
wo techniques commonly used to study the expression patterns of genes that play a role in development are Northern blotting and in situ hybridization. As described in Chapter 21, Northern blotting is used to detect RNA that is transcribed from a particular gene. In this method, a specific RNA is detected by using a short segment of cloned DNA as a probe. The DNA probe, which is labeled, is complementary to the RNA that the researcher wishes to detect. After the DNA probe binds to the RNA within a blot of a gel, the RNA is visualized as a labeled band on a nylon membrane. For example, a DNA probe that is complementary to the bicoid mRNA could be used to specifically detect the amount of that mRNA in a blot.
A second technique, termed fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), is used to identify the locations of genes on chromosomes. This technique is also used to locate gene products within oocytes, embryos, and larvae. Thus, it has been commonly used by developmental geneticists to understand the expression patterns of genes during development. The micrograph in Figure 26.8b is derived from the application of the FISH technique. In this case, the probe was complementary to bicoid mRNA.
Now here is the question. Suppose a researcher has three different Drosophila strains that have loss-of-function mutations in the bicoid gene. We will call them bicoid-A, bicoid-B, and bicoid-C; the wild type is designated bicoid+. To study these mutations,
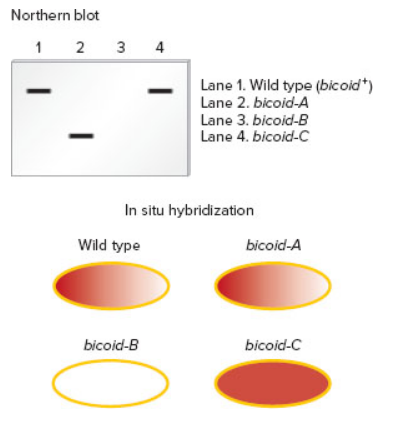
A. How can phenotypically normal female flies be homozygous for a loss-of-function allele in the bicoid gene?
B. Explain the type of mutation (e.g., deletion, point mutation, etc.) in each of the three strains. Explain how the mutation may cause a loss of normal function for the bicoid gene product.
C. Discuss how the use of both techniques provides more definitive information than the application of just one of the techniques.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 26 Solutions
Genetics: Analysis and Principles
- Explain in a small summary how: What genetic information can be obtained from a Punnet square? What genetic information cannot be determined from a Punnet square? Why might a Punnet Square be beneficial to understanding genetics/inheritance?arrow_forwardIn a small summary write down:arrow_forwardNot part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forward
- Noggin mutation: The mouse, one of the phenotypic consequences of Noggin mutationis mispatterning of the spinal cord, in the posterior region of the mouse embryo, suchthat in the hindlimb region the more ventral fates are lost, and the dorsal Pax3 domain isexpanded. (this experiment is not in the lectures).a. Hypothesis for why: What would be your hypothesis for why the ventral fatesare lost and dorsal fates expanded? Include in your answer the words notochord,BMP, SHH and either (or both of) surface ectoderm or lateral plate mesodermarrow_forwardNot part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forwardNot part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStaxCase Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStaxCase Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning





