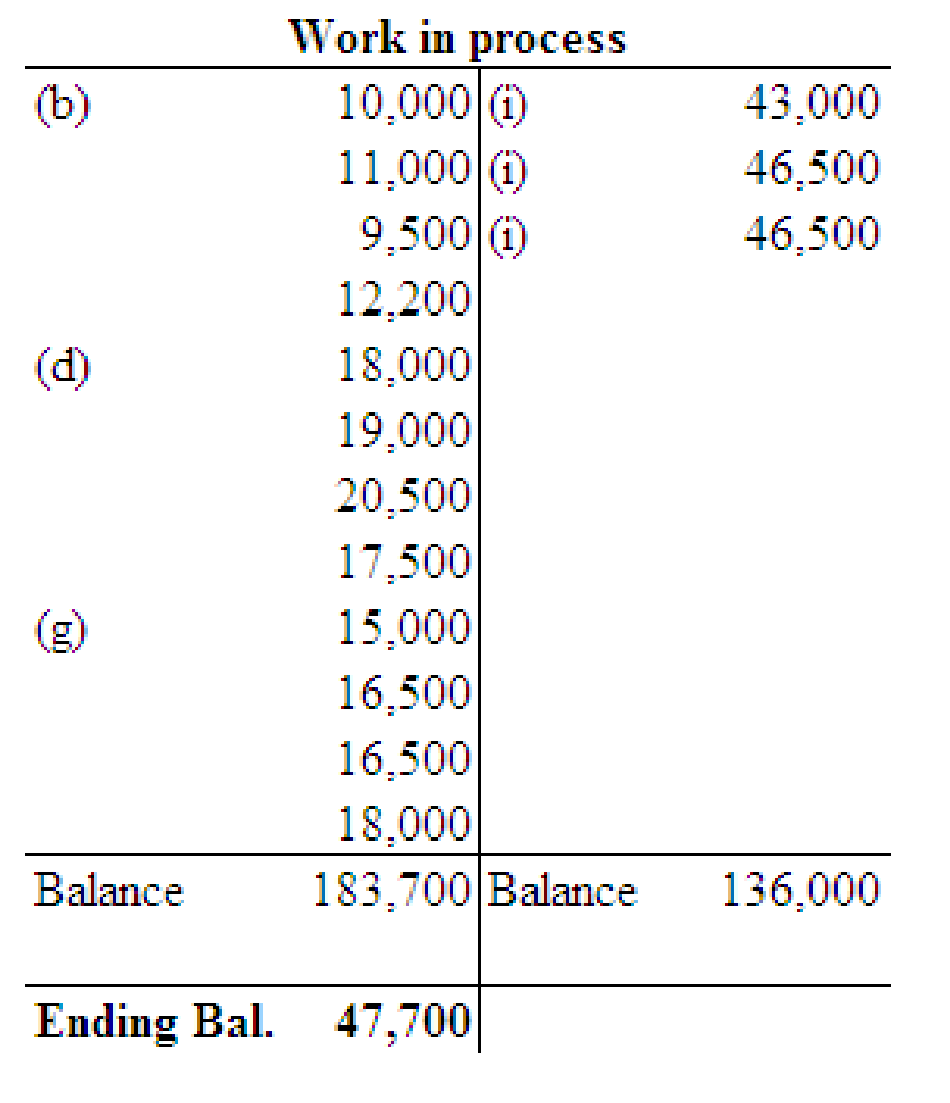
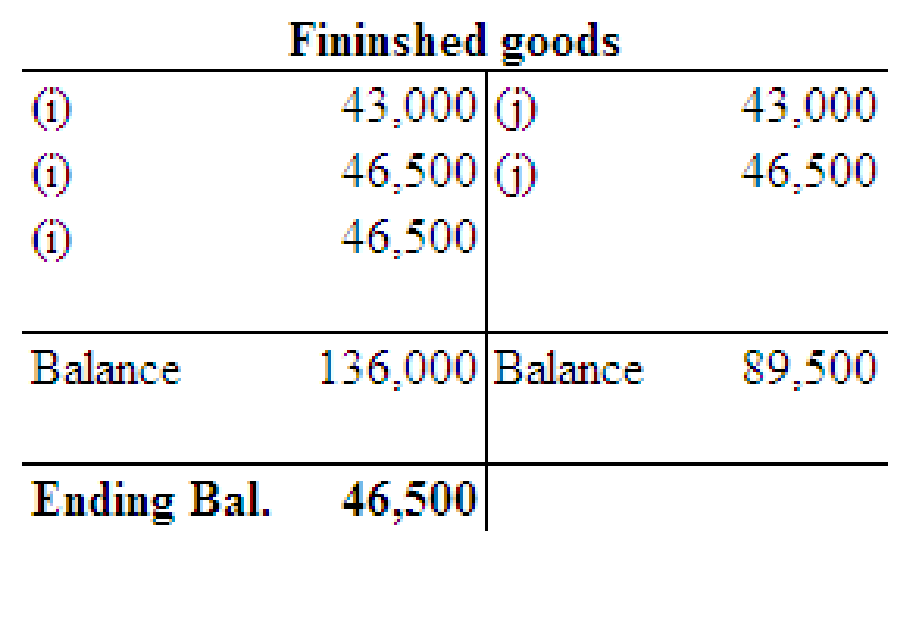
Post the entries to the work in process and finished goods T accounts and determine the ending balances in these accounts.
3.
Compute the balance in the job cost ledger and verify whether the balance agrees with that in the work in process control account.
3.
Explanation of Solution
The balance of the job cost ledger (Job No.204) is $47,700
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Accounting from Heintz and Parry)
- What was the net cash flow provided by opening activities for horizon industries?arrow_forwardBlue Oak, Inc., uses direct labor hours to allocate overhead costs. If Blue Oak estimates $60,000 of overhead and 75,000 hours of direct labor this period, the overhead applied when 6,000 direct labor hours are used should be_____. a. $4,200.33 b. $4,800.00 c. $5,125.48 d. $5,865.75arrow_forwardGiven answer with step by step calculationarrow_forward
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning





