
Concept explainers
Solve the following problem over the interval from
(a) Analytically.
(b) Euler's method.
(c) Heun's method without iteration.
(d) Ralston's method.
(e) Fourth-order RK method.
(a)
To calculate: The solution of the initial value problem
Answer to Problem 2P
Solution: The solution to the initial value problem is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The initial value problem
Formula used:
To solvean initial value problem of the form
Calculation:
Rewrite the provided differential equation as,
Integrate both sides to get,
Now use the initial condition
Hence, the analytical solution of the initial value problem is
(b)
To calculate: The solution of the initial value problem
Answer to Problem 2P
Solution: For
| t | y |
| 0 | 1 |
| 0.25 | 1.25 |
| 0.5 | 1.809017 |
| 0.75 | 2.817765 |
| 1 | 4.496385 |
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The initial value problem
Formula used:
Solvean initial value problem of the form
Calculation:
From the initial condition
Thus, evaluate the function
Further,
Proceed further and use the following MATLAB code to implement Euler’s method and solve the differential equation.
Execute the above code to obtain the solutions stored in matrix
The results thus obtained are tabulated as,
| T | y |
| 0 | 1 |
| 0.25 | 1.25 |
| 0.5 | 1.809017 |
| 0.75 | 2.817765 |
| 1 | 4.496385 |
(c)
To calculate: The solution of the initial value problem
Answer to Problem 2P
Solution: The solutions are tabulated as,
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The initial value problem
Formula used:
Solve an initial value problem of the form
In the above expression,
Calculation:
From the initial condition
Thus, evaluate the function
And,
Thus,
Proceed further and use the following MATLAB code to implement Heun’s method and solve the differential equation.
Execute the above code to obtain the solutions stored in matrix
Theresults thus obtained aretabulated as,
(d)
To calculate: The solution of the initial value problem
Answer to Problem 2P
Solution: The solutions are tabulated as,
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The initial value problem
Formula used:
Solve an initial value problem of the form
In the above expression,
Calculation:
From the initial condition
Thus, evaluate the function
And,
Thus,
Proceed further and use the following MATLAB code to implement Ralston’s method and solve the differential equation.
Execute the above code to obtain the solutions stored in matrix
The results thus obtained are tabulated as,
(e)
To calculate: The solution of the initial value problem
Answer to Problem 2P
Solution: The solutions are tabulated as,
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The initial value problem
Formula used:
Solve an initial value problem of the form
In the above expression,
Calculation:
From the initial condition
Ans,
And,
And,
Therefore,
Proceed further and use the following MATLAB code to implement RK method of order four, solve the differential equation, and compare the results obtained from part (a) to part (e) on a single plot.
Execute the above code to obtain the solutions stored in matrix
The results thus obtained are tabulated as,
Plot for all the methods along with the analytical solution
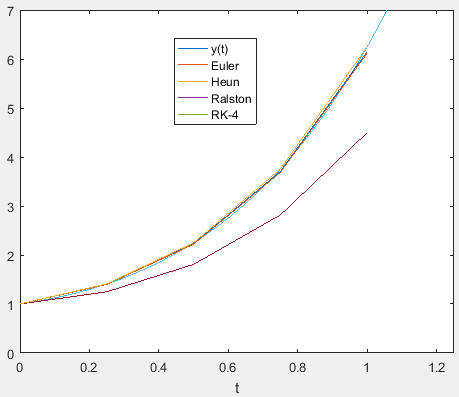
From the graph, it is inferred that the RK method of order 4 is the best approximation to the solution.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
EBK NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ENGINEERS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
College Algebra Essentials (5th Edition)
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)
Elementary Statistics ( 3rd International Edition ) Isbn:9781260092561
College Algebra (7th Edition)
- Q3)A: Given H(x,y)=x2-x+ y²as a first integral of an ODEs, find this ODES corresponding to H(x,y) and show the phase portrait by using Hartman theorem and by drawing graph of H(x,y)-e. Discuss the stability of critical points of the corresponding ODEs.arrow_forwardQ/ Write Example is First integral but not Conservation system.arrow_forwardQ/ solve the system X° = -4X +2XY-8 y°= 2 4y² - x2arrow_forward
- Q4: Discuss the stability critical point of the ODES x + sin(x) = 0 and draw phase portrait.arrow_forwardUsing Karnaugh maps and Gray coding, reduce the following circuit represented as a table and write the final circuit in simplest form (first in terms of number of gates then in terms of fan-in of those gates). HINT: Pay closeattention to both the 1’s and the 0’s of the function.arrow_forwardRecall the RSA encryption/decryption system. The following questions are based on RSA. Suppose n (=15) is the product of the two prime numbers 3 and 5.1. Find an encryption key e for for the pair (e, n)2. Find a decryption key d for for the pair (d, n)3. Given the plaintext message x = 3, find the ciphertext y = x^(e) (where x^e is the message x encoded with encryption key e)4. Given the ciphertext message y (which you found in previous part), Show that the original message x = 3 can be recovered using (d, n)arrow_forward
- Theorem 1: A number n ∈ N is divisible by 3 if and only if when n is writtenin base 10 the sum of its digits is divisible by 3. As an example, 132 is divisible by 3 and 1 + 3 + 2 is divisible by 3.1. Prove Theorem 1 2. Using Theorem 1 construct an NFA over the alphabet Σ = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}which recognizes the language {w ∈ Σ^(∗)| w = 3k, k ∈ N}.arrow_forwardRecall the RSA encryption/decryption system. The following questions are based on RSA. Suppose n (=15) is the product of the two prime numbers 3 and 5.1. Find an encryption key e for for the pair (e, n)2. Find a decryption key d for for the pair (d, n)3. Given the plaintext message x = 3, find the ciphertext y = x^(e) (where x^e is the message x encoded with encryption key e)4. Given the ciphertext message y (which you found in previous part), Show that the original message x = 3 can be recovered using (d, n)arrow_forwardFind the sum of products expansion of the function F(x, y, z) = ¯x · y + x · z in two ways: (i) using a table; and (ii) using Boolean identities.arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage


 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning





