
Adequate information:
Opening value of saving 1,48,000
Closing value of saving 1,98,000
To compute: Dollar weighted average return.
Introduction: Dollar weighted average return is a way to measure an investment’s performance.
Explanation of Solution
Assuming that an investment was made for $148,000.
Thus, all the values in addition and investment in account are considered as outflow of cash flow and all the values of withdrawal and final value are considered as inflow of cash.
PV of inflow = PV of outflow
IRR can be computed using the following formula in excel:
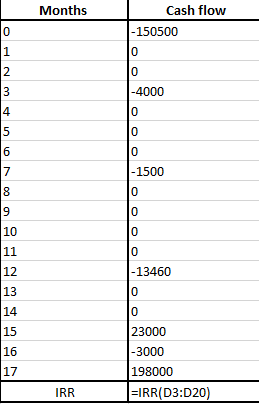
Following is the calculated answer using the above mentioned formula:
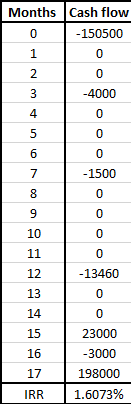
The above return has been calculated on monthly basis.
So, as per the question the dollar weighted average return between first and last date can be calculated by multiplying it by 17 (1/1/2016-5/3/2017)
Dollar weight average return is 27.32%
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Investments, 11th Edition (exclude Access Card)
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage  Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach to Conducting a Q...AccountingISBN:9781305080577Author:Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. RittenbergPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach to Conducting a Q...AccountingISBN:9781305080577Author:Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. RittenbergPublisher:South-Western College Pub





