
MASTERY PROBLEM
Bob’s Acme Supermarket has been in operation for many years, offering high-quality groceries, produce, and meat at reasonable prices. Accounting records are maintained on a departmental basis with assignment of direct expenses and allocation of indirect expenses through the use of various procedures. Selected operating information for the year ended December 31, 20--, is as follows:
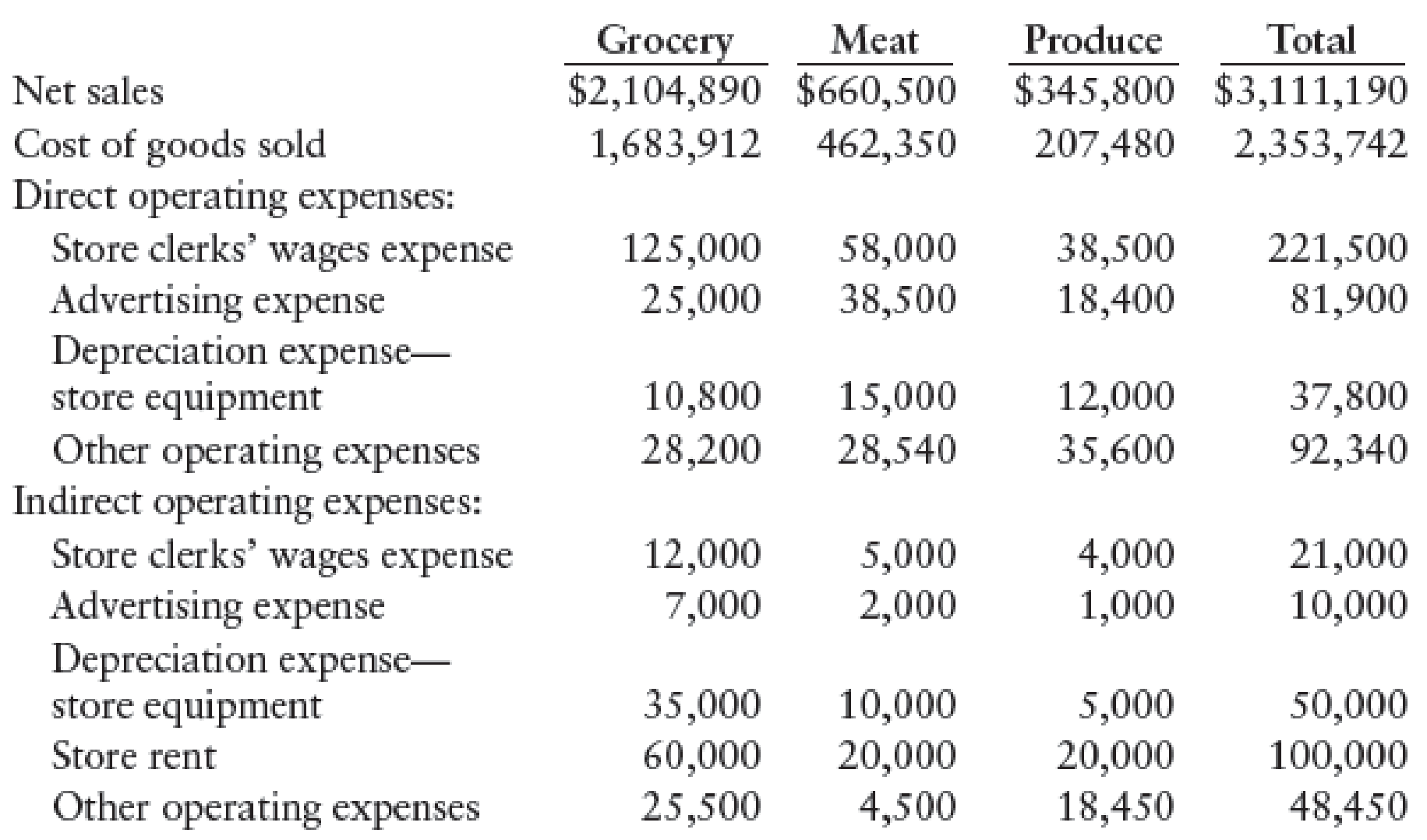
REQUIRED
1. (a) Prepare an income statement showing departmental operating income.
(b) Compute the gross profit percentage and operating income percentage for each department (round to the nearest tenth of a percent).
2. (a) Prepare an income statement showing departmental and total direct operating margins.
(b) Compute the departmental direct operating margin percentage for each department (round to the nearest tenth of a percent).
3. Should Bob be concerned about the profitability of the three departments? Should any of the departments be discontinued?
1-a
Prepare an income statement for A Supermarket for the year ended December 31, 20--, showing the departmental operating income.
Explanation of Solution
Departmental operating income: The departmental income statement reports the departmental operating income, which is the excess of departmental gross profit over the operating expenses incurred.
Formula for departmental operating income:
Prepare an income statement for A Supermarket for the year ended December 31, 20--, showing the departmental operating income.
| A Supermarket | ||||
| Income Statement | ||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 20-- | ||||
| Grocery | Meat | Produce | Total | |
| Sales | $2,104,890 | $660,500 | $345,800 | $3,111,190 |
| Cost of goods sold | 1,683,912 | 462,350 | 207,480 | 2,353,742 |
| Gross profit | $420,978 | $198,150 | $138,320 | $757,448 |
| Operating expenses: | ||||
| Store clerks’ wages expense | $137,000 | $63,000 | $42,500 | $242,500 |
| Advertising expense | 32,000 | 40,500 | 19,400 | 91,900 |
| Depreciation expense-Equipment | 45,800 | 25,000 | 17,000 | 87,800 |
| Store rent | 60,000 | 20,000 | 20,000 | 100,000 |
| Other operating expenses | 53,700 | 33,040 | 54,050 | 140,790 |
| Total operating expenses | 328,500 | 181,540 | 152,950 | 662,990 |
| Operating income | $92,478 | $16,610 | $(14,630) | $94,458 |
Table (1)
Thus, the income statement of A Supermarket shows a departmental operating income (loss) of $92,478 and $16,610, and $(14,630) for grocery, meat, and produce departments respectively.
b.
Ascertain the gross profit percentage and operating income percentage for all the departments.
Explanation of Solution
Gross profit percentage: The percentage of gross profit generated by every dollar of net sales is referred to as gross profit percentage. This ratio measures the profitability of a company by quantifying the amount of income earned from sales revenue generated after cost of goods sold are paid. The higher the ratio, the more ability to cover operating expenses.
Formula to compute gross profit percentage:
Operating income percentage: This ratio gauges the operating profitability by quantifying the amount of operating income earned from business operations from the sales generated.
Formula of operating income percentage:
Ascertain the departmental gross profit percentage for all the departments.
| Departments | Departmental Gross Profit | ÷ | Sales | = | Departmental Gross Profit Percentage |
| Grocery | $420,978 | ÷ | $2,104,890 | = | 20% |
| Meat | 198,150 | ÷ | 660,500 | = | 30% |
| Produce | 138,320 | ÷ | 345,800 | = | 40% |
Table (2)
Note: Refer to Table (1) for the value and computation of departmental gross profit for all the departments.
Ascertain the operating income percentage for both the departments.
| Departments | Operating Income | ÷ | Sales | = | Operating Income Percentage |
| Grocery | $92,478 | ÷ | $2,104,890 | = | 4.4% |
| Meat | 16,610 | ÷ | 660,500 | = | 2.5% |
| Produce | (14,630) | ÷ | 345,800 | = | (4.2)% |
Table (3)
Note: Refer to Table (1) for the value and computation of operating income for all the departments.
Thus, the departmental gross profit percentage of Departments Grocery, Meat, and Produce is 20%, 30%, and 40%, and the operating income percentage of Departments Grocery, Meat, and Produce is 4.4%, 2.5% and (4.2)%.
2-a
Prepare an income statement for A Supermarket for the year ended December 31, 20--, showing the departmental direct operating margin for all the departments and the total company.
Explanation of Solution
Departmental direct operating margin: The departmental income statement reports the departmental direct operating margin, which is the excess of departmental gross profit over the direct operating expenses incurred.
Formula for departmental direct operating margin:
Prepare an income statement for A Supermarket for the year ended December 31, 20--, showing the departmental direct operating margin for all the departments and the total company.
| A Supermarket | ||||
| Income Statement | ||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 20-- | ||||
| Grocery | Meat | Produce | Total | |
| Sales | $2,104,890 | $660,500 | $345,800 | $3,111,190 |
| Cost of goods sold | 1,683,912 | 462,350 | 207,480 | 2,353,742 |
| Gross profit | $420,978 | $198,150 | $138,320 | $757,448 |
| Direct operating expenses: | ||||
| Store clerks’ wages expense | $125,000 | $58,000 | $38,500 | $221,500 |
| Advertising expense | 25,000 | 38,500 | 18,400 | 81,900 |
| Depreciation expense-Equipment | 10,800 | 15,000 | 12,000 | 37,800 |
| Other operating expenses | 28,200 | 28,540 | 35,600 | 92,340 |
| Total operating expenses | 189,000 | 140,040 | 104,500 | 433,540 |
| Direct operating margin | $231,978 | $58,110 | $33,820 | $323,908 |
| Indirect operating expenses: | ||||
| Store clerks’ wages expense | $21,000 | |||
| Advertising expense | 10,000 | |||
| Depreciation expense-Equipment | 50,000 | |||
| Store rent | 100,000 | |||
| Other operating expenses | 48,450 | |||
| Total operating expenses | 229,450 | |||
| Operating income | $94,458 | |||
Table (4)
Thus, the income statement of A Supermarket shows a departmental direct operating margin of $231,978 and $58,110, and $33,820 for grocery, meat, and produce departments respectively, and total operating income of $94,458.
b.
Compute the departmental direct operating margin percentage of all the departments.
Explanation of Solution
Direct operating margin percentage: This ratio gauges the operating profitability by quantifying the amount of direct operating income earned from business operations from the sales generated.
Formula of direct operating margin percentage:
Ascertain the direct operating margin percentage for all the departments.
| Departments | Direct Operating Margin | ÷ | Sales | = | Direct Operating Margin Percentage |
| Grocery | $231,978 | ÷ | $2,104,890 | = | 11.0% |
| Meat | 58,110 | ÷ | 660,500 | = | 8.8% |
| Produce | 33,820 | ÷ | 345,800 | = | 9.8% |
Table (5)
Note: Refer to Table (4) for the value and computation of direct operating margin for all the departments.
Thus, the departmental direct operating margin percentage of grocery, meat, and produce departments is 11.0%, 8.8%, and 9.8% respectively.
3.
Explain whether B should be concerned about the profitability of A Supermarket and whether to discontinue any of the departments.
Explanation of Solution
B should not concerned of the profitability of any of the departments of A Supermarket because the operating income of the department produce might not be effective, but the direct operating margin of the department is $33,820. So, produce department should not be discontinued because the operating income of the company would be reduced by $33,820, the direct operating margin of the produce department.
Thus, none of the departments should be discontinued.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
- Please provide the solution to this general accounting question with accurate financial calculations.arrow_forwardI am looking for help with this general accounting question using proper accounting standards.arrow_forwardI need help solving this general accounting question with the proper methodology.arrow_forward
- Can you help me solve this general accounting question using the correct accounting procedures?arrow_forwardI am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid accounting standards.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting problem using appropriate accounting principles?arrow_forward
- I need guidance with this general accounting problem using the right accounting principles.arrow_forwardI need the correct answer to this general accounting problem using the standard accounting approach.arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution to this general accounting question with accurate financial calculations.arrow_forward
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning





