
Introduction:
Net Operating Income:
An income generated from the revenue of the business after deduction all operating expenses of the business refers to net operating income. In other words, net operating income is the difference between the revenue generated and expenses that are directly incurred for the revenue generation of the business. Net Operating income is the key indicator of the profitability and financial soundness of the company.
Payment of interest, taxes,
To prepare:
The three-column comparative income statement of Windmire manufacturers that shows the operating income without the special order, income received from new business and income from normal business and new business.
Answer to Problem 4BPSB
Solution:
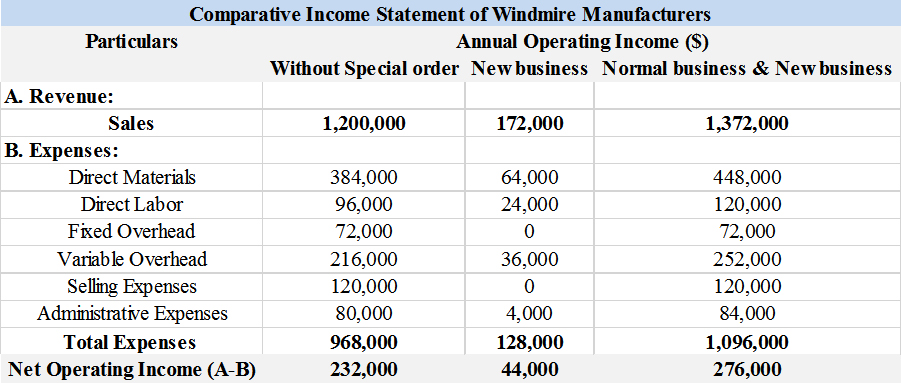
Explanation of Solution
Net Operating Income is calculated by using the formula:
An operating expenses includes cost of goods sold and selling, general and administrative expenses.
Step-1:
Calculation of net operating income without special order:
Revenue:
Given,
Sales unit=300,000 packages
Cost per package=$4
Therefore the revenue from sales for Windmire Manufacturers will be 300,000*$4=$1,200,000
Revenue for Windmire Manufacturers without special order:
Expenses:
Given,
1. Direct Materials: $384,000
2. Direct Labor: $96,000
3.
Fixed Overhead: 25% on overhead i.e. 25% on $288,000= $72,000
Variable Overhead: 75% on overhead i.e.75% on $288,000= $216,000
4. Selling Expenses: $120,000
5. Administrative Expenses: $80,000
Total expenses of Windmire Manufacturers:
Net Operating Income for Windmire Manufacturers without special order:
Step-2:
Calculation of net operating income from new business:
Revenue:
Given,
Sales Units: 50,000 Packages
Cost Per Package: $3.44
Therefore the revenue from sales for Windmire Manufacturers will be 50,000*3.44=$172,000
Revenue for Windmire Manufacturers from new business: $172,000
Expenses:
1. Direct Materials:
Given,
Direct Materials for 300,000 units: $384,000
So Direct Materials for 50,000 units is:
Note: Direct Materials are 100% Variable.
2. Direct Labor
Direct Labor for 300,000 units: $96,000
Direct Labor cost per unit: $96,000/300,000=0.32
Given Direct Labor costs per unit for additional units would be 50% higher than usual labor rate.
Direct Labor costs per unit for 50,000 units will be 0.48 i.e. (0.32+0.32*50%)
So Direct Labor for new business 50,000 units is:
50,000*0.48=$24,000
3. Overhead:
Fixed Overhead: There is no additional fixed costs incurred in new business. Fixed Costs are fixed at 25% from 250,000 to 400,000 units.
Variable Overhead for 300,000 units: 75% on Overhead i.e. 75% on $288,000=$216,000
So Variable Overhead for 50,000 units:
50,000*216,000/300,000=$36,000
4. Selling Expenses:
There is no additional selling expenses for accepting the new business.
5. Administrative Expenses:
Given that new business would increase administrative expenses by $5,000 fixed amount.
Total expenses of Windmire Manufacturers:
Net Operating Income for Windmire Manufacturers from new business:
Step-3:
Calculation of net operating income from normal business and new business:
Revenue:
Given,
Sales Units in normal business: 300,000 Packages
Cost Per Package: $4
Sales Units in new business: 50,000
Cost Per Package: $3.44
Therefore the revenue from sales for Windmire Manufacturers will be
Revenue for Windmire Manufacturers from normal and new business: $1,372,000
Expenses:
1. Direct Materials:
Given,
Direct Material for normal business: $384,000
So Direct Materials for new business 50,000 units is:
50,000*384,000/300,000=$64,000
Therefore Direct Materials for both normal and new business:
2. Direct Labor
Direct Labor for normal business 300,000 units: $96,000
So Direct Labor for new business 50,000 units is: $24,000
Therefore Direct Labor for normal and new business:
3. Overhead:
Overhead for normal business 300,000 units: $288,000
Fixed Overhead:
Fixed Overhead for normal business is 25% of total overhead: $72,000
Fixed Overhead for new business: There is no additional fixed costs incurred in new business. Fixed Costs are fixed at 25% from 250,000 to 400,000 units.
Therefore Fixed Overhead for both normal and new business is:
Variable Overhead:
Variable Overhead for normal business 300,000 units: 75% on Overhead i.e. 75% on $288,000= $216,000
Variable Overhead for new business 50,000 units:
Therefore Variable Overhead for normal and new business:
4. Selling Expenses:
Selling Expenses for normal business 300,000 units: $120,000
Selling Expenses for new business 50,000 units: $0
Therefore the selling expenses for normal and new business:
5. Administrative Expenses:
Administrative Expenses for normal business 300,000 units: $80,000
Administrative Expenses for new business 50,000 units: $4,000
Therefore Administrative Expenses for normal and new business:
Total expenses of Windmire Manufacturers:
Net Operating Income for Windmire Manufacturers from normal and new business:
Hence from the comparative income statement of Windmire manufactures, the net operating income for its normal and new business is $276,000.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
FUND.ACCT.PRIN -ONLINE ONLY >I<
- Question: 22 - Hader company has actual sales of $82,000 in April and $63,000 in May. It expects sales of $78,000 in June and $92,000 in July and in August. Assuming that sales are the only source of cash inflows and that half of them are for cash and the remainder are collected evenly over the following 2 months, what are the firm's expected cash receipts for June, July, and August?need answerarrow_forwardA piece of equipment is purchased for $34,750 and has a salvage value of $4,350. The estimated life is 8 years and the method of depreciation is straight-line. Shipping costs total $950 and installation costs are $820. The book value at the end of year 8 is_. a. $3,110 b. $3,200 c. $2,000 d. $4,350 MCQarrow_forwardMCQarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





