
MASTERPHYS:KNIGHT'S PHYSICS ACCESS+WKB
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780135245033
Author: Knight
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 25, Problem 5CQ
Rank in order, from most positive to most negative, the potential
energies
field of FIGURE Q25.5. Explain.
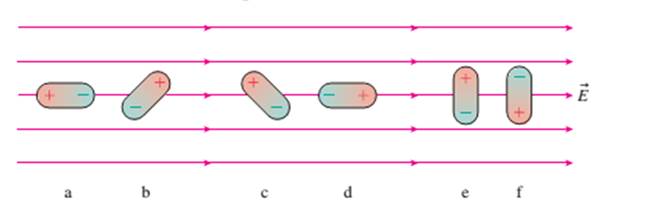
FIGURE Q25.5
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Imagine a planet where gravity mysteriously acts tangent to the equator and in the eastward directioninstead of radially inward. Would this force do work on an object moving on the earth? What is the sign ofthe work, and does it depend on the path taken? Explain by using the work integral and provide a sketch ofthe force and displacement vectors. Provide quantitative examples.
If a force does zero net work on an object over a closed loop, does that guarantee the force is conservative? Explain with an example or counterexample
A futuristic amusement ride spins riders in a horizontal circle of radius 5 m at a constant speed. Thefloor drops away, leaving riders pinned to the wall by friction (coefficient µ = 0.4). What minimum speedensures they don’t slip, given g = 10 m/s²? Draw diagram (or a few) showing all forces, thevelocity of the rider, and their acceleration
Chapter 25 Solutions
MASTERPHYS:KNIGHT'S PHYSICS ACCESS+WKB
Ch. 25 - a. Charge q1is distance r from a positive point...Ch. 25 - FIGURE Q25.2 shows the potential energy of a...Ch. 25 - An electron moves along the trajectory of FIGURE...Ch. 25 - Two protons are launched with the same speed from...Ch. 25 - Rank in order, from most positive to most...Ch. 25 - FIGURE Q25.6 shows the electric potential along...Ch. 25 - A capacitor with plates separated by distance d is...Ch. 25 - Prob. 8CQCh. 25 - FIGURE Q25.9 shows two points inside a capacitor....Ch. 25 - FIGURE Q25.10 shows two points near a positive...
Ch. 25 - ll. FIGURE Q25.11 shows three points near two...Ch. 25 - Reproduce FIGURE Q25.12 on your paper. Then draw a...Ch. 25 - I. The electric field strength is 20,000 N/C...Ch. 25 - The electric field strength is 50,000 N/C inside a...Ch. 25 - A proton is released from rest at the positive...Ch. 25 - A proton is released from rest at the positive...Ch. 25 - Prob. 5EAPCh. 25 - What is the electric potential energy of the group...Ch. 25 - What is the electric potential energy of the group...Ch. 25 - Two positive point charges are 5.0 cm apart. If...Ch. 25 - A water molecule perpendicular to an electric...Ch. 25 - FIGURE EX25.10 shows the potential energy of an...Ch. 25 - What is the speed of a proton that has been...Ch. 25 - I What is the speed of an electron that has been...Ch. 25 - What potential difference is needed to accelerate...Ch. 25 - Prob. 14EAPCh. 25 - A proton with an initial speed of 800,000 m/s is...Ch. 25 - Prob. 16EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 17EAPCh. 25 - In proton-beam therapy, a higher-energy beam of...Ch. 25 - Prob. 19EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 20EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 21EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 22EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 23EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 24EAPCh. 25 - Two 2.0-cm-diameter disks spaced 2.0 mm apart form...Ch. 25 - In FIGURE EX25.26, a proton is fired with a speed...Ch. 25 - Prob. 27EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 28EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 29EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 30EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 31EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 32EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 33EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 34EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 35EAPCh. 25 - A 5.0-cm-diamtere metal ball has a surface charge...Ch. 25 - Prob. 37EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 38EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 39EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 40EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 41EAPCh. 25 - The four 1.0 g sphere shown in FIGURE P25.42 are...Ch. 25 - A proton’s speed as it passes point A is 50,000...Ch. 25 - Prob. 44EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 45EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 46EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 47EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 48EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 49EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 50EAPCh. 25 - What is the escape speed of an electron launched...Ch. 25 - Prob. 52EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 53EAPCh. 25 - Il A 2.0-mm-diameter glass bead is positively...Ch. 25 - Prob. 55EAPCh. 25 - Il A proton is fired from far away toward the...Ch. 25 - Prob. 57EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 58EAPCh. 25 - Il One form of nuclear radiation, beta decay,...Ch. 25 - Il Two 10-cm-diameterelectrodes 0.50 cm a part...Ch. 25 - Il Two 10-cm-diameter electrodes 0.50 cm apart...Ch. 25 - Il Electrodes of area A are spaced distance d...Ch. 25 - Prob. 63EAPCh. 25 - Il Two spherical drops of mercury each have a...Ch. 25 - Prob. 65EAPCh. 25 - Il FIGURE P25.66 shows two uniformly charged...Ch. 25 - Prob. 67EAPCh. 25 - Il The arrangement of charges shown in FIGURE...Ch. 25 - Il FIGURE P25.69 shows a thin rod of length L and...Ch. 25 - Il FIGURE P25.69 shows a thin rod of length L and...Ch. 25 - I FIGURE P25.71 shows a thin rod with charge Q...Ch. 25 - Prob. 72EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 73EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 74EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 75EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 76EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 77EAPCh. 25 - Il A proton and an alpha particle (q = +2e, m = 4...Ch. 25 - Ill Bead A has a mass of 15 g and a charge of —5.0...Ch. 25 - Il Two 2.0-mm-diameter beads, C and D, are 10 mm...Ch. 25 - Il A thin rod of length L and total charge Q has...Ch. 25 - Il A hollow cylindrical shell of length L and...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Your RL circuit has a characteristic time constant of 19.5 ns, and a resistance of 4.60 MQ. (a) What is the inductance (in H) of the circuit? 0.00897 × H (b) What resistance (in MQ) should you use (instead of the 4.60 MQ resistor) to obtain a 1.00 ns time constant, perhaps needed for quick response in an oscilloscope? 8.97 * ΜΩarrow_forwardYour RL circuit has a characteristic time constant of 19.5 ns, and a resistance of 4.60 MQ. (a) What is the inductance (in H) of the circuit? H (b) What resistance (in MQ) should you use (instead of the 4.60 MQ resistor) to obtain a 1.00 ns time constant, perhaps needed for quick response in an oscilloscope? ΜΩarrow_forwardAt a distance of 0.212 cm from the center of a charged conducting sphere with radius 0.100cm, the electric field is 485 N/C . What is the electric field 0.598 cm from the center of the sphere? At a distance of 0.196 cmcm from the axis of a very long charged conducting cylinder with radius 0.100cm, the electric field is 485 N/C . What is the electric field 0.620 cm from the axis of the cylinder? At a distance of 0.202 cm from a large uniform sheet of charge, the electric field is 485 N/C . What is the electric field 1.21 cm from the sheet?arrow_forward
- A hollow, conducting sphere with an outer radius of 0.260 m and an inner radius of 0.200 m has a uniform surface charge density of +6.67 × 10−6 C/m2. A charge of -0.800 μC is now introduced into the cavity inside the sphere. What is the new charge density on the outside of the sphere? Calculate the strength of the electric field just outside the sphere. What is the electric flux through a spherical surface just inside the inner surface of the sphere?arrow_forwardA point charge of -3.00 μC is located in the center of a spherical cavity of radius 6.60 cm inside an insulating spherical charged solid. The charge density in the solid is 7.35 × 10−4 C/m3. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field inside the solid at a distance of 9.10 cm from the center of the cavity. Find the direction of this electric field.arrow_forwardAn infinitely long conducting cylindrical rod with a positive charge λ per unit length is surrounded by a conducting cylindrical shell (which is also infinitely long) with a charge per unit length of −2λ and radius r1, as shown in the figure. What is E(r), the radial component of the electric field between the rod and cylindrical shell as a function of the distance r from the axis of the cylindrical rod? Express your answer in terms of λ, r, and ϵ0, the permittivity of free space. What is σinner, the surface charge density (charge per unit area) on the inner surface of the conducting shell? What is σouterσouter, the surface charge density on the outside of the conducting shell? (Recall from the problem statement that the conducting shell has a total charge per unit length given by −2λ.) What is the radial component of the electric field, E(r), outside the shell?arrow_forward
- A very long conducting tube (hollow cylinder) has inner radius aa and outer radius b. It carries charge per unit length +α, where αα is a positive constant with units of C/m. A line of charge lies along the axis of the tube. The line of charge has charge per unit length +α. Calculate the electric field in terms of α and the distance r from the axis of the tube for r<a. Calculate the electric field in terms of α and the distance rr from the axis of the tube for a<r<b. Calculate the electric field in terms of αα and the distance r from the axis of the tube for r>b. What is the charge per unit length on the inner surface of the tube? What is the charge per unit length on the outer surface of the tube?arrow_forwardTwo small insulating spheres with radius 9.00×10−2 m are separated by a large center-to-center distance of 0.545 m . One sphere is negatively charged, with net charge -1.75 μC , and the other sphere is positively charged, with net charge 3.70 μC . The charge is uniformly distributed within the volume of each sphere. What is the magnitude E of the electric field midway between the spheres? Take the permittivity of free space to be ϵ0 = 8.85×10−12 C2/(N⋅m2) . What is the direction of the electric field midway between the spheres?arrow_forwardA conducting spherical shell with inner radius aa and outer radius bb has a positive point charge Q located at its center. The total charge on the shell is -3Q, and it is insulated from its surroundings. Derive the expression for the electric field magnitude in terms of the distance r from the center for the region r<a. Express your answer in terms of some or all of the variables Q, a, b, and appropriate constants. Derive the expression for the electric field magnitude in terms of the distance rr from the center for the region a<r<b. Derive the expression for the electric field magnitude in terms of the distance rr from the center for the region r>b. What is the surface charge density on the inner surface of the conducting shell? What is the surface charge density on the outer surface of the conducting shell?arrow_forward
- A small sphere with a mass of 3.00×10−3 g and carrying a charge of 4.80×10−8 C hangs from a thread near a very large, charged insulating sheet, as shown in the figure (Figure 1). The charge density on the sheet is −2.20×10−9 C/m2 . Find the angle of the thread.arrow_forwardA small conducting spherical shell with inner radius aa and outer radius bb is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and outer radius d (Figure 1). The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge −2q. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field in terms of q and the distance rr from the common center of the two shells for r<a. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field for a<r<b. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field for b<r<c.arrow_forwardA cube has sides of length L = 0.800 m . It is placed with one corner at the origin as shown in the figure. The electric field is not uniform but is given by E→=αxi^+βzk^, where α=−3.90 and β= 7.10. What is the sum of the flux through the surface S5 and S6? What is the sum of the flux through the surface S2 and S4? Find the total electric charge inside the cube.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY