
College Physics Volume 1 (Chs. 1-16); Mastering Physics with Pearson eText -- ValuePack Access Card -- for College Physics (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134151779
Author: Hugh D. Young, Philip W. Adams, Raymond Joseph Chastain
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 24, Problem 1MCP
A ray from an object passes through a thin lens, as shown in Figure 24.39. What can we conclude about the lens from this ray?
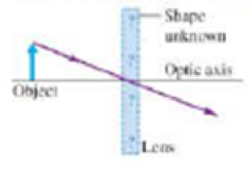
Figure 24.39
Multiple-Choice Problem 1.
- A. It is a converging lens.
- B. It is a diverging lens.
- C. It is not possible to tell which type of lens it is.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 24 Solutions
College Physics Volume 1 (Chs. 1-16); Mastering Physics with Pearson eText -- ValuePack Access Card -- for College Physics (10th Edition)
Ch. 24 - If a spherical mirror is immersed in water, does...Ch. 24 - For what range of object positions does a concave...Ch. 24 - If a screen is placed at the location of a real...Ch. 24 - Is it possible to view a virtual image directly...Ch. 24 - Prob. 5CQCh. 24 - On a sunny day, you can use the suns rays and a...Ch. 24 - A person looks at her reflection in the concave...Ch. 24 - What happens to the image produced by a converging...Ch. 24 - Without measuring its radius of curvature (which...Ch. 24 - Without measuring its radii of curvature (which is...
Ch. 24 - A spherical air bubble in water can function as a...Ch. 24 - Optical telescopes having a principal mirror only...Ch. 24 - A ray from an object passes through a thin lens,...Ch. 24 - If a single lens forms a real image, we can...Ch. 24 - If a single lens forms a virtual image, we can...Ch. 24 - An object lies outside the focal port of a...Ch. 24 - An object lies outside the focal point of a...Ch. 24 - Prob. 6MCPCh. 24 - An object is placed a distance 2f away from a...Ch. 24 - In order to form an image with a converging lens...Ch. 24 - A ray from an object passes through a thin lens,...Ch. 24 - As you move an object from just outside to just...Ch. 24 - As you move an object from just outside to just...Ch. 24 - You have a shiny salad bowl with a spherical shape...Ch. 24 - A candle 4.85 cm tall is 39.2 cm to the left of a...Ch. 24 - Two plane mirrors form a 60 wedge as shown in...Ch. 24 - An object is placed between two plane mirrors...Ch. 24 - If you run away from a plane mirror at 2.40 m/s,...Ch. 24 - A concave spherical mirror has a radius of...Ch. 24 - A concave spherical mirror has a radius of...Ch. 24 - The diameter of Mars is 6794 km. and its minimum...Ch. 24 - A concave mirror has a radius of curvature of 34.0...Ch. 24 - Rearview mirror. A mirror on the passenger side of...Ch. 24 - Examining your image in a convex mirror whose...Ch. 24 - A coin is placed next to the convex side of a thin...Ch. 24 - Consider a concave mirror that has a focal length...Ch. 24 - A spherical, concave shaving mirror has a radius...Ch. 24 - An object 0.600 cm tall is placed 16.5 cm to the...Ch. 24 - Repeat the previous problem for the case in which...Ch. 24 - The thin glass shell shown in Figure 24.43 has a...Ch. 24 - Dental mirror. A dentist uses a curved mirror to...Ch. 24 - The left end of a long glass rod 6.00 cm in...Ch. 24 - Prob. 19PCh. 24 - The left end of a long glass rod 8.00 cm in...Ch. 24 - A large aquarium has portholes of thin transparent...Ch. 24 - Focus of the eye. The cornea of the eye has a...Ch. 24 - A speck of dirt is embedded 3.50 cm below the...Ch. 24 - A skin diver is 2.0 m below the surface of a lake....Ch. 24 - A person is swimming 1.0 m beneath the surface of...Ch. 24 - A converging lens with a focal length of 7.00 cm...Ch. 24 - A converging lens with a focal length of 90.0 cm...Ch. 24 - You are standing 0.50 m in front of a lens that...Ch. 24 - Figure 24.44 shows an object and its image formed...Ch. 24 - Set up: 1s+1s=1f. The type of lens determines the...Ch. 24 - Figure 24.46 shows an object and its image formed...Ch. 24 - The two surfaces of a plastic converging lens have...Ch. 24 - A lens has an index of refraction of 1.7 and a...Ch. 24 - Set Up: Use 1f=(n1)(1R11R2) to calculate f and...Ch. 24 - The lens of the eye. The crystalline lens of the...Ch. 24 - The cornea as a simple lens. The cornea behaves as...Ch. 24 - An insect 3.75 mm tall is placed 22.5 cm to the...Ch. 24 - Two double-convex thin lenses each have surfaces...Ch. 24 - A converging meniscus lens (see Figure 24.30) with...Ch. 24 - A converging lens with a focal length of 12.0 cm...Ch. 24 - Combination of lenses, I. When two lenses are used...Ch. 24 - Set Up: Apply 1s+1s=1f with f = 35.0 cm. We know...Ch. 24 - Combination of lenses, II. Two thin lenses with a...Ch. 24 - A lens forms a real image that is 214 cm away from...Ch. 24 - A converging lens has a focal length of 14.0 cm...Ch. 24 - A converging lens forms an image of an...Ch. 24 - A diverging lens with a focal length of 48.0 cm...Ch. 24 - When an object is 16.0 cm from a lens, an image is...Ch. 24 - Figure 24.48 shows a small plant near a thin lens....Ch. 24 - Figure 24.49 shows a small plant near a thin lens....Ch. 24 - Figure 24.50 shows a small plant near a thin lens....Ch. 24 - Prob. 52GPCh. 24 - Where must you place an object in front of a...Ch. 24 - Set Up: Use 1s+1s=1f. A plot of 1f versus 1s...Ch. 24 - A concave mirror is to form an image of the...Ch. 24 - A lens has one convex surface of radius 6.00 cm...Ch. 24 - A 3 80-nm-tall object 24.0 cm from the center of...Ch. 24 - A lensmaker wants to make a magnifying glass from...Ch. 24 - An object is placed 18.0 cm from a screen, (a) At...Ch. 24 - In the text, Equations 24.4 and 24.7 were derived...Ch. 24 - A lens in a liquid. A lens obeys Snell s law,...Ch. 24 - Refraction of liquids. The focal length of a...Ch. 24 - Refraction of liquids. The focal length of a...Ch. 24 - If you place a concave mirror with a focal length...Ch. 24 - Refraction of liquids. The focal length of a...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
1. Why is the quantum-mechanical model of the atom important for understanding chemistry?
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
23. How many significant figures are there in the following values?
a. 0.05 × 10-4 b. 0.00340
c. 7.2 × 104 ...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
10.71 Identify each of the following as an acid or a base: (10.1)
H2SO4
RbOH
Ca(OH)2
HI
...
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Why are BSL-4 suits pressurized? Why not just wear tough regular suits?
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Where is transitional epithelium found and what is its importance at those sites?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Two culture media were inoculated with four different bacteria. After incubation, the following results were ob...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You are standing a distance x = 1.75 m away from this mirror. The object you are looking at is y = 0.29 m from the mirror. The angle of incidence is θ = 30°. What is the exact distance from you to the image?arrow_forwardFor each of the actions depicted below, a magnet and/or metal loop moves with velocity v→ (v→ is constant and has the same magnitude in all parts). Determine whether a current is induced in the metal loop. If so, indicate the direction of the current in the loop, either clockwise or counterclockwise when seen from the right of the loop. The axis of the magnet is lined up with the center of the loop. For the action depicted in (Figure 5), indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop (clockwise, counterclockwise or zero, when seen from the right of the loop). I know that the current is clockwise, I just dont understand why. Please fully explain why it's clockwise, Thank youarrow_forwardA planar double pendulum consists of two point masses \[m_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}, \qquad m_2 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}\]connected by massless, rigid rods of lengths \[L_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{m}, \qquad L_2 = 1.20~\mathrm{m}.\]The upper rod is hinged to a fixed pivot; gravity acts vertically downward with\[g = 9.81~\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}.\]Define the generalized coordinates \(\theta_1,\theta_2\) as the angles each rod makes with thedownward vertical (positive anticlockwise, measured in radians unless stated otherwise).At \(t=0\) the system is released from rest with \[\theta_1(0)=120^{\circ}, \qquad\theta_2(0)=-10^{\circ}, \qquad\dot{\theta}_1(0)=\dot{\theta}_2(0)=0 .\]Using the exact nonlinear equations of motion (no small-angle or planar-pendulumapproximations) and assuming the rods never stretch or slip, determine the angle\(\theta_2\) at the instant\[t = 10.0~\mathrm{s}.\]Give the result in degrees, in the interval \((-180^{\circ},180^{\circ}]\).arrow_forward
- What are the expected readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the circuit in the figure below? (R = 5.60 Ω, ΔV = 6.30 V) ammeter I =arrow_forwardsimple diagram to illustrate the setup for each law- coulombs law and biot savart lawarrow_forwardA circular coil with 100 turns and a radius of 0.05 m is placed in a magnetic field that changes at auniform rate from 0.2 T to 0.8 T in 0.1 seconds. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field.• Calculate the induced electric field in the coil.• Calculate the current density in the coil given its conductivity σ.arrow_forward
- An L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forwardA long, straight wire carries a current of 10 A along what we’ll define to the be x-axis. A square loopin the x-y plane with side length 0.1 m is placed near the wire such that its closest side is parallel tothe wire and 0.05 m away.• Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop using Ampere’s law.arrow_forwardDescribe the motion of a charged particle entering a uniform magnetic field at an angle to the fieldlines. Include a diagram showing the velocity vector, magnetic field lines, and the path of the particle.arrow_forward
- Discuss the differences between the Biot-Savart law and Coulomb’s law in terms of their applicationsand the physical quantities they describe.arrow_forwardExplain why Ampere’s law can be used to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid but not outside.arrow_forward3. An Atwood machine consists of two masses, mA and m B, which are connected by an inelastic cord of negligible mass that passes over a pulley. If the pulley has radius RO and moment of inertia I about its axle, determine the acceleration of the masses mA and m B, and compare to the situation where the moment of inertia of the pulley is ignored. Ignore friction at the axle O. Use angular momentum and torque in this solutionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Convex and Concave Lenses; Author: Manocha Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CJ6aB5ULqa0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY