
Introduction:
Net Operating Income:
An income generated from the revenue of the business after deduction all operating expenses of the business refers to net operating income. In other words, net operating income is the difference between the revenue generated and expenses that are directly incurred for the revenue generation of the business. Net Operating income is the key indicator of the profitability and financial soundness of the company.
Payment of interest, taxes,
To prepare:
The three-column comparative income statement of Jones manufacturers that shows the operating income without the special order, income received from new business and income from normal business and new business.
Answer to Problem 4APSA
Solution:
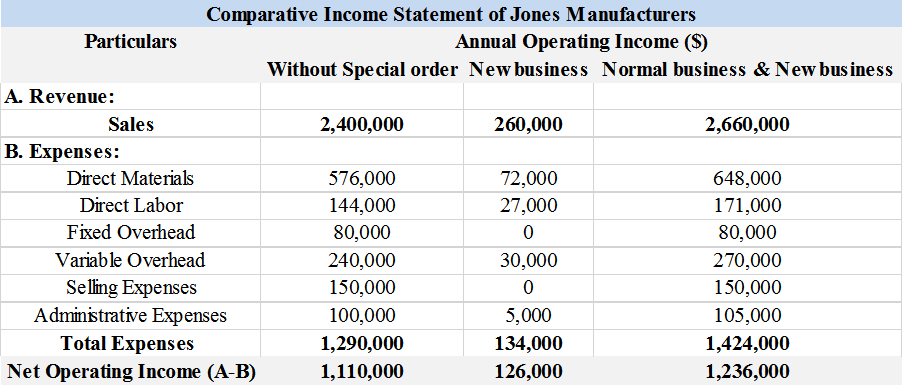
Explanation of Solution
Net Operating Income is calculated by using the formula:
An operating expenses includes cost of goods sold and selling, general and administrative expenses.
Step-1:
Calculation of net operating income without special order:
Revenue:
Given,
Sales unit=400,000 packages
Cost per package=$6
Therefore the revenue from sales for Jones Manufacturers will be
Revenue for Jones Manufacturers without special order: $2,400,000
Expenses:
Given,
1. Direct Materials:
2. Direct Labor:
3.
4. Selling Expenses:
5. Administrative Expenses:
Total expenses of Jones Manufacturers:
Net Operating Income for Jones Manufacturers without special order:
Step-2:
Calculation of net operating income from new business:
Revenue:
Given,
Sales Units: 50,000 Packages
Cost Per Package: $5.20
Therefore the revenue from sales for Jones Manufacturers will be
Revenue for Jones Manufacturers from new business: $260,000
Expenses:
1. Direct Materials:
Given,
Direct Materials for 400,000 units: $576,000
So Direct Materials for 50,000 units is:
Note: Direct Materials are 100% Variable.
2. Direct Labor
Direct Labor for 400,000 units:
Direct Labor cost per unit:
Given Direct Labor costs per unit for additional units would be 50% higher than usual labor rate.
Direct Labor costs per unit for 50,000 units will be
So Direct Labor for new business 50,000 units is:
3. Overhead:
Fixed Overhead: There is no additional fixed costs incurred in new business. Fixed Costs are fixed at 25% from 350,000 t0 500,000 units.
Variable Overhead for 400,000 units: 75% on Overhead i.e.
So Variable Overhead for 50,000 units:
4. Selling Expenses:
There is no additional selling expenses for accepting the new business.
5. Administrative Expenses:
Given that new business would increase administrative expenses by $5,000 fixed amount.
Total expenses of Jones Manufacturers:
Net Operating Income for Jones Manufacturers from new business:
Step-3:
Calculation of net operating income from normal business and new business:
Revenue:
Given,
Sales Units in normal business: 400,000 Packages
Cost Per Package: $6
Sales Units in new business: 50,000
Cost Per Package: $5.20
Therefore the revenue from sales for Jones Manufacturers will be
Revenue for Jones Manufacturers from normal and new business:
Expenses:
1. Direct Materials:
Given,
Direct Material for normal business:
So Direct Materials for new business 50,000 units is:
Therefore Direct Materials for both normal and new business:
$576,000+$72,000=$648,000
2. Direct Labor
Direct Labor for normal business 400,000 units:
So Direct Labor for new business 50,000 units is:
Therefore Direct Labor for normal and new business:
3. Overhead:
Overhead for normal business 400,000 units:
Fixed Overhead:
Fixed Overhead for normal business is 25% of total overhead: $80,000
Fixed Overhead for new business: There is no additional fixed costs incurred in new business. Fixed Costs are fixed at 25% from 350,000 t0 500,000 units.
Therefore Fixed Overhead for both normal and new business is:
Variable Overhead:
Variable Overhead for normal business 400,000 units: 75% on Overhead i.e. 75% on $320,000= $240,000
Variable Overhead for new business 50,000 units:
Therefore Variable Overhead for normal and new business:
4. Selling Expenses:
Selling Expenses for normal business 400,000 units:
Selling Expenses for new business 50,000 units: $0
Therefore the selling expenses for normal and new business:
5. Administrative Expenses:
Administrative Expenses for normal business 400,000 units:
Administrative Expenses for new business 50,000 units:
Therefore Administrative Expenses for normal and new business:
Total expenses of Jones Manufacturers:
Net Operating Income for Jones Manufacturers from normal and new business:
Hence from the comparative income statement of Jones manufactures, the net operating income for its normal and new business is .
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Fundamental Accounting Principles -Hardcover
- Computer Haven sells laptops. During June 2021, it sold 320 laptops at a $1,650 average price each. The June 2021 budget included sales of 350 laptops at an average price of $1,550 each. Compute the sales price variance and the sales volume variance for June 2021.arrow_forwardWhat are the total product cost for the company?arrow_forwardHardy Technologies reports that at an activity level of 6,800 machine-hours in a month, its total variable inspection cost is $320,000 and its total fixed inspection cost is $150,000. What would be the average fixed inspection cost per unit at an activity level of 7,100 machine-hours in a month? Assume that this level of activity is within the relevant range.arrow_forward
- Need help answering question B? Negus Enterprises has an inventory conversion period of 55 days, an average collection period of 42 days, and a payables deferral period of 20 days. Assume that cost of goods sold is 80% of sales. Assume a 365-day year. Do not round intermediate calculations. A. What is the length of the firm's cash conversion cycle? Round your answer to the nearest whole number. 77 days B. If annual sales are $4,635,500 and all sales are on credit, what is the firm's investment in accounts receivable? Round your answer to the nearest dollar. $ C.) How many times per year does Negus Enterprises turn over its inventory? Round your answer to two decimal places. 6.64arrow_forwardI need the correct answer to this general accounting problem using the standard accounting approach.arrow_forwardPlease provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using accurate calculations.arrow_forward
- Provide accounting answer pleasearrow_forwardHow much will cypress need to borrow during December?arrow_forwardThe actual cost of direct materials is $37.50 per pound, while the standard cost per pound is $35.25. During the current period, 5,200 pounds were used in production. What is the direct materials price variance?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





