
Concept explainers
1.
Prepare general journal entries to record transactions (a) through (k) and make compound entries for (b), (d), and (h), with separate debits for each job.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Job order costing is one of the methods of cost accounting under which cost is collected and gathered for each job, work order, or project separately. It is a system by which a factory maintains a separate record of each particular quantity of product that passes through the factory. Job order costing is used when the products produced are significantly different from each other.
Prepare
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| a. | Material | 45,000 | |
| Accounts payable | 45,000 | ||
| (To record the purchase of materials on account.) | |||
| b. | Work in process | 10,000 | |
| Work in process | 11,000 | ||
| Work in process | 9,500 | ||
| Work in process | 12,200 | ||
| Materials | 42,700 | ||
| (To record issuance of direct materials for the job: job no.201,202,203,204) | |||
| c. | Factory | 7,500 | |
| Materials | 7,500 | ||
| (To record the issuance of indirect materials) | |||
| d. | Work in process | 18,000 | |
| Work in process | 19,000 | ||
| Work in process | 20,500 | ||
| Work in process | 17,500 | ||
| Wages payable | 75,000 | ||
| (To record direct labor incurred for the job: job no.201,202,203,204) | |||
| e. | Factory overhead | 11,000 | |
| Wages payable | 11,000 | ||
| (To record the indirect labor charged to production) | |||
| f. | Factory overhead | 7,000 | |
| Cash | 7,000 | ||
| (To record the payment of electricity bill, heating oil, and repairs bills for the factory and charge made to production) | |||
| g. | Factory overhead | 40,000 | |
| | 40,000 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expense on factory equipment) | |||
| h. | Work in process | 15,000 | |
| Work in process | 16,500 | ||
| Work in process | 16,500 | ||
| Work in process | 18,000 | ||
| Factory overhead | 66,000 | ||
| (To record applied factory overhead to the job: job no.201,202,203,204) | |||
| i. | Finished goods (Product C) | 43,000 | |
| Work in process | 43,000 | ||
| (To record the transfer of Job no. 201 to Product C) | |||
| Finished goods (Product D) | 46,500 | ||
| Work in process | 46,500 | ||
| (To record the transfer of Job no.202 to Product D) | |||
| Finished goods (Product E) | 46,500 | ||
| Work in process | 46,500 | ||
| (To record the transfer of Job no.203 to Product E) | |||
| j. | Accounts receivable | 47,000 | |
| Sales | 47,000 | ||
| (To record sale of product C) | |||
| Cost of goods sold | 43,000 | ||
| Finished goods (Product C) | 43,000 | ||
| (To record cost of goods sold on finished goods of Product C) | |||
| Accounts receivable | 49,000 | ||
| Sales | 49,000 | ||
| (To record sale of product D) | |||
| Cost of goods sold | 46,500 | ||
| Finished goods (Product D) | 46,500 | ||
| (To record cost of goods sold on finished goods of Product D) | |||
| k. | Factory overhead | 500 | |
| Cost of goods sold (2) | 500 | ||
| (To record cost of goods sold) |
(Table 1)
Working note:
(1) Calculate the actual factory overhead:
(2) Calculate the cost of goods sold:
2.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Post the entries to the work in process and finished goods T accounts and determine the ending balances in these accounts.
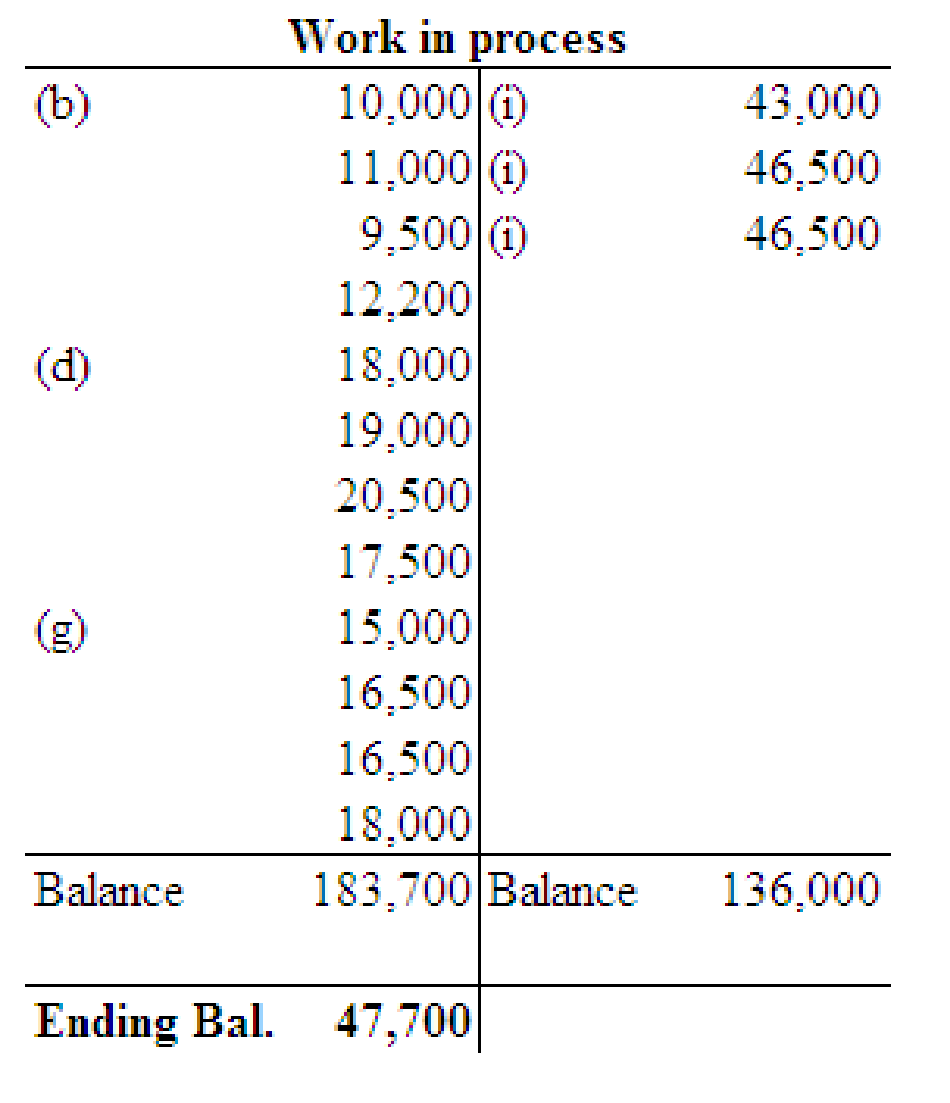
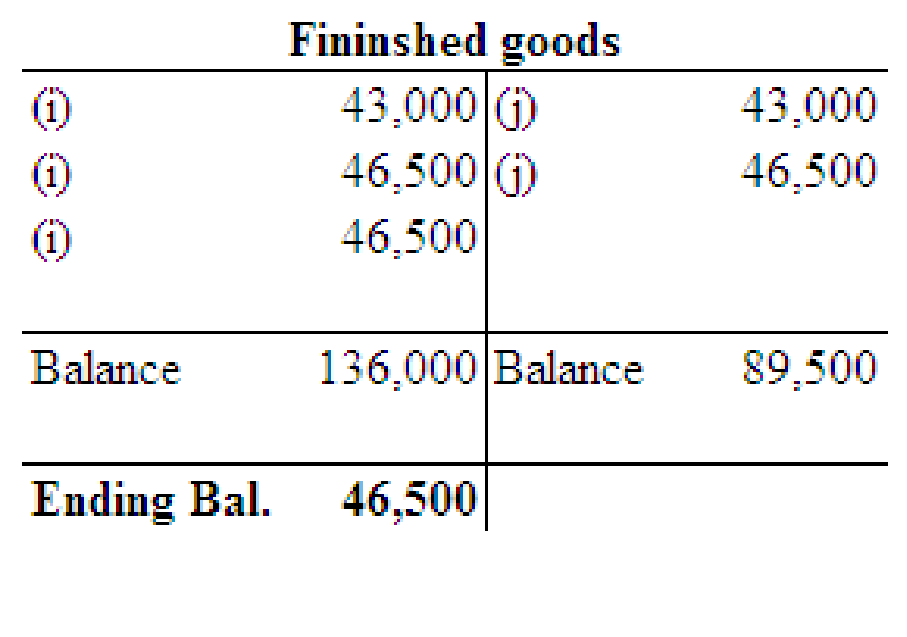
3.
Compute the balance in the job cost ledger and verify whether the balance agrees with that in the work in process control account.
3.
Explanation of Solution
The balance of the job cost ledger (Job No.204) is $47,700
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
Bundle: College Accounting, Chapters 1-27, Loose-leaf Version, 23rd + Cengagenowv2, 2 Terms Printed Access Card
- Can you help me find the accurate solution to this financial accounting problem using valid principles?arrow_forwardCan you demonstrate the accurate method for solving this financial accounting question?arrow_forwardCan you explain this financial accounting question using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forward
- Jasmine Manufacturing Inc. assigns overhead to specific production jobs based on machine hours. At the beginning of the current year, estimated overhead costs were $840,000, and estimated machine hours were 60,000. By the end of the year, actual overhead costs were $875,000, and actual machine hours were 62,500.arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting question using the correct accounting procedures?arrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this general accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forward
- Profit margin?arrow_forwardAlec Manufacturing produces a single product, with a selling price of $18 and a variable cost of $11. Fixed costs are $175,000 per period. What volume of sales in units is needed to earn a profit of $105,000 per period?arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting problem using appropriate accounting principles?arrow_forward
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning





